Thermostat 4 Click
R600.00 ex. VAT
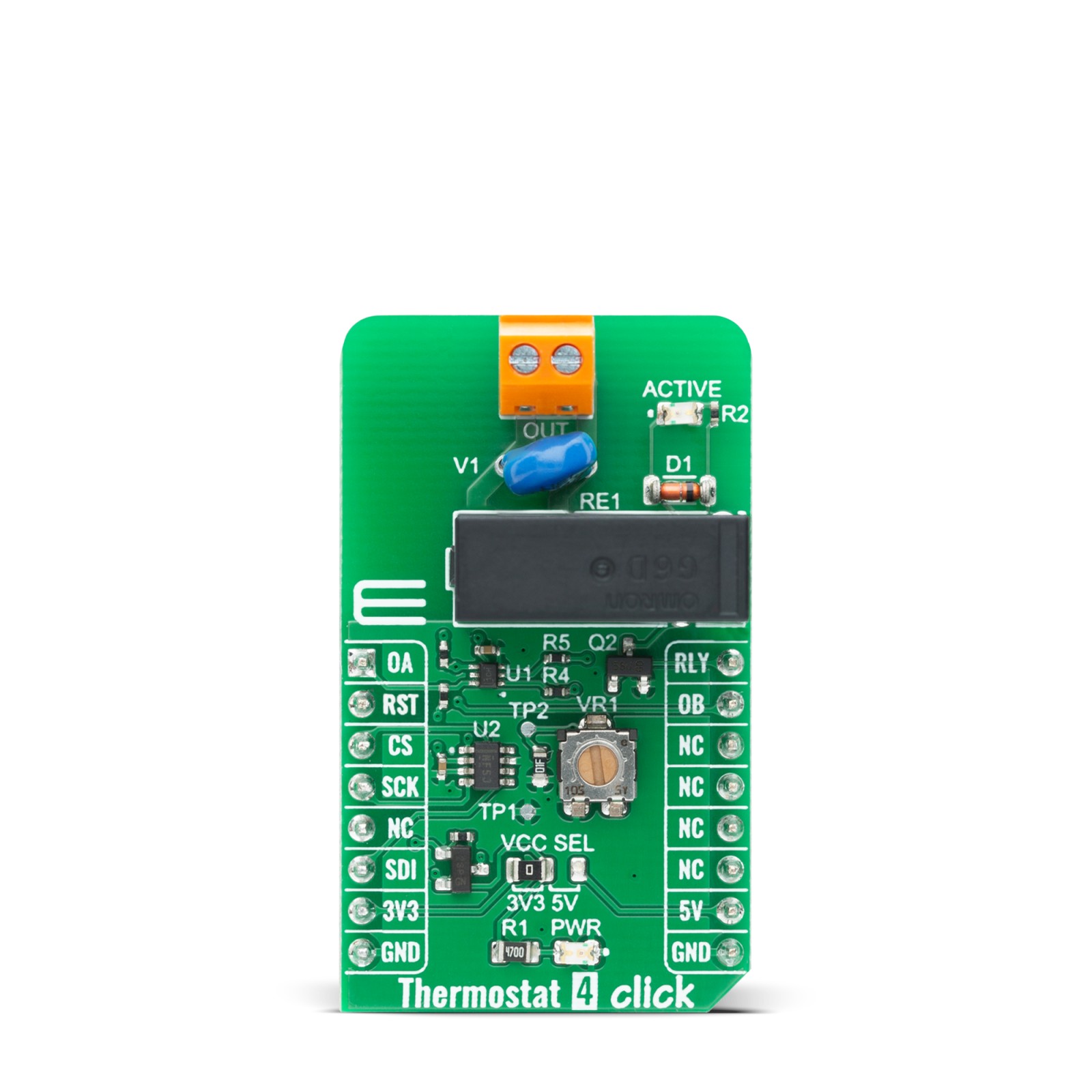
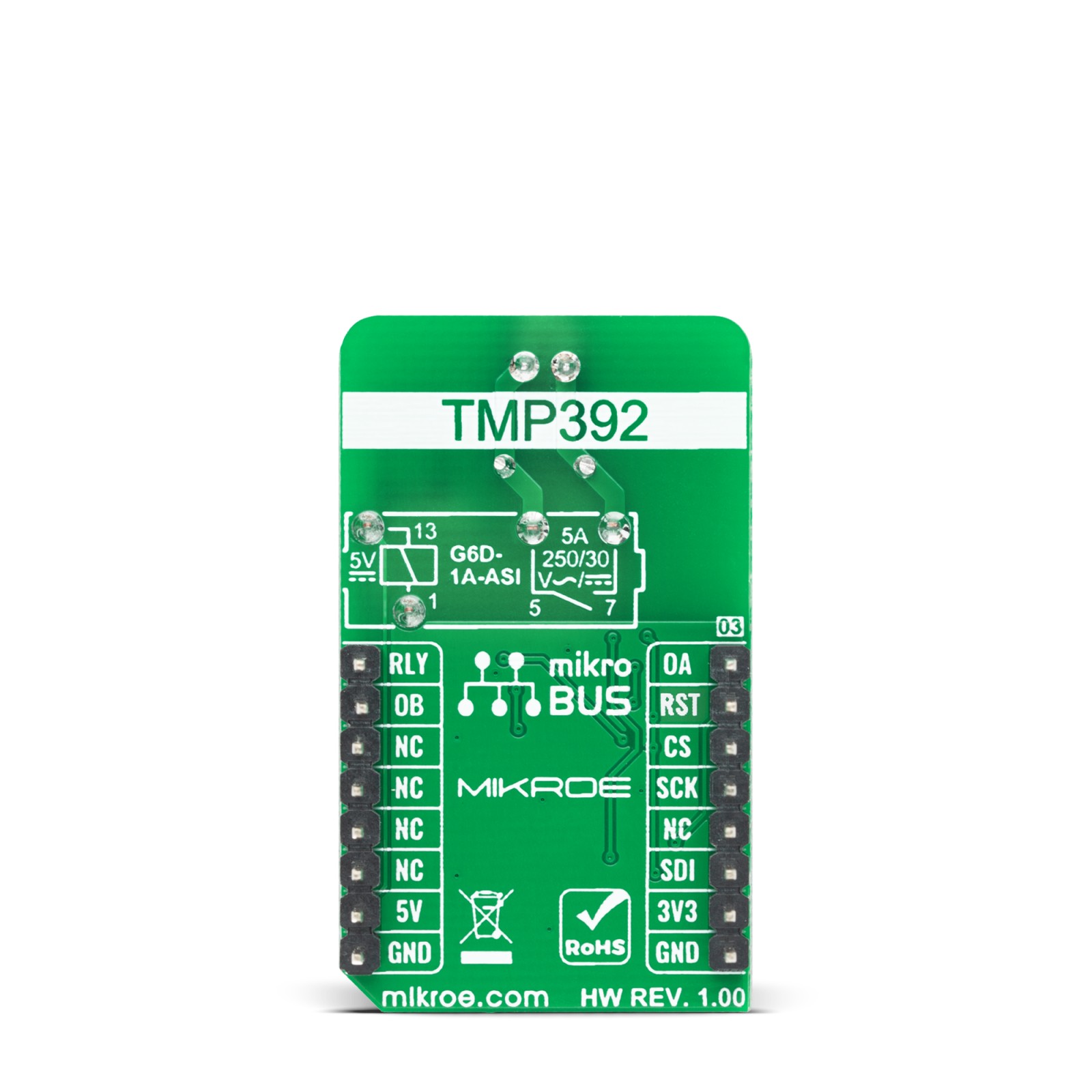
Thermostat 4 Click is complete solution that senses the temperature of a physical system and can performs actions so that the system’s temperature is maintained near a desired setpoint. It’s based on Texas Instruments TMP392, a resistor programmable temperature switch that enable protection and detection of system thermal events from 30°C to 130°C. It offers dual overtemperature (hot and warm) detection. The trip temperatures option is programmed by changing trimmer resistance value for channel A and digital potentiometer resistance value over SPI interface for channel B. The Thermostat 4 Click also contains a high-quality relay from Omron, that can be used to open or close an electric circuit. Despite its small size, it can be used with voltage up to 30VDC/220AC and current up to 5A.
Thermostat 4 Click board™ is supported by a mikroSDK compliant library, which includes functions that simplify software development. This Click board™ comes as a fully tested product, ready to be used on a system equipped with the mikroBUS™ socket.
Stock: Lead-time applicable.
| 5+ | R570.00 |
| 10+ | R540.00 |
| 15+ | R510.00 |
| 20+ | R490.80 |










.jpg)








