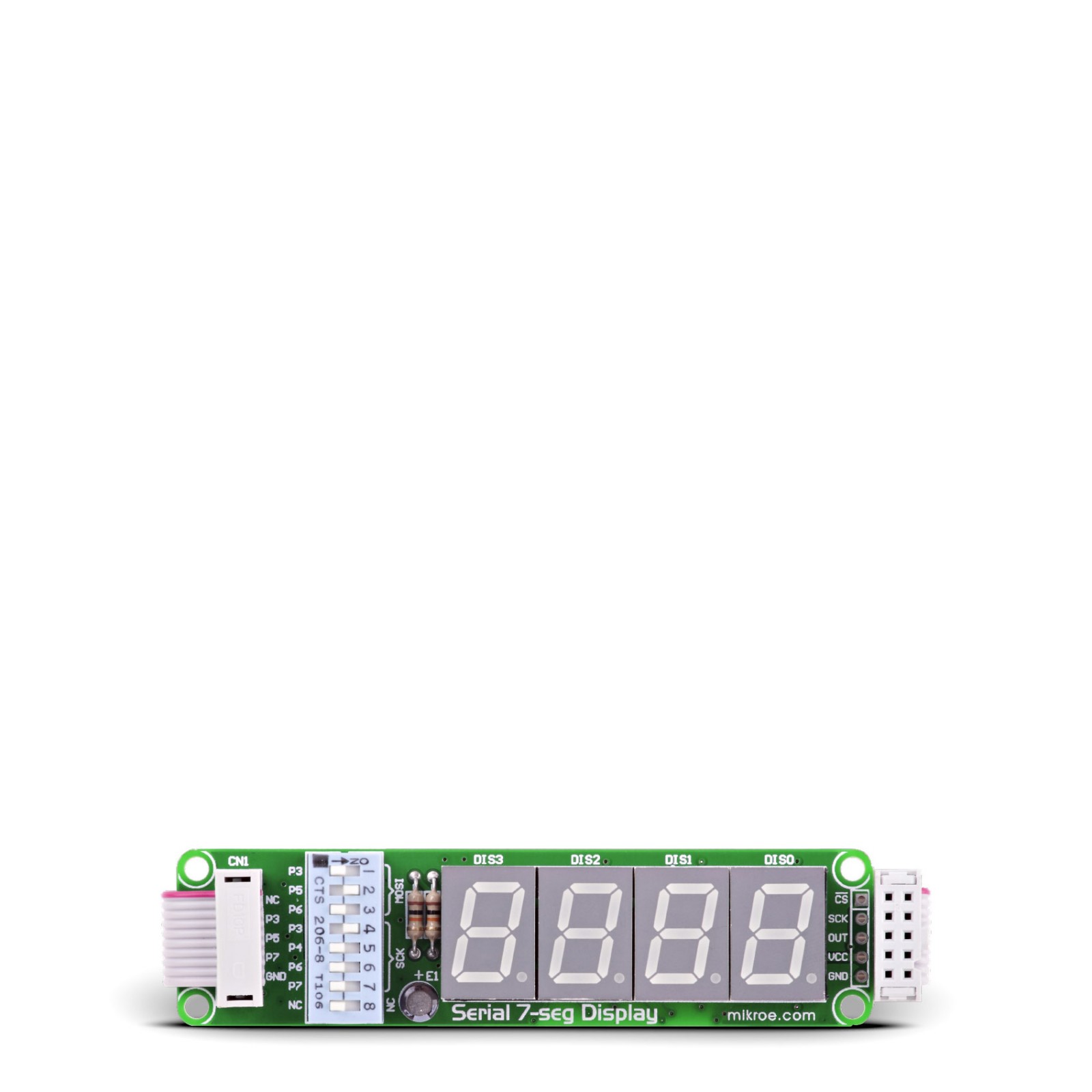
Serial 7-seg Display Board
R620.00 ex. VAT
The Serial 7-seg Display Board features an onboard SPI interfaced, LED display driver MAX7219 and 4 common-cathode LED displays. The board is connected to a prototype device via an IDC10 connector and comes with examples.
Stock: Lead-time applicable.
| 5+ | R589.00 |
| 10+ | R558.00 |
| 15+ | R527.00 |
| 20+ | R507.16 |