MR Angle Click
R400.00 ex. VAT
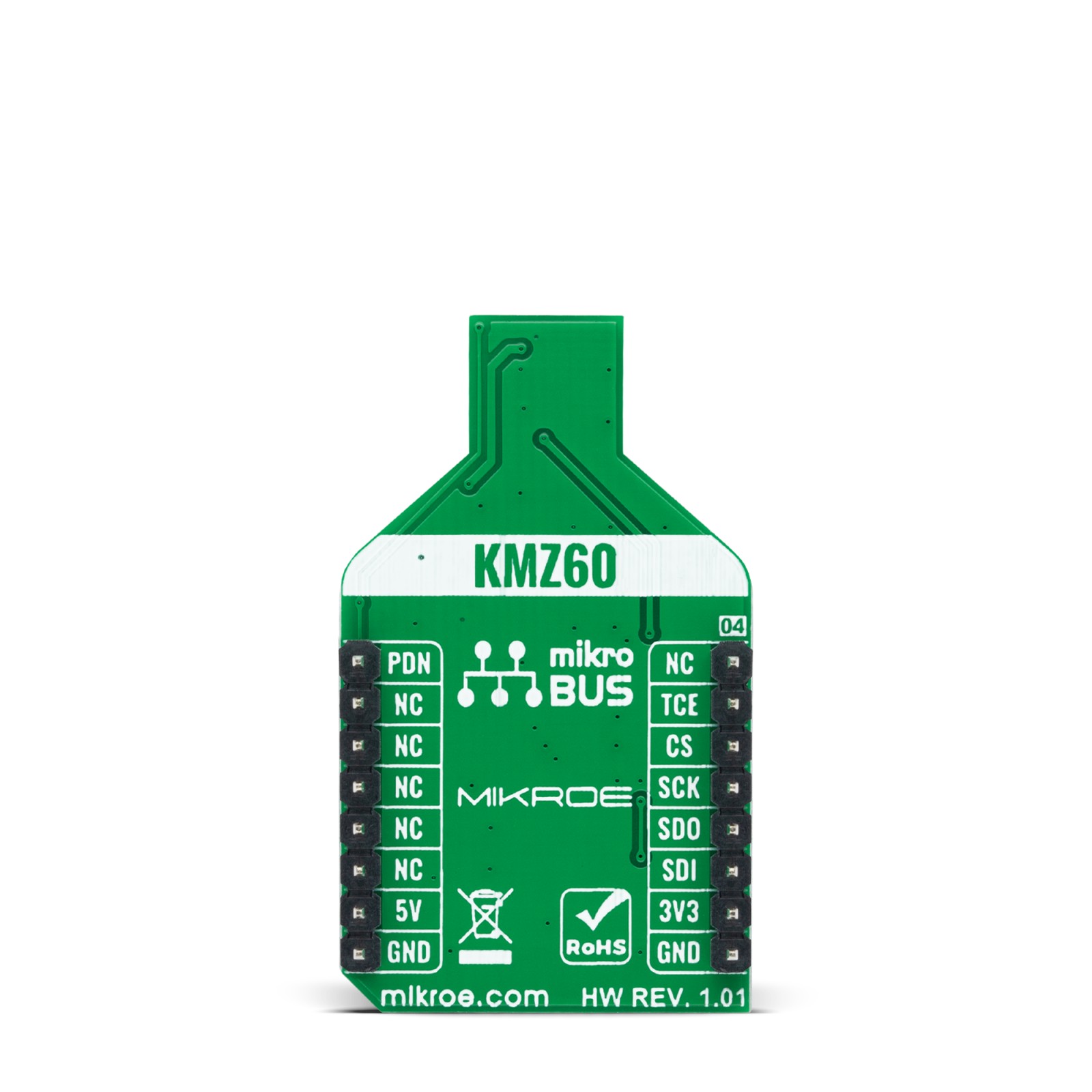
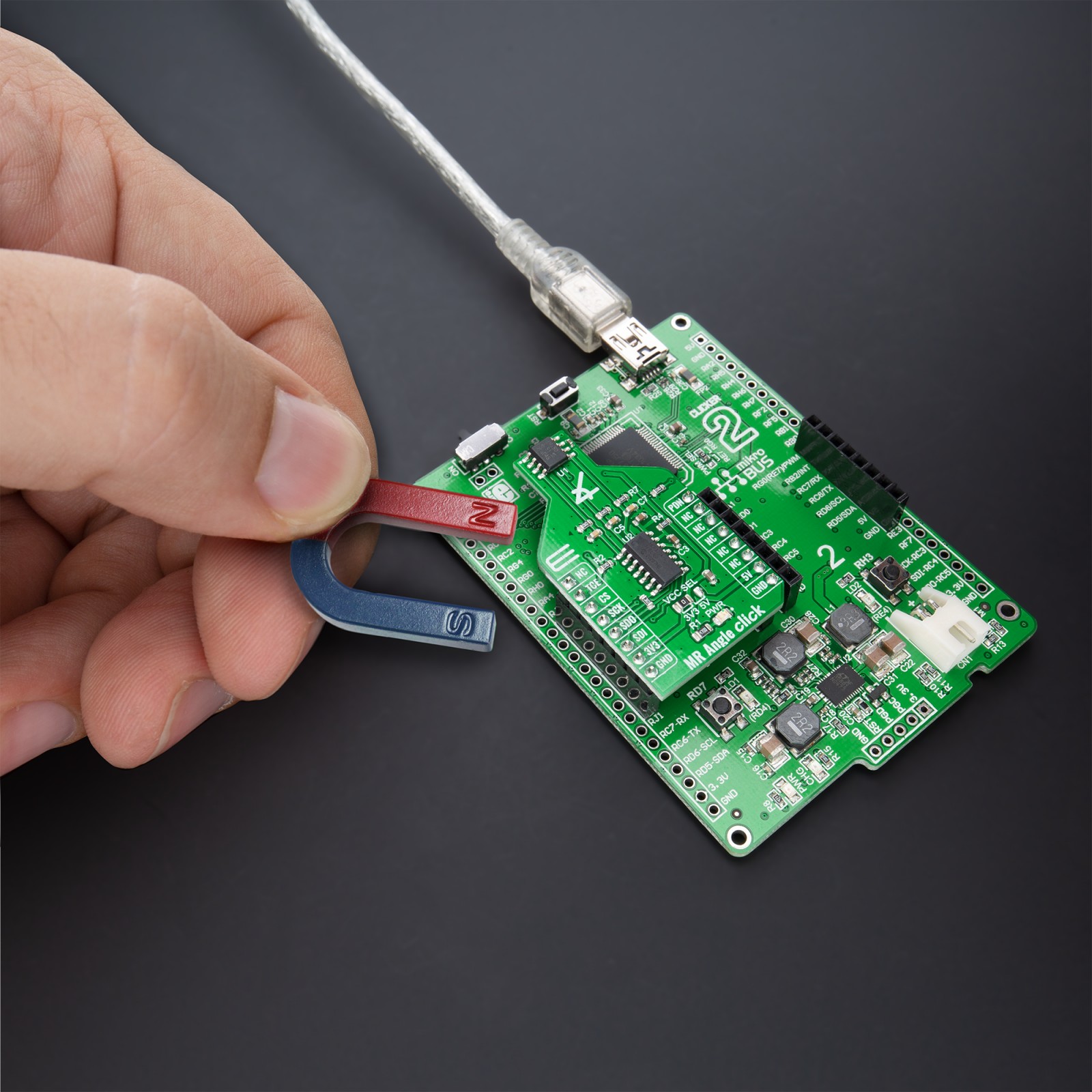
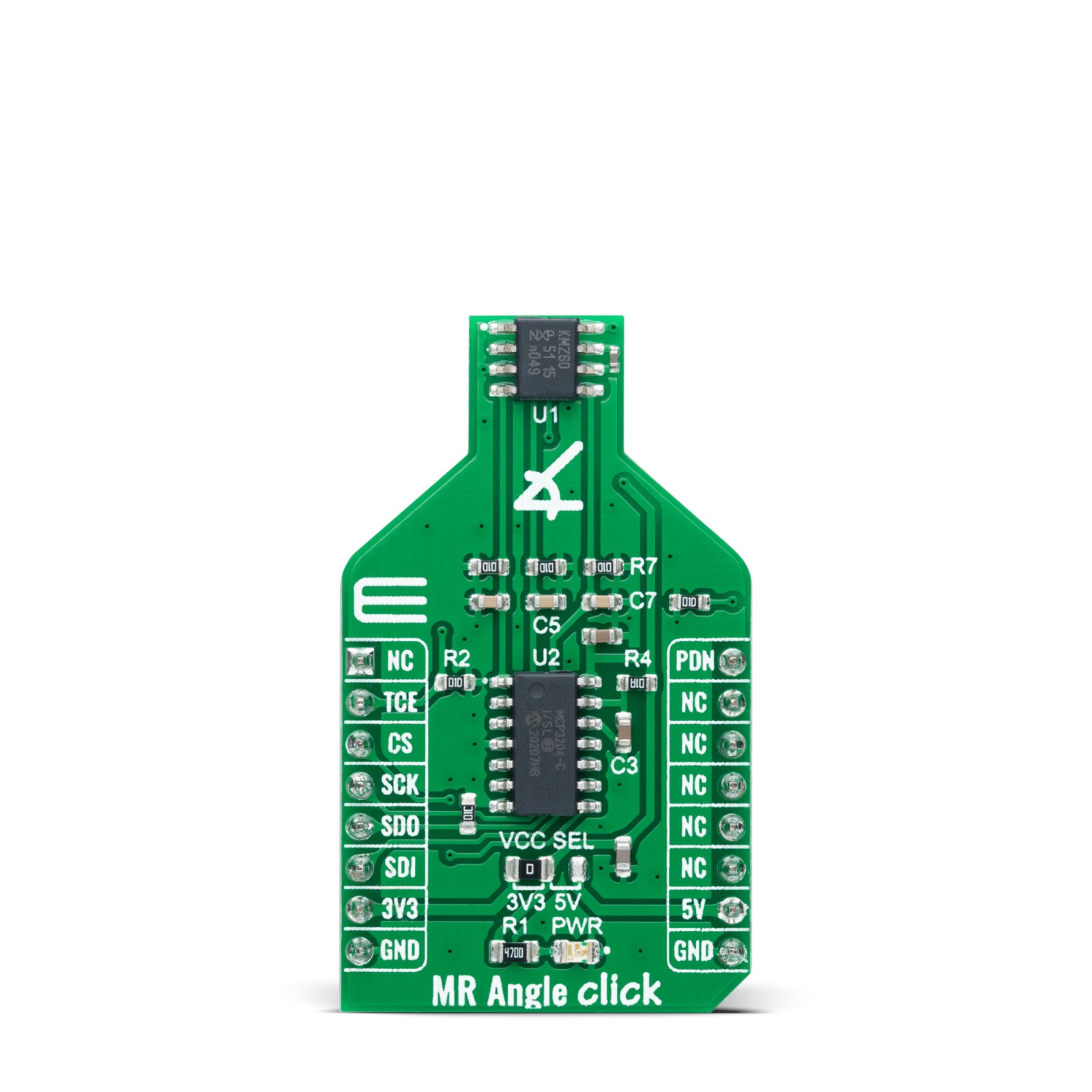
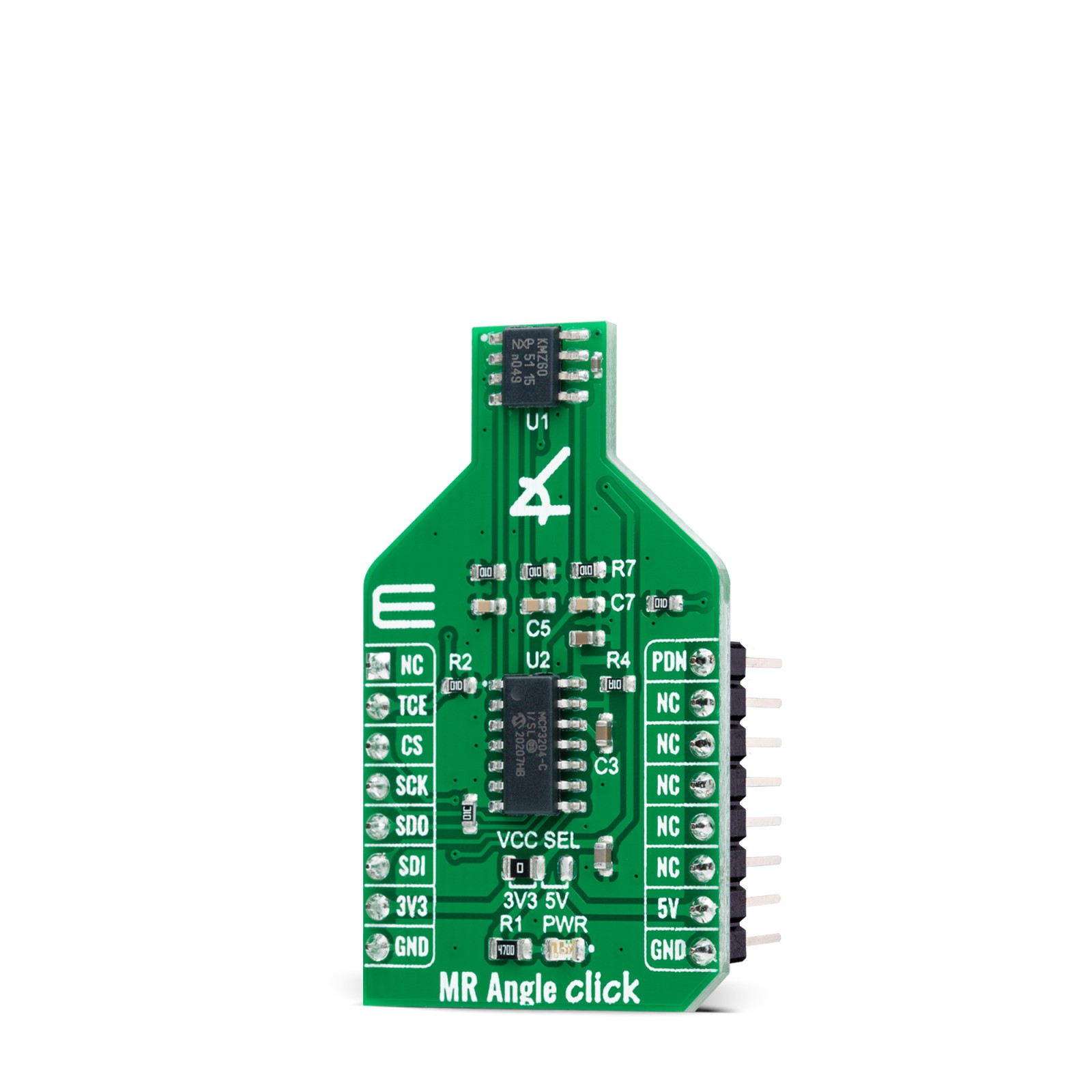
MR Angle Click is a compact add-on board that contains a magnetoresistive sensor with an integrated amplifier. This board features the KMZ60, a high precision sensor for magnetic angle measurement with single-ended cosine and sine outputs from NXP Semiconductors. The MR sensor element comes with two Wheatstone bridges for cosine and sine signals, supports functions for control circuit and signal amplification, and enables angular measurements with high accuracy by an excellent linearity and temperature drift behavior. The KMZ60 is fully automotive qualified as well as applicable for industrial and consumer applications. This Click board™ is suitable for rotor position detection for BLDC motors and Electronic Power Steering (EPS) applications, steering angle measurement, window wiper position detection, and general contactless angular measurement (e.g., throttle valves or actuators).
MR Angle Click is supported by a mikroSDK compliant library, which includes functions that simplify software development. This Click board™ comes as a fully tested product, ready to be used on a system equipped with the mikroBUS™ socket.
Stock: Lead-time applicable.
| 5+ | R380.00 |
| 10+ | R360.00 |
| 15+ | R340.00 |
| 20+ | R327.20 |









.jpg)








