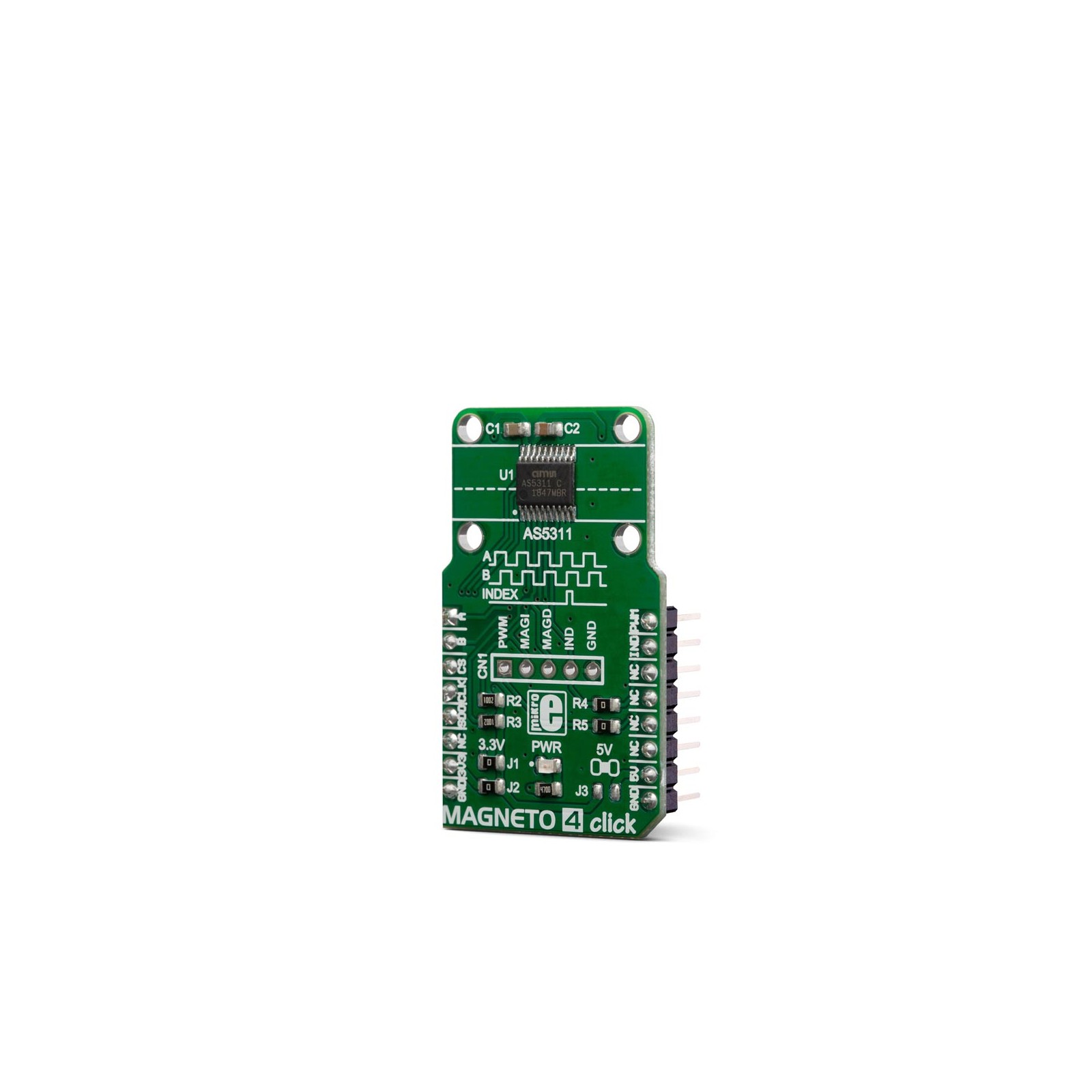
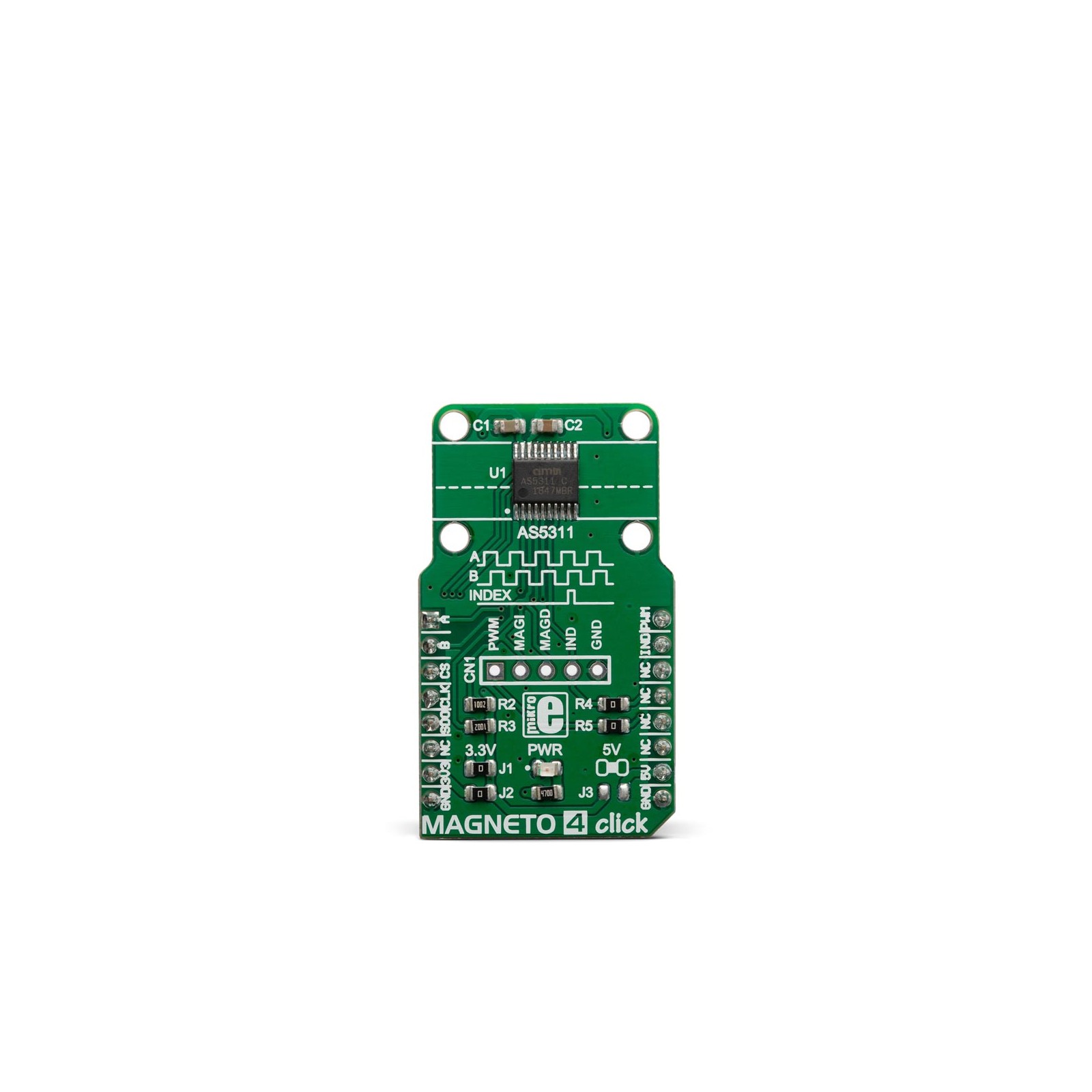
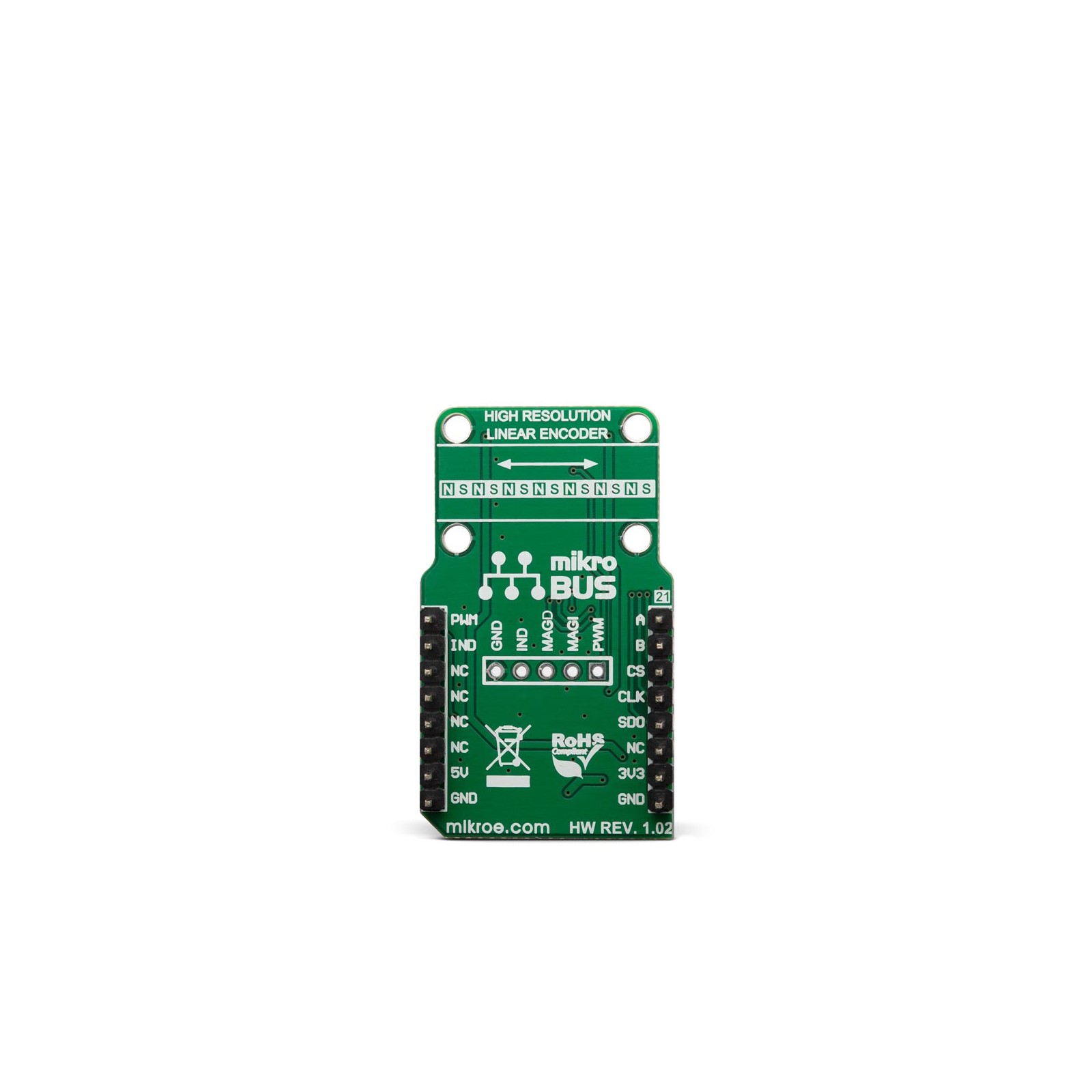
Magneto 4 Click
R635.00 ex. VAT
Magneto 4 click is a high-resolution magnetic encoder Click board™ which allows contactless motion sensing down to 0.5µm. It features the AS5311, a complete integrated solution with Hall elements, low-noise analog front-end, and digital signal processing (DSP) sections, on the same die. Thanks to the internal DSP processing, the AS5311 can output the absolute movement detection over the serial interface as a bit stream, or as a PWM signal. The AS5311 IC also offers a high-resolution incremental output with the additional index option. The device is supposed to be used with the multi-pole magnetic strip or ring.
Magneto 4 click is supported by a mikroSDK compliant library, which includes functions that simplify software development. This Click board™ comes as a fully tested product, ready to be used on a system equipped with the mikroBUS™ socket.
Stock: Lead-time applicable.
| 5+ | R603.25 |
| 10+ | R571.50 |
| 15+ | R539.75 |
| 20+ | R519.43 |
Besides the mikroBUS™, some of the pins are also available via the additional header on the Click board™ itself. Featuring very high absolute movement sensing resolution (12 bits over 2.0mm, 488nm), and incremental movement with the resolution of 1.95µm per step and traveling speed up to 650mm/second, this Click board™ can be used in robotics, as a servo drive feedback, micro-actuator feedback, as a replacement of optical encoders, and other similar high-precision motion measurement applications.
How does it work?
Magneto 4 click is based on the AS5311, a high resolution magnetic linear encoder by ams which integrates Hall elements, a low-noise analog front-end, and a digital signal processing (DSP), on the same die. It is a System-on-Chip used for performing highly accurate measurements. It is designed to be used along with a multi-pole magnetic strip or ring. A pole length should be 1.0mm, while the strip should be placed about 3mm above the IC surface. The magnetic strip movement is translated into a 12-bit word on the output. In other words, the output is cycled from 0 to 4095 for each 2mm the strip moves. Also, this means that the movement resolution goes down to 488nm per LSB.
.jpg)
The AS5311 can output the movement data in several different formats: it can either output the bit-string over the serial interface, or by using the 12-bit pulse-width modulated signal (PWM). The pulse width of the PWM signal starts with 1µs and is increased for every 0.488μm. The maximum pulse width is 4095µs, which corresponds to a magnet movement of 2mm.
The incremental outputs allow this Click board™ to be used in place of a mechanical or optical quadrature encoder. These two outputs are phase-shifted for 90 degrees: the output A leads output B when the magnet is moving from right to left and vice-versa: output B leads output A when the magnet is moving from left to right. The resolution of the incremental outputs is 10 bits per pole pair (1024 steps), which results in a step length of 1.95μm. An additional index pin is triggered for each pulse pair. These pins can be disabled by using the Chip Select (CS) pin: whenever the CS pin is at a HIGH logic level, all the incremental output pins (A, B, Index) are disabled (fixed at a HIGH logic state). To prevent flickering in border-conditions, there is a hysteresis of 2 LSBs implemented.
The serial interface is very similar to SPI. However, depending on the correlation between the Chip Select pin and the clock signal logic state, two data modes are available: if the CS pin is pulled to a HIGH logic state (or floating) during the clock HIGH pulse, the AS5311 will report the magnitude (strength) of the magnetic field. Else, it will output the absolute linear position data. The output data contains both the magnetic/positional data bits (11 bits) and status bits (5 bits). The status report includes offset compensation status, “CORDIC” overflow status, linearity alarm status, and two magnetic field strength status bits.
The AS5311 can use either two hardware pins (MagINCn, MagENCn) routed to the additional header, or two status bits within the status report. These two bits/pins are used to describe the magnitude of the magnetic field. The datasheet refers to three different magnetic field magnitudes: green, yellow, and red. The green status represents the optimal strength of the magnetic field. The yellow status indicated that the obtained data may not be accurate, while the red status indicates that the magnetic field generated by the multi-pole strip or ring is weak and it is not recommended to use it.
For proper operation of the Click board™, a multi-pole magnetic strip should be properly placed above the IC so that it can move along x-axis only. To support correct placing, the Click board™ comes with four holes, which can be used to accurately position the strip in place. Please refer to the datasheet for more details about the magnetic strip positioning.
The Click board™ can work with MCUs that use with both 3.3V and 5V supply voltages. The power supply selection on this click is a bit specific: to select 3.3V, both SMD jumpers grouped under the 3.3V label should be populated, while the SMD jumper under the 5V label should not be populated. Selecting 5V is done by removing two SMD jumpers under the 3.3V label and populating one SMD jumper under the 5V label. Please note that populating all the SMD jumpers at once may lead to malfunction.
Specifications
Type
Magnetic
Applications
Featuring very high movement sensing resolution, for both the absolute and incremental outputs, this Click board™ can be used in robotics, as a servo drive feedback, micro-actuator feedback, as a replacement for optical encoders, and other similar high-precision motion measurement applications.
On-board modules
AS5311, a high-resolution magnetic linear encoder, by ams
Key Features
An accurate movement sensing based on the Hall effect, integrated system on chip solution requires a low count of external components, multiple interface options (incremental, serial, PWM…), readings of the magnetic field magnitude, categorization by the field magnitude (red, yellow, green), additional header with optional pins, etc.
Interface
GPIO,PWM,SPI
Feature
No ClickID
Compatibility
mikroBUS™
Click board size
M (42.9 x 25.4 mm)
Input Voltage
3.3V or 5V
Pinout diagram
This table shows how the pinout on Magneto 4 click corresponds to the pinout on the mikroBUS™ socket (the latter shown in the two middle columns).
ADDITIONAL PINS
| Label | Description |
| PWR | PWM output (244Hz, 1μs per step) |
| MAGI | Magnet field magnitude increase; active LOW: indicates a distance reduction between the magnet and the device surface. |
| MAGD | Magnet field magnitude decrease; active LOW: indicates a distance increase between the device and the magnet. |
| IND | Incremental output Index; pulses to indicate each transition of the magnetic poles. |
| GND | Ground reference. |
Onboard settings and indicators
| Label | Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| LD1 | PWR | – | Power LED Indicator |
| J1, J2 | 3.3V | Populated | Power supply voltage selection: populated for 3.3V (J3 unpopulated) |
| J3 | 5V | Unpopulated | Power supply voltage selection: populated for 5V (J1, J2 unpopulated) |
Note: Do not populate J1, J2, and J3 SMD jumpers all at once. Please select a single operating voltage and populate the respective SMD jumpers, accordingly. 3.3V is selected by default.
Software support
We provide a library for the Magneto 4 click on our LibStock page, as well as a demo application (example), developed using MikroElektronika compilers. The demo can run on all the main MikroElektronika development boards.
Library Description
The library contains functions for reading the magnetic field strength in order to detect the magnetic strip. The user has the functions available for reading the linear position of the sensor on the magnetic tape, and functions that return full information about the state of the magnetic field and encoder, for example the direction of the movement , the number of steps …
Key functions:
int32_t magneto4_getEncoderPosition()– Encoder position.uint16_t magneto4_getMagneticField()– Magnetic field strength.void magneto4_setStartPosition(int32_t encoderPos)– Set start encoder position.
Examples description
The application is composed of the three sections :
- System Initialization – It starts the SPI module and sets the necessary gpio pins for click operation.
- Application Initialization – Initializes Driver init and sets start encoder position on the zero. Reads and logs magnetic field strength values. For starting an encoder, it is necessary that the magnetic field strength is greater than 3000.
- Application Task – Reads and logs the linear position of the sensor on the magnetic tape. When moving the sensor from left to right, one step is added and when moving from right to left, the position for 1 step is reduced.
void applicationTask()
{
encoderPosition = magneto4_getEncoderPosition();
if(oldPosition != encoderPosition)
{
IntToStr(encoderPosition, demoBuffer);
mikrobus_logWrite(" Encoder position : ", _LOG_TEXT);
mikrobus_logWrite(demoBuffer, _LOG_LINE);
mikrobus_logWrite("------------------------", _LOG_LINE);
}
oldPosition = encoderPosition;
}
The full application code, and ready to use projects can be found on our LibStock page.
Other mikroE Libraries used in the example:
SPIUARTGPIO
Additional notes and informations
Depending on the development board you are using, you may need USB UART click, USB UART 2 click or RS232 click to connect to your PC, for development systems with no UART to USB interface available on the board. The terminal available in all MikroElektronika compilers, or any other terminal application of your choice, can be used to read the message.
mikroSDK
This click board is supported with mikroSDK - MikroElektronika Software Development Kit. To ensure proper operation of mikroSDK compliant click board demo applications, mikroSDK should be downloaded from the LibStock and installed for the compiler you are using.
For more information about mikroSDK, visit the official page.
Resources
Downloads
| Weight | 19 g |
|---|---|
| Brand | MikroElektronika |