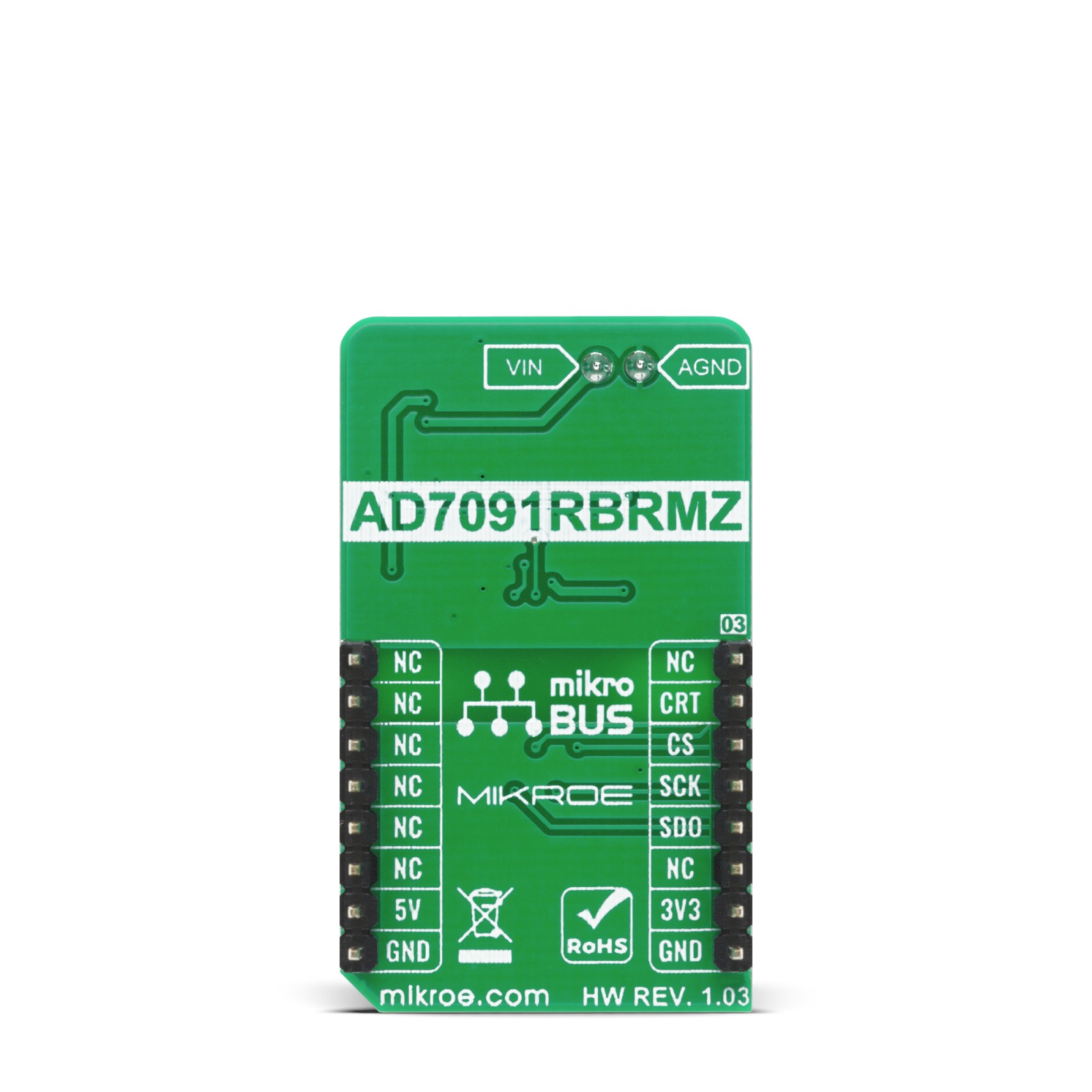
ISO ADC 2 Click
R1,050.00 ex. VAT
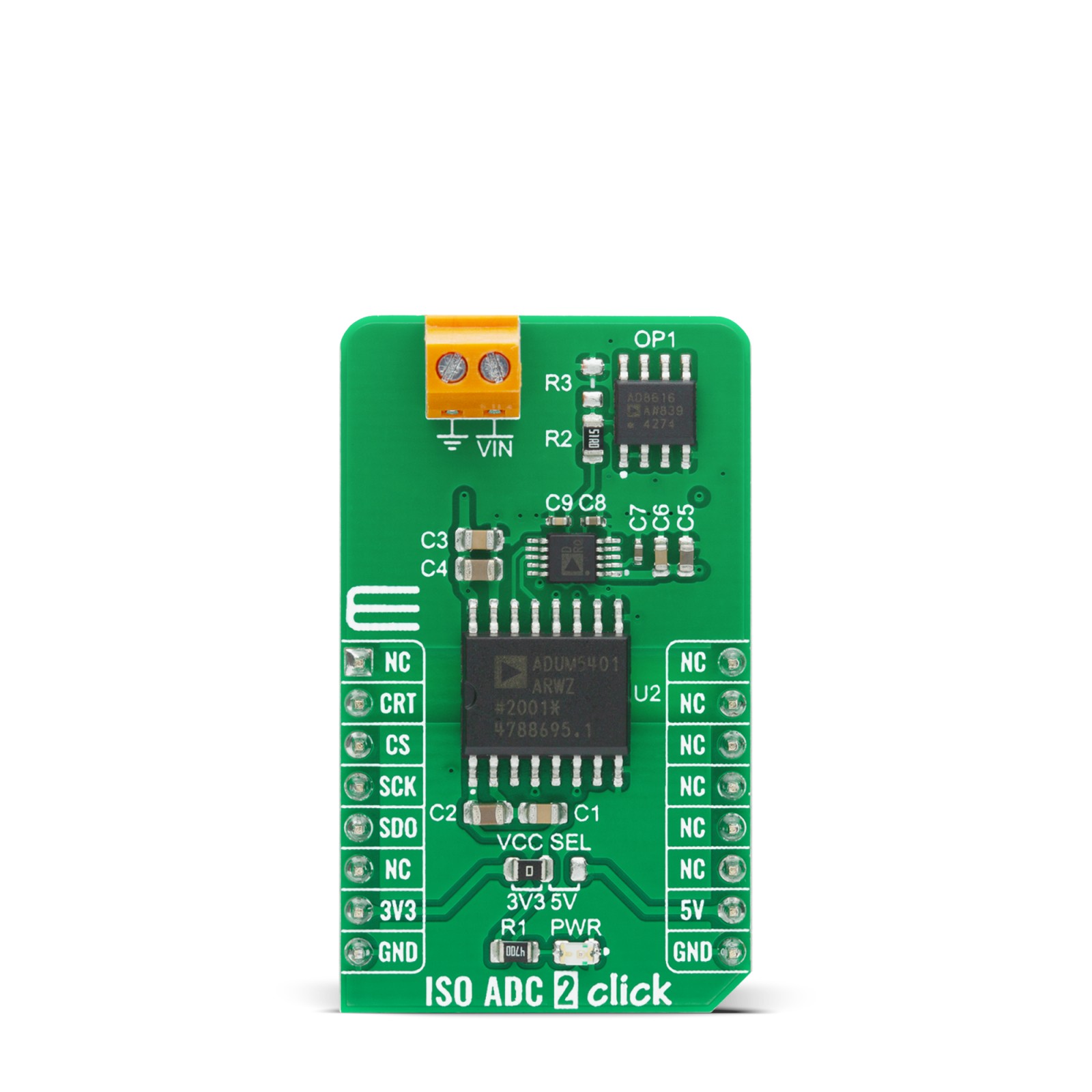
ISO ADC 2 Click is a compact add-on board that represents a completely isolated 12-bit, 300 kSPS data acquisition system. This board features the AD7091R, successive-approximation analog-to-digital converter (ADC) from Analog Devices. It uses the 3-wire SPI serial interface for data communication, achieving up to 1 MSPS throughput rate. This Click board™ also features the ADuM5401, isolated DC-DC converter used to isolate the logic signals, power, and feedback paths in the DC-DC converter resulting in total isolation solution. Many features such as high throughput rate with ultralow power consumption, wide input bandwidth, accuracy, and speed make it an ideal choice for a wide variety of industrial measurements, data acquisition systems, monitoring functions, and many more.
ISO ADC 2 Click is supported by a mikroSDK compliant library, which includes functions that simplify software development. This Click board™ comes as a fully tested product, ready to be used on a system equipped with the mikroBUS™ socket.
Stock: Lead-time applicable.
| 5+ | R997.50 |
| 10+ | R945.00 |
| 15+ | R892.50 |
| 20+ | R858.90 |











.jpg)