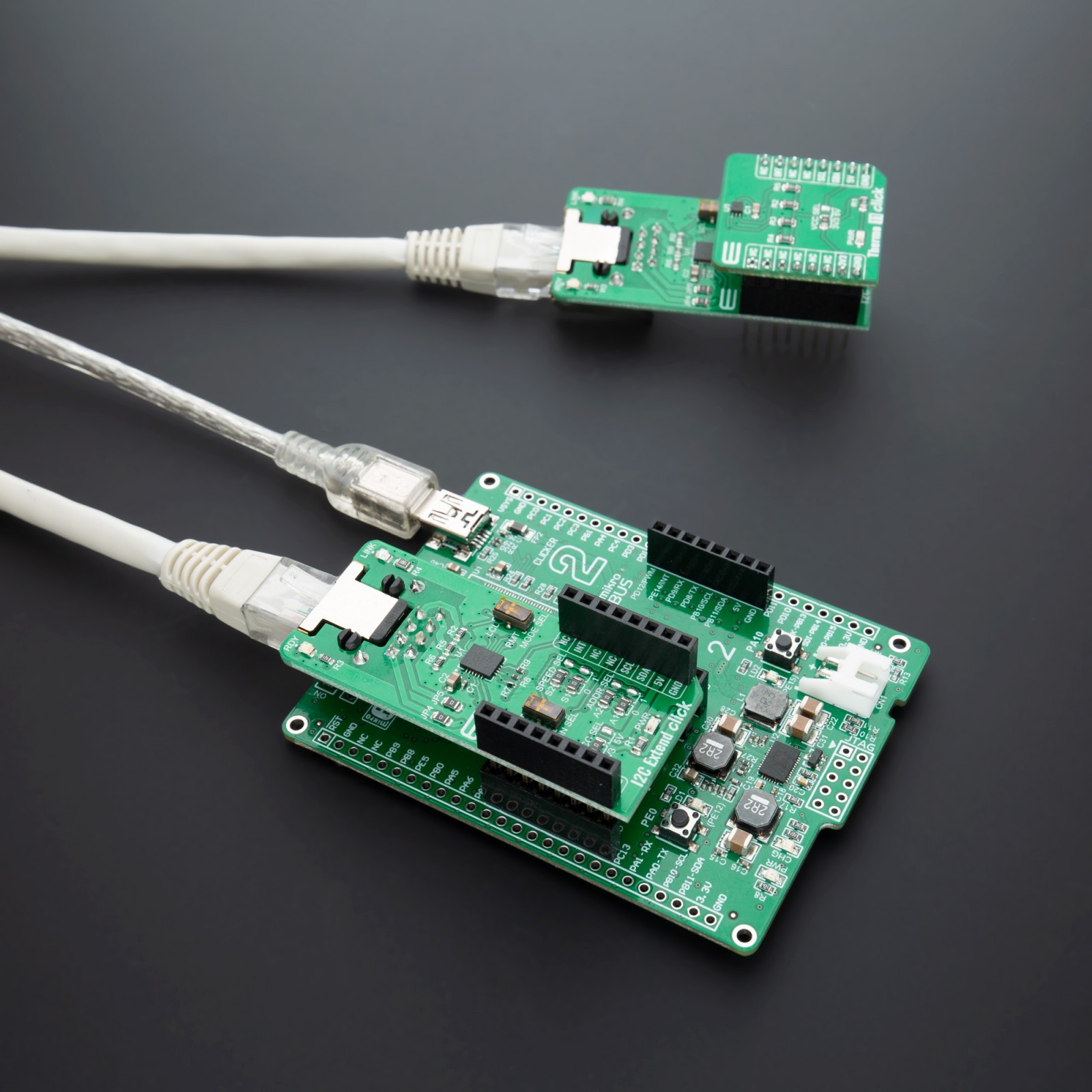
I2C Extend Click
R585.00 ex. VAT
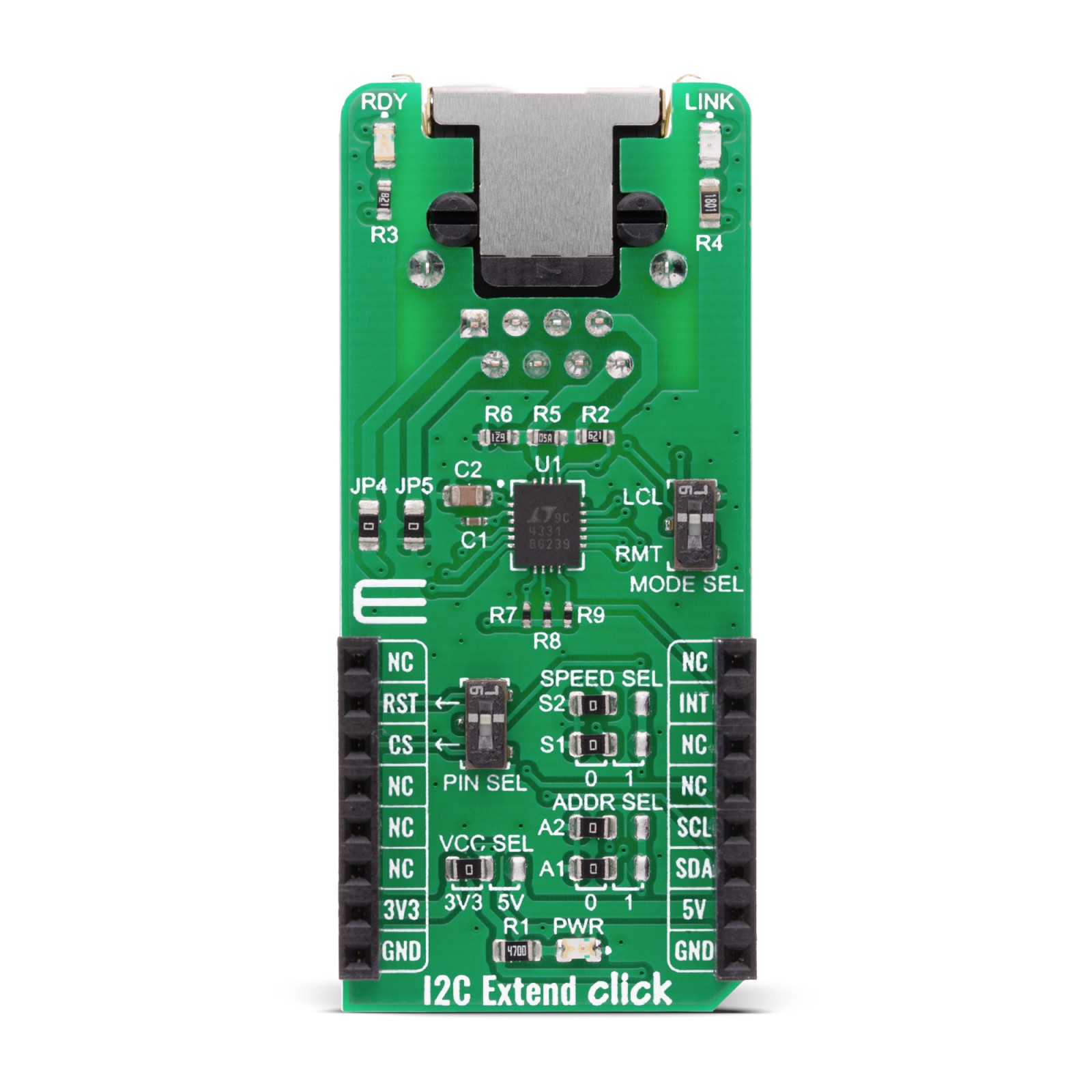
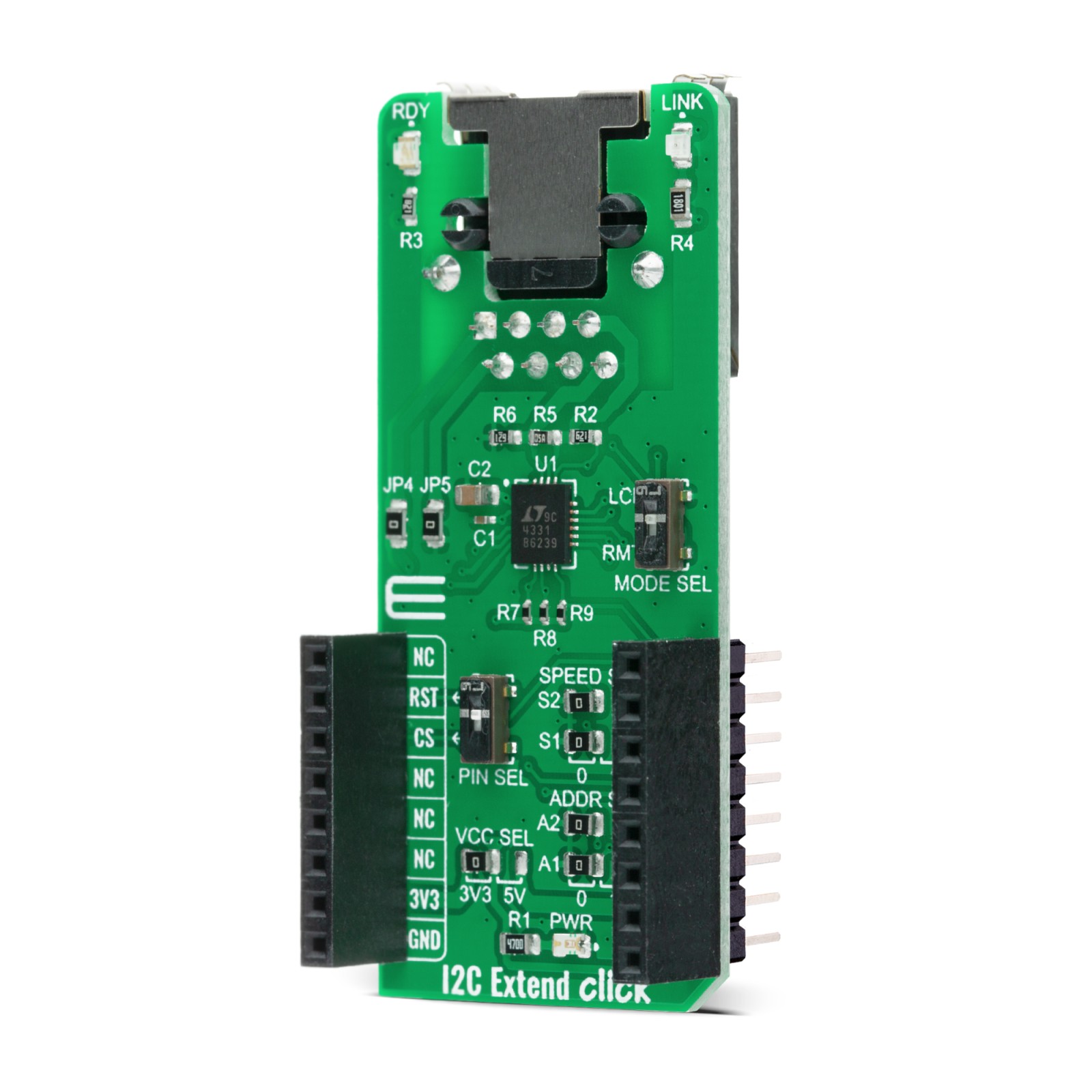
I2C Extend Click is a compact add-on board for applications that require extending the I2C communication bus over a long distance. This board features the LTC4331 – an I2C slave device extender over a rugged differential link, from Analog Devices. It is a point-to-point SMBus compatible I2C slave device extender, designed for operation in high noise industrial environments while supporting up to 1MHz serial clock, ±40kV ESD protection on link pins, selectable link baud rates and more. All these features make I2C Extend Click an excellent choice for various applications that require extending the I2C bus over a long distance, such as sensor installations, industrial control, lighting system control, sound system control, etc.
I2C Extend Click is supported by a mikroSDK compliant library, which includes functions that simplify software development. This Click board™ comes as a fully tested product, ready to be used on a system equipped with the mikroBUS™ socket.
Stock: Lead-time applicable.
| 5+ | R555.75 |
| 10+ | R526.50 |
| 15+ | R497.25 |
| 20+ | R478.53 |
How does it work?
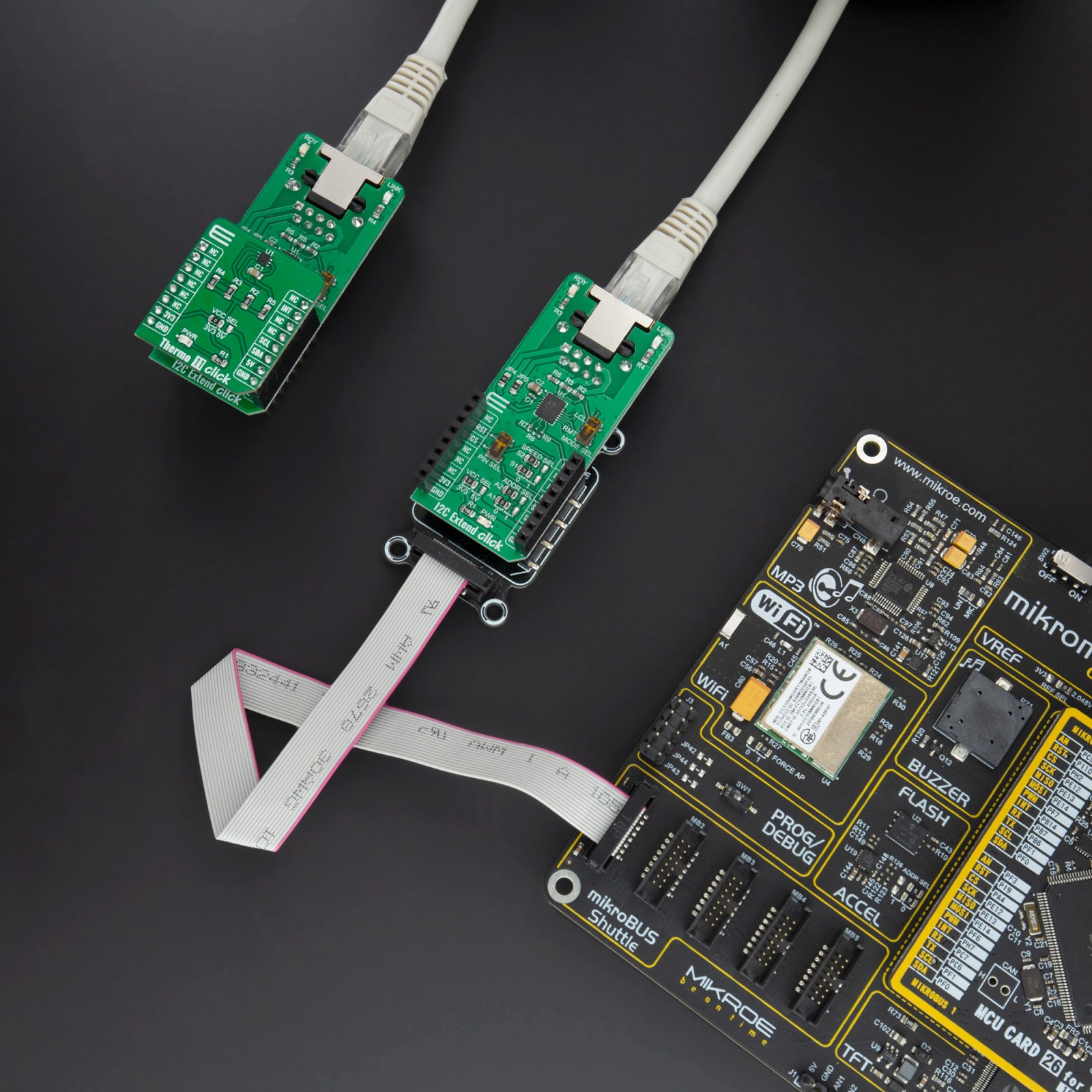
I2C Extend Click is based on the LTC4331, which is a point-to-point compatible I2C slave device extender designed for operation in high noise industrial environments. Using a ±60V fault protected differential transceiver, the LTC4331 can extend an I2C/SMBus bus, including remote interrupt function and a control signal, over a single twisted pair differential link. Thanks to selectable link baud rates, the I2C bus can be extended up to 1200m, depending on the link speed and external factors such as environmental noise level, humidity, cable quality, etc. Standard twisted-pair cables with RJ45 connectors can be used, the same as in the ethernet devices, etc.

Besides the I2C protocol extension, I2C Extend click also supports local to remote control and interrupt functions. Local to remote control ensures that the values set on the local side CTRL pin propagate to the remote side CTRL pin over the differential link. Users can choose pin on the mikroBUS™ socket used for that purpose (CS or RST), using the onboard jumper named PIN SEL. Interrupt pin acts as an open-drain output in local mode and an input in remote mode. Basically, an interrupt signal on the INT pin in the I2C Extend Click is mirrored from the remote network to the local network using the differential link. On the remote side INT is an input pin that can be connected to remote I2C slave devices, while on the local side, it is operating as an open-drain output that can be connected to a shared local interrupt line.
Because of the dual functionality of the I2C Extend Click, the user needs to set the mode of operation of the Click board™. That is easily achieved using the onboard MODE switch, with two positions: local mode (LCL), where this Click board™ is in I2C slave mode and remote mode (RMT) where this Click board™ is in I2C master mode. Besides mode selection, I2C Extend Click can also link speed and I2C address selection jumpers onboard, named “SPEED SEL” and “ADDR SEL”, respectively.
This Click board™ has Link status (LINK) and ready status (RDY) LEDs, making troubleshooting as easy as possible. In remote mode, LINK LED is active when the device establishes link communication. When in local mode, LINK LED is active after the LTC4331’s I2C interface has joined the I2C bus in addition to establishing link communication.The RDY LED is active after the device’s I2C interface has joined the bus.
This Click Board™ is designed to operate with both 3.3V and 5V logic levels that can be selected via VCC SEL jumper. This allows for both 3.3V and 5V capable MCUs to use the I2C communication lines properly.
Specifications
Type
I2C
Applications
Ideal for applications that require extending the I2C bus over a long distance, such as sensor installation, industrial control, lighting system control, sound system control, and more
On-board modules
LTC4331 – I2C slave device extender over rugged differential link from Analog Devices
Key Features
Designed for operation in high noise industrial environments while supporting Up to 1MHz serial clock, ±40kV ESD protection on link pins, selectable link baud rates and many more
Interface
GPIO,I2C
Feature
No ClickID
Compatibility
mikroBUS™
Click board size
L (57.15 x 25.4 mm)
Input Voltage
3.3V or 5V
Pinout diagram
This table shows how the pinout on I2C Extend Click corresponds to the pinout on the mikroBUS™ socket (the latter shown in the two middle columns).
Onboard settings and indicators
| Label | Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| LD1 | PWR | – | Power LED Indicator |
| LD2 | RDY | – | Ready Status LED Indicator |
| LD3 | LINK | – | Link Status LED Indicator |
| JP1 | VCC SEL | Left | Power Voltage Level Selection: Left position 3V3, Right position 5V |
| JP2-JP3 | ADDR SEL | Left | I2C Address Selection: Left position 0, Right position 1 |
| JP6-JP7 | SPEED SEL | Left | Link Speed Selection: Left position 0, Right position 1 |
| SW1 | PIN SEL | Upper | Local/Remote Control Selection: Upper position RST, Lower position CS |
| SW2 | MODE SEL | Upper | Mode Selection: Upper position LCL, Lower position RMT |
I2C Extend Click electrical specifications
| Description | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply Voltage | 3.3 | – | 5.5 | V |
| Extension Range | – | – | 1200 | m |
| Serial Clock Frequency | – | – | 1 | MHz |
Software Support
We provide a library for the I2C Extend Click on our LibStock page, as well as a demo application (example), developed using MIKROE compilers. The demo can run on all the main MIKROE development boards.
Library Description
The library covers all the necessary functions to control I2C Extend Click board™. A library performs the communication with the LTC4331 I2C Slave Device Extender Over Rugged Differential Link via I2C interface.
Key functions:
void i2cextend_generic_write ( uint8_t reg, uint8_t tx_data )– Generic write data function.uint8_t i2cextend_generic_read ( uint8_t reg )– Generic read data function.uint8_t i2cextend_rmt_read ( uint8_t rmt_slave_addr, uint8_t reg )– Generic read data in Remote Mode function.
Examples description
The application is composed of three sections :
- System Initialization – Initializes I2C, sets INT pin as input and RST nad CS pin as outputs and begins to write log.
- Application Initialization – Initialization driver enables – I2C, check communication with device 6DOF IMU 11 Click connected to the I2C Extend Click ( Remote Mode ), set default configuration and start measurement.
- Application Task – (code snippet) This is an example which demonstrates the use of I2C Extend Click board. In this example, we read Accel and Mag axis of the connected 6DOF IMU 11 Click boards to the I2C Extend Click ( Remote Mode ) which is connected by a LAN cable to I2C Extend Click ( Local Mode ) placed in the mikroBUS 1. Results are being sent to the Usart Terminal where you can track their changes. All data logs write on USB uart changes for every 2 sec.
void application_task ( )
{
mikrobus_logWrite( " Accel | Mag ", _LOG_LINE );
mikrobus_logWrite( "------------------------", _LOG_LINE );
i2cextend_6dofimu11_get_axis( C6DOFIMU11_REG_ACCEL_XOUT_L );
mikrobus_logWrite( " X :", _LOG_TEXT );
IntToStr( axis, log_text );
mikrobus_logWrite( log_text, _LOG_TEXT );
mikrobus_logWrite( " | ", _LOG_TEXT );
i2cextend_6dofimu11_get_axis( C6DOFIMU11_REG_MAG_XOUT_L );
mikrobus_logWrite( " X :", _LOG_TEXT );
IntToStr( axis, log_text );
mikrobus_logWrite( log_text, _LOG_LINE );
i2cextend_6dofimu11_get_axis( C6DOFIMU11_REG_ACCEL_YOUT_L );
mikrobus_logWrite( " Y :", _LOG_TEXT );
IntToStr( axis, log_text );
mikrobus_logWrite( log_text, _LOG_TEXT );
mikrobus_logWrite( " | ", _LOG_TEXT );
i2cextend_6dofimu11_get_axis( C6DOFIMU11_REG_MAG_YOUT_L );
mikrobus_logWrite( " Y :", _LOG_TEXT );
IntToStr( axis, log_text );
mikrobus_logWrite( log_text, _LOG_LINE );
i2cextend_6dofimu11_get_axis( C6DOFIMU11_REG_ACCEL_ZOUT_L );
mikrobus_logWrite( " Z :", _LOG_TEXT );
IntToStr( axis, log_text );
mikrobus_logWrite( log_text, _LOG_TEXT );
mikrobus_logWrite( " | ", _LOG_TEXT );
i2cextend_6dofimu11_get_axis( C6DOFIMU11_REG_MAG_ZOUT_L );
mikrobus_logWrite( " Z :", _LOG_TEXT );
IntToStr( axis, log_text );
mikrobus_logWrite( log_text, _LOG_LINE );
mikrobus_logWrite( "------------------------", _LOG_LINE );
Delay_ms( 1000 );
}
Additional Functions :
- void i2cextend_6dofimu11_get_axis ( uint8_t axis_out_reg )
- Read axis.
The full application code, and ready to use projects can be found on our LibStock page.
Other MIKROE Libraries used in the example:
- I2C
- UART
- Conversions
Additional notes and informations
Depending on the development board you are using, you may need USB UART click, USB UART 2 click or RS232 click to connect to your PC, for development systems with no UART to USB interface available on the board. The terminal available in all MIKROE compilers, or any other terminal application of your choice, can be used to read the message.
mikroSDK
This Click board™ is supported with mikroSDK – MIKROE Software Development Kit. To ensure proper operation of mikroSDK compliant Click board™ demo applications, mikroSDK should be downloaded from the LibStock and installed for the compiler you are using.
For more information about mikroSDK, visit the official page.
Resources
Downloads
| Weight | 23 g |
|---|---|
| Brand | MikroElektronika |