FRAM Click
R185.00 ex. VAT
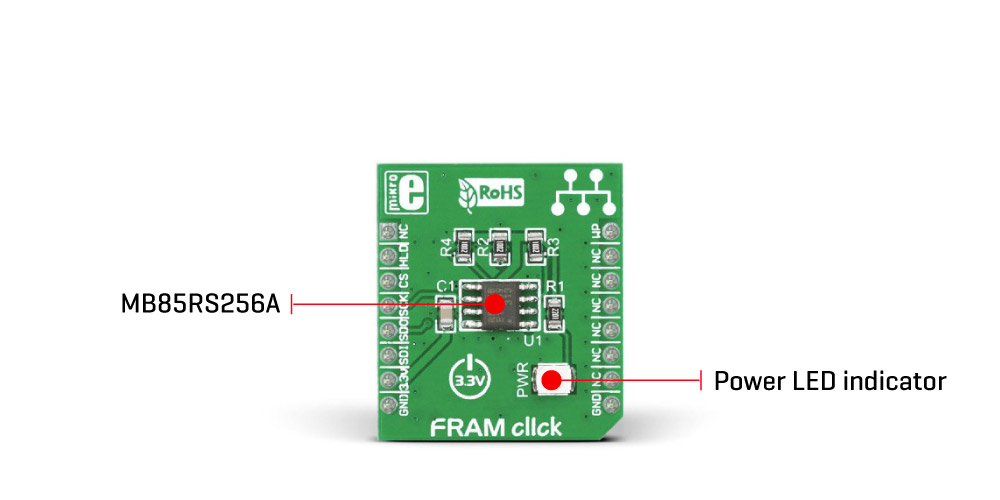
FRAM Click is a compact add-on board representing a highly reliable ferroelectric random access memory solution. This board features the MB85RS256A, a memory FRAM from Fujitsu. The MB85RS256A is a 256 Kbit serial FRAM module and comes in a configuration of 32,768 words x 8 bits, using the ferroelectric process and silicon gate CMOS process technologies for forming nonvolatile memory cells. This SPI configurable FRAM performs read and write operations like RAM, providing reliable data retention for 10 years while eliminating the complexities, overhead, and system-level reliability problems caused by EEPROM and other nonvolatile memories. This Click board™ makes the perfect solution for the development of nonvolatile memory applications requiring frequent or rapid writes and unlimited endurance.
FRAM Click is supported by a mikroSDK compliant library, which includes functions that simplify software development. This Click board™ comes as a fully tested product, ready to be used on a system equipped with the mikroBUS™ socket.
Stock: 1 available immediately.