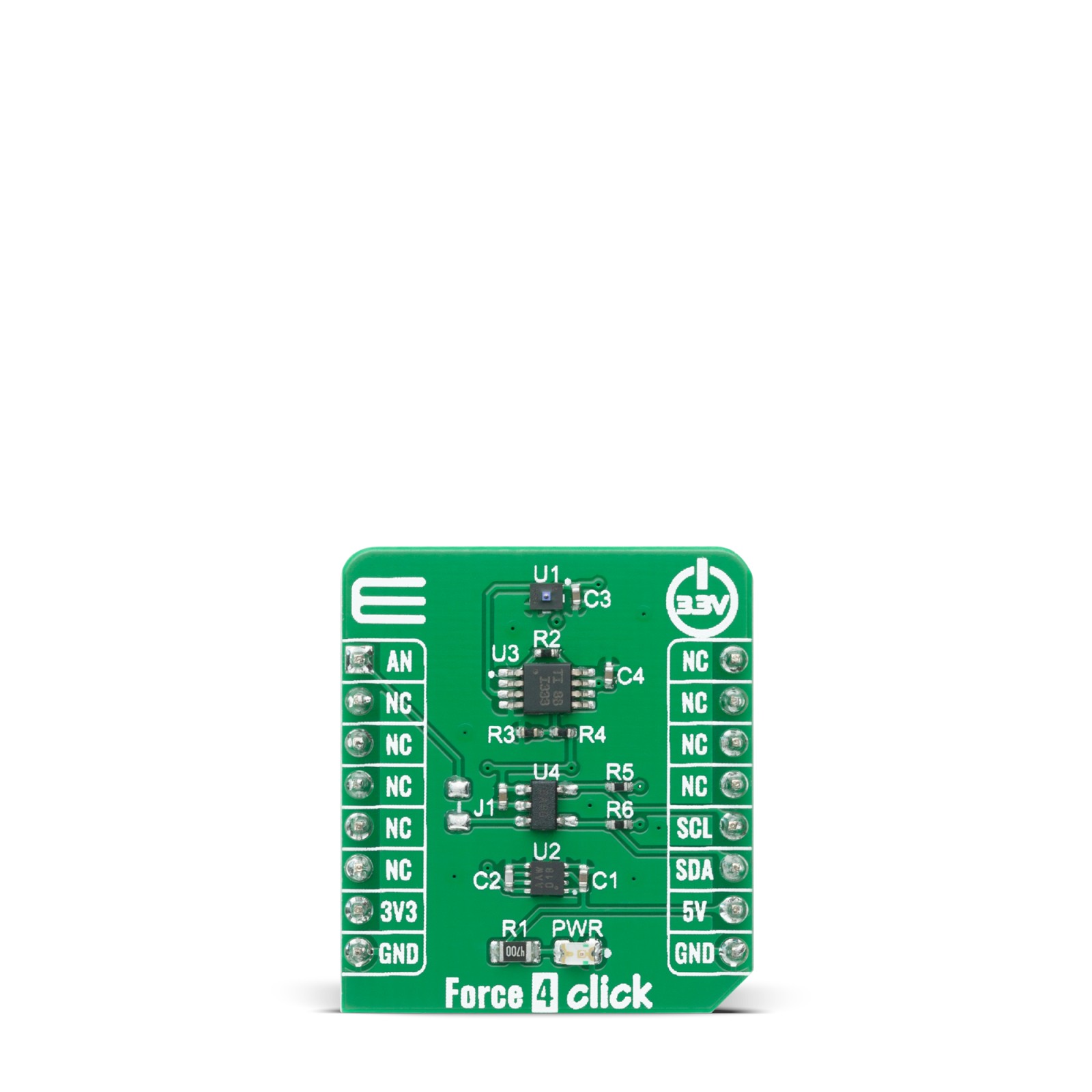
Force 4 Click
R460.00 ex. VAT
Force 4 Click is based on HSFPAR003A piezoresistive force sensor from Alpsalpine. This product is a force sensor using the effect of a piezoresistive bridge circuit formed on silicon diaphragm. Piezoresistive force sensors achieve higher linearity than other force sensors. To help with stability and accuracy Force 4 Click also includes MCP1101-33 a high precision buffered voltage reference as a power supply to a force sensor that allows high stability and accuracy of output voltage readings.
Force 4 Click board™ is supported by a mikroSDK compliant library, which includes functions that simplify software development. This Click board™ comes as a fully tested product, ready to be used on a system equipped with the mikroBUS™ socket.
Stock: Lead-time applicable.
| 5+ | R437.00 |
| 10+ | R414.00 |
| 15+ | R391.00 |
| 20+ | R376.28 |











.jpg)