Flash 7 Click
R200.00 ex. VAT
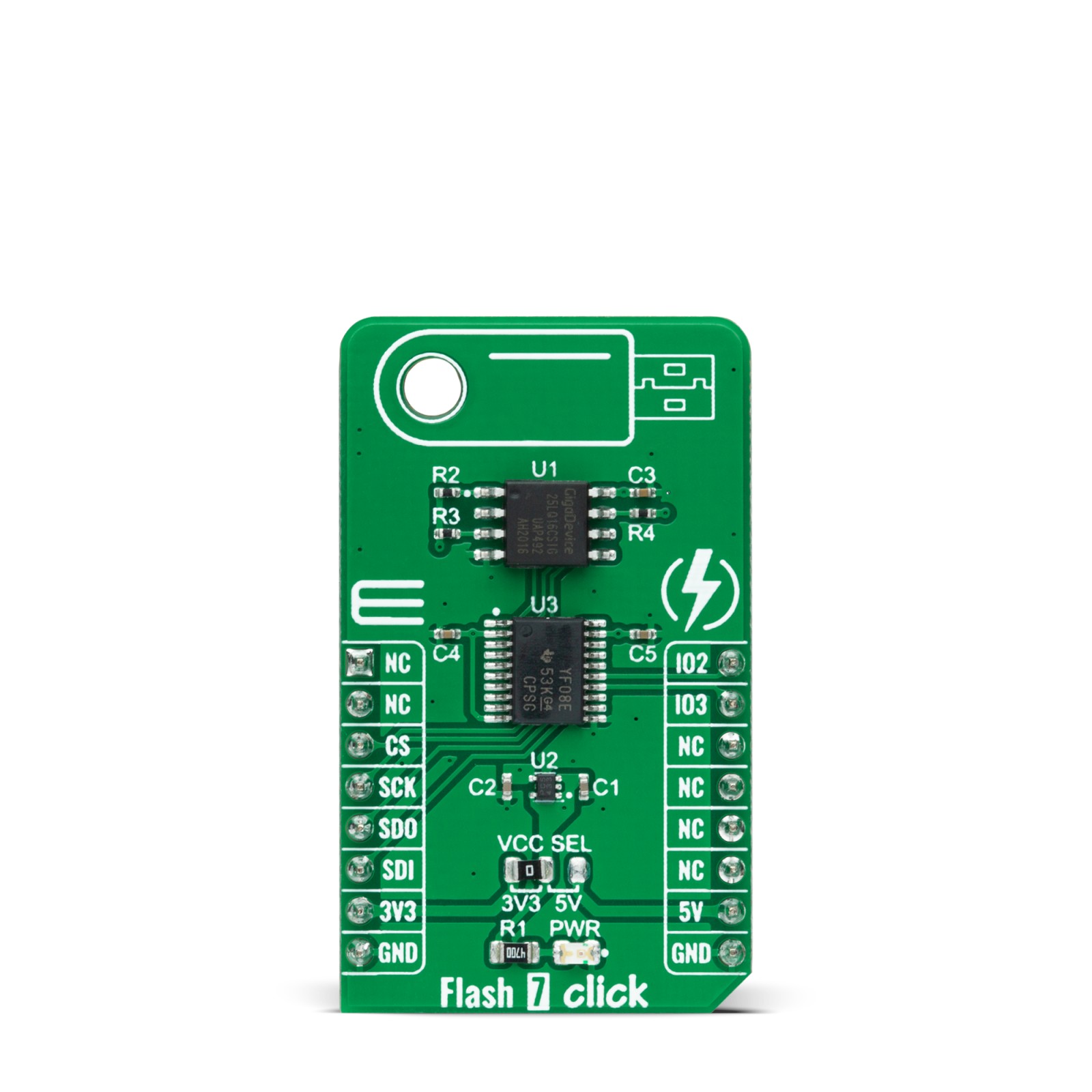
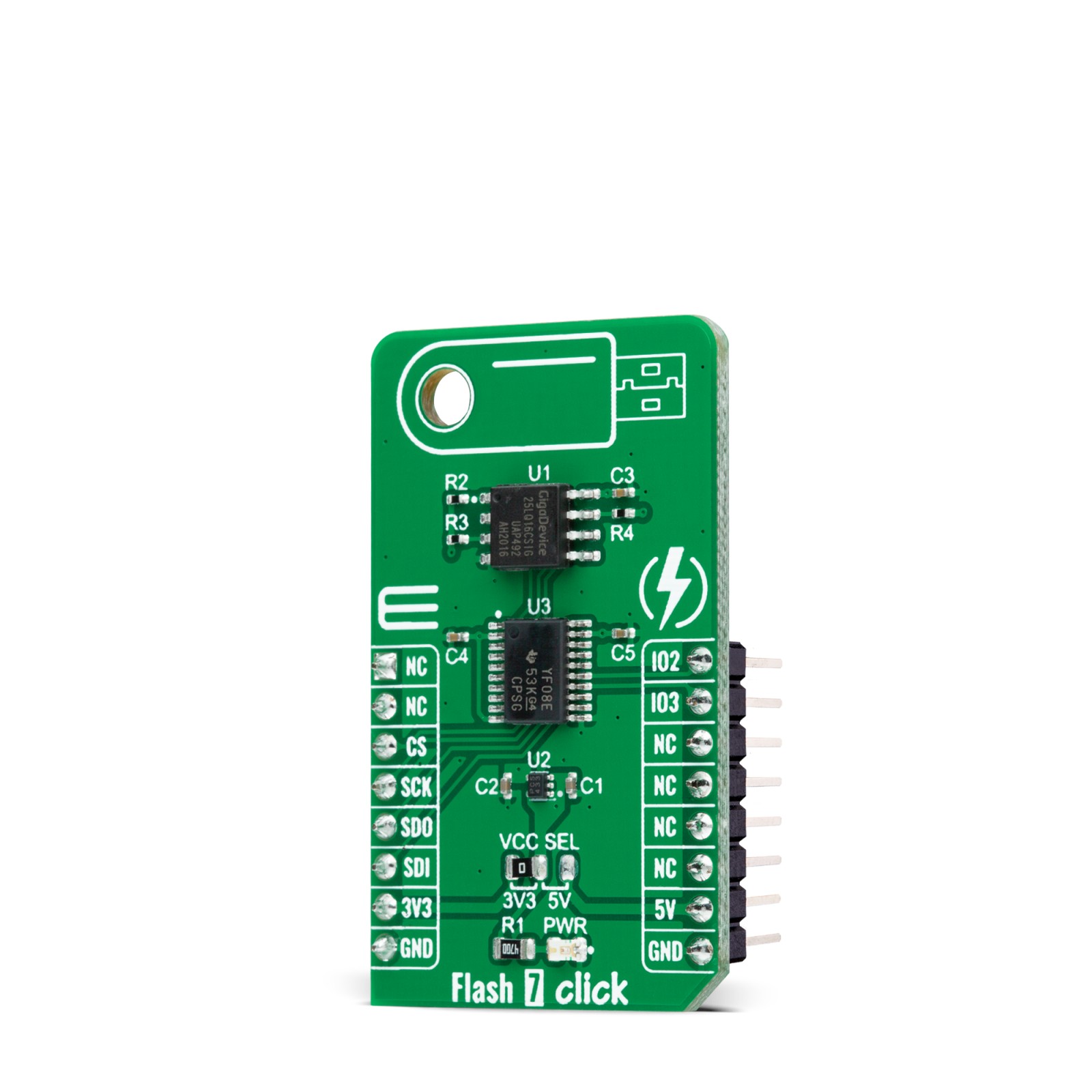
Flash 7 Click is a compact add-on board that contains a high-performance memory solution. This board features the GD25LQ16C, a high-performance 16Mbit SPI NOR Flash Memory solution with advanced security features from GigaDevice Semiconductor. It is specifically designed to meet the different needs in various electronic applications in terms of density, performance, reliability, and security while providing low power consumption. It requires only 6 signals to communicate between the MCU and the memory, thus reduces the design complexity and offers a reduction in board space and total system cost. This Click board™ provides a storage solution for systems with limited space in various embedded applications.
Flash 7 Click is supported by a mikroSDK compliant library, which includes functions that simplify software development. This Click board™ comes as a fully tested product, ready to be used on a system equipped with the mikroBUS™ socket.
Stock: Lead-time applicable.
| 5+ | R190.00 |
| 10+ | R180.00 |
| 15+ | R170.00 |
| 20+ | R163.60 |