EPOS Module Click
R1,200.00 ex. VAT
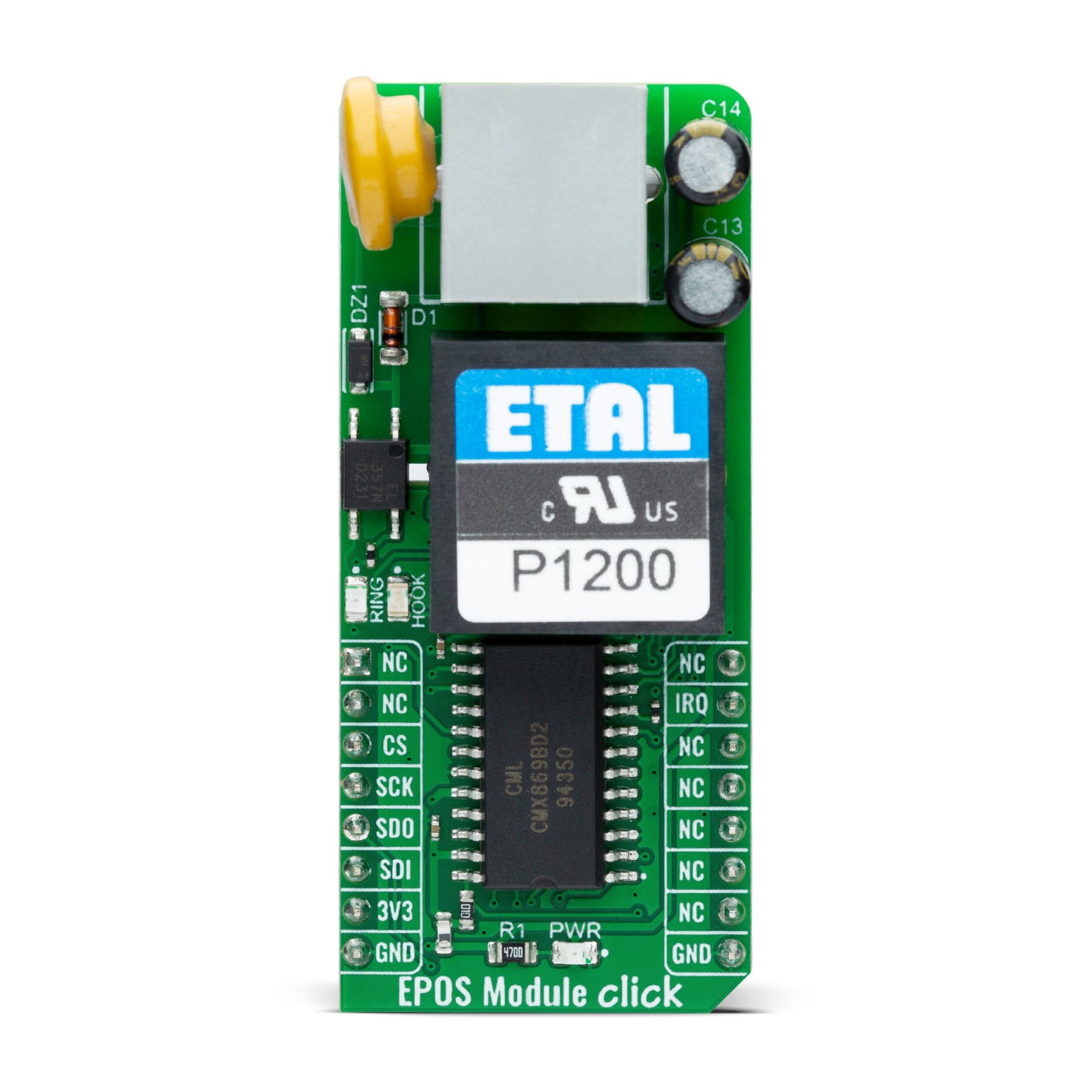
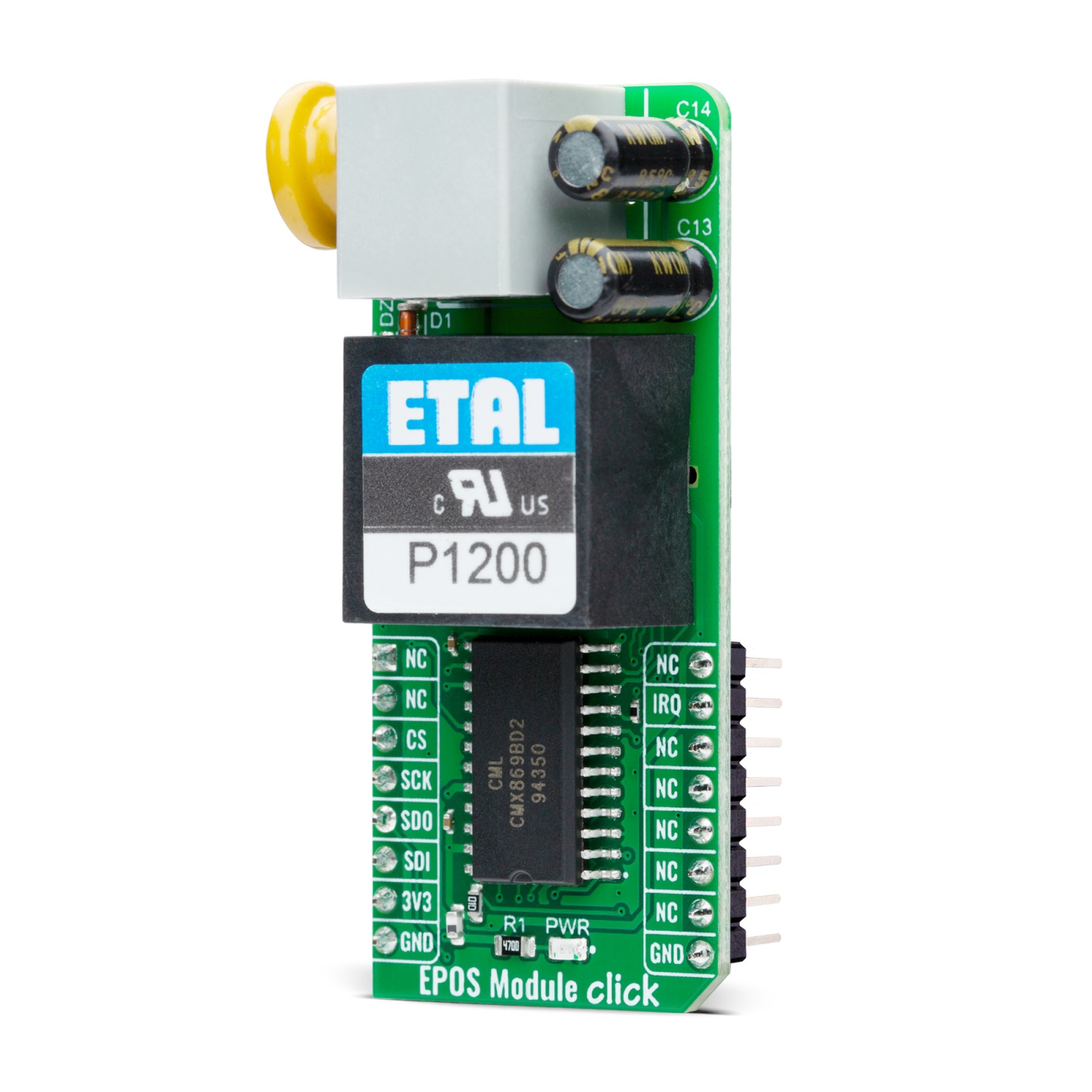
EPOS Module Click is a compact add-on board that provides a low-power modem solution for use in EPOS terminals and telephone-based systems. It is based on the CMX869B, a multi-standard v.32 bis modem from CML Micro, which supports multiple communication protocols. The CMX869B has built-in functions such as DTMF encoding/decoding and a Powersave mode to optimize energy consumption. It also includes a fully isolated telephone interface via the P1200 transformer for reliable communication. This Click board™ communicates with the host MCU through a standard 4-wire SPI interface and includes visual indicators for line status. It is ideal for applications like EPOS terminals, telephone telemetry systems, remote utility meter readings, security systems, and industrial control.
EPOS Module Click board™ is supported by a mikroSDK compliant library, which includes functions that simplify software development. This Click board™ comes as a fully tested product, ready to be used on a system equipped with the mikroBUS™ socket.
Stock: Lead-time applicable.
| 5+ | R1,140.00 |
| 10+ | R1,080.00 |
| 15+ | R1,020.00 |
| 20+ | R981.60 |
NOTE: To ensure the EPOS Module Click board™ meets global telecom isolation standards, it is essential to implement appropriate isolation measures. Using any SPI Isolator Click board™ is advisable to enhance the safety and reliability of your project and should be positioned between the line side of the EPOS Module Click and the system in use. These precautions help comply with international telecom standards, which may require isolation up to 6500V in some countries.
Warning: Telecom isolation requirements vary significantly across different countries. Always consult the telecom regulations specific to your country before connecting to the line. The users are responsible for ensuring compliance with local telecom standards and regulations.
How does it work?
EPOS Module Click is based on the CMX869B, a multi-standard v.32 bis modem from CML Micro, which supports multiple protocols while offering low power consumption. This low-power modem solution is designed for applications involving EPOS (Electronic Point of Sale) terminals and telephone-based systems. The CMX869B supports standards such as ITU V.32 bis, V.22 bis, V.22, V.21, and Bell 202 and 103, making it adaptable for numerous communication scenarios. It operates at data rates of up to 14.400bps and features automatic fallback to 4.800bps, with capabilities like retrain rate re-negotiation and automatic detection of V.22 and V.22 bis modems. This Click board™ is ideal for use in EPOS terminals, telephone telemetry systems, remote utility meter reading, security systems, industrial control, and other applications.

In addition to its robust modem functions, the CMX869B includes a high-quality DTMF (Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency) encoder and decoder, making it suitable for managing call signaling and detection in telephone systems. The modem can also transmit and detect user-programmed single and dual-tone signals, as well as handle modem calling and answering tones, ensuring compatibility with various proprietary communication protocols beyond standard modem operations. The Click board™ also offers a fully isolated EPOS/telephone-based connection, thanks to its built-in P1200 transformer, which ensures smooth communication while providing complete electrical isolation.
Data and control exchanges between the CMX869B and the host MCU are made through a C-BUS interface, compatible with a standard 4-wire SPI interface of the mikroBUS™ socket. The board also uses the mikroBUS™ socket’s IRQ pin for interrupt requests related to call states like busy, dialing, and connected statuses, a red RING LED to indicate ringing signals, and a blue HOOK LED that serves as a hookswitch indicator to manage the line interface’s connectivity status (0-OFF, 1-ON). An additional feature of the CMX869B is the Powersave mode, which conserves energy by deactivating all circuits except the essential C-BUS (SPI) interface.
This Click board™ can be operated only with a 3.3V logic voltage level. The board must perform appropriate logic voltage level conversion before using MCUs with different logic levels. Also, it comes equipped with a library containing functions and an example code that can be used as a reference for further development.
Specifications
Type
Signal Processing
Applications
Ideal for EPOS terminals, telephone telemetry systems, remote utility meter readings, security systems, and industrial control
On-board modules
CMX869B – multi-standard low power v.32 bis modem from CML Microcircuits
Key Features
Supporting multiple protocols (v.32 bis, V.22 bis, V.22, V.21, Bell 202, Bell 103), DTMF encoder and decoder for call signaling and detection, fully isolated telephone interface with integrated P1200 transformer, SPI interface, Powersave mode, ringing and hookswitch status indicators, and more
Interface
SPI
Feature
No ClickID
Compatibility
mikroBUS™
Click board size
L (57.15 x 25.4 mm)
Input Voltage
3.3V
Pinout diagram
This table shows how the pinout on EPOS Module Click corresponds to the pinout on the mikroBUS™ socket (the latter shown in the two middle columns).
Onboard settings and indicators
| Label | Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| LD1 | PWR | – | Power LED Indicator |
| LD2 | RING | – | Ring LED Indicator |
| LD3 | HOOK | – | Hook State LED Indicator |
EPOS Module Click electrical specifications
| Description | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply Voltage | – | 3.3 | – | V |
Software Support
We provide a library for the EPOS Module Click as well as a demo application (example), developed using MIKROE compilers. The demo can run on all the main MIKROE development boards.
Package can be downloaded/installed directly from NECTO Studio Package Manager (recommended), downloaded from our LibStock™ or found on MIKROE github account.
Library Description
This library contains API for EPOS Module Click driver.
Key functions
-
eposmodule_handshake_initThis function performs a handshake init which resets the device settings to default. -
eposmodule_dialThis function dials the selected number by alternating between DTMF and No-tone. -
eposmodule_send_messageThis function sends an array of bytes via V.23 FSK 1200bps modem in start-stop 8.1 mode.
Example Description
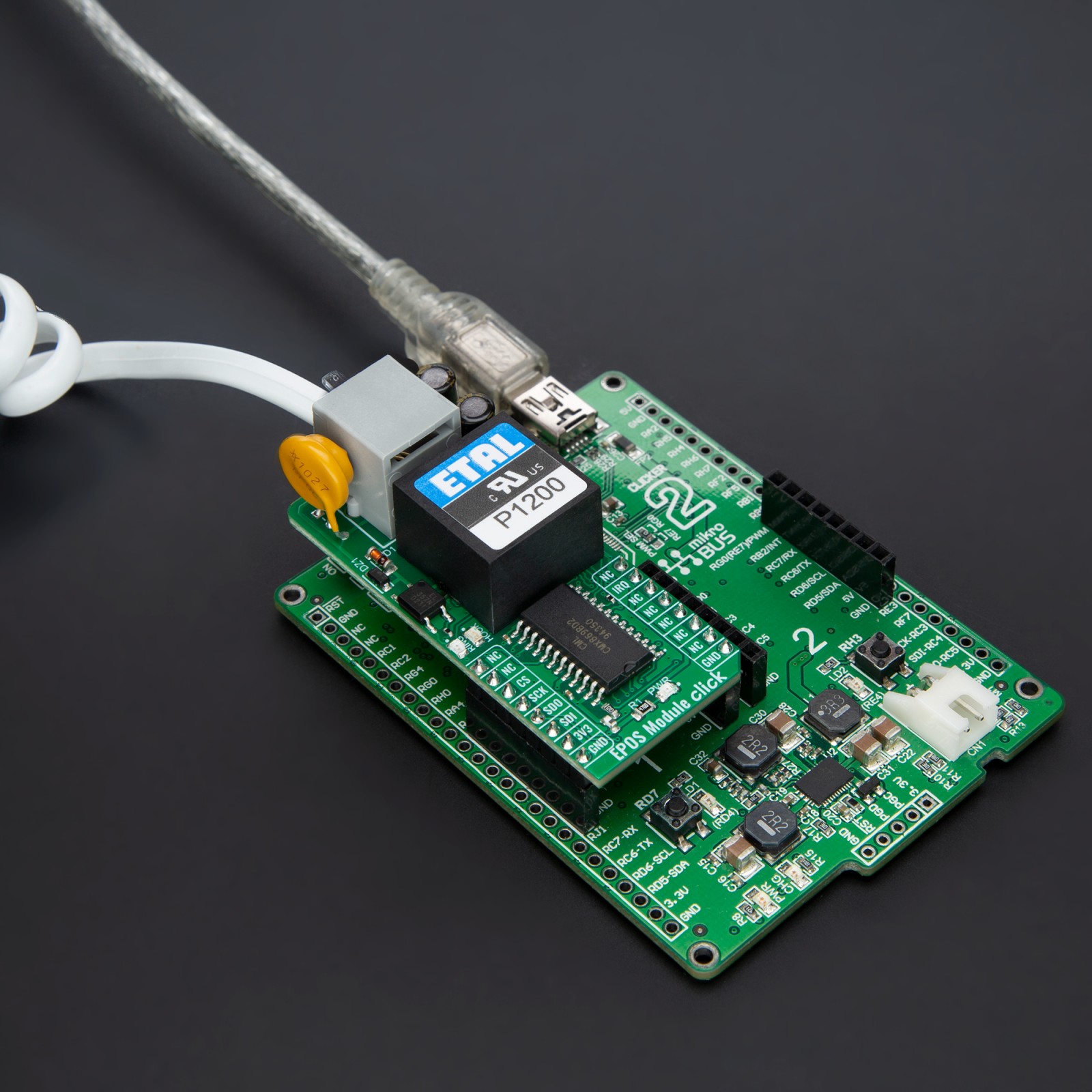
This example demonstrates the use of EPOS Module Click by showing the communication between the two click boards connected to PBX system.
void application_task ( void )
{
uint8_t state = EPOSMODULE_STATE_IDLE;
uint32_t time_cnt = 0;
uint8_t msg_cnt = 0;
eposmodule_handshake_init ( &eposmodule );
#if ( DEMO_APP == APP_DIALING )
log_printf( &logger, "rn Hook OFFrn" );
eposmodule_hook_off ( &eposmodule );
Delay_ms ( 4000 );
log_printf( &logger, " Dial: %srn", ( char * ) DIAL_NUMBER );
eposmodule_dial ( &eposmodule, DIAL_NUMBER );
eposmodule.rx_mode &= EPOSMODULE_RX_LEVEL_MASK; // No change in rx level setting
eposmodule.rx_mode |= ( EPOSMODULE_RX_MODE_DTMF_TONES | EPOSMODULE_RX_TONE_DETECT_CALL_PROG );
eposmodule_set_receive_mode ( &eposmodule, eposmodule.rx_mode );
for ( ; ; )
{
Delay_ms ( 1 );
if ( !eposmodule_get_irq_pin ( &eposmodule ) )
{
time_cnt = 0;
state = EPOSMODULE_STATE_IRQ_SET;
}
if ( ( EPOSMODULE_STATE_IRQ_SET == state ) && !eposmodule_call_progress ( &eposmodule ) )
{
if ( time_cnt < EPOSMODULE_TIMING_BUSY )
{
log_printf( &logger, " Busyrn" );
break;
}
else if ( time_cnt < EPOSMODULE_TIMING_DISCONNECTED )
{
log_printf( &logger, " Disconnectedrn" );
break;
}
else if ( time_cnt < EPOSMODULE_TIMING_RINGING )
{
log_printf( &logger, " Ringingrn" );
state = EPOSMODULE_STATE_RINGING;
}
}
if ( ( EPOSMODULE_STATE_RINGING == state ) && ( time_cnt > EPOSMODULE_TIMING_CALL_PROGRESS ) )
{
log_printf( &logger, " Call in progressrn" );
state = EPOSMODULE_STATE_CALL_IN_PROGRESS;
time_cnt = 0;
}
if ( ( EPOSMODULE_STATE_CALL_IN_PROGRESS == state ) && !( time_cnt % EPOSMODULE_TIMING_SEND_MESSAGE ) )
{
log_printf( &logger, " Send message %urn", ( uint16_t ) msg_cnt++ );
eposmodule_send_message ( &eposmodule, TEXT_TO_SEND, strlen ( TEXT_TO_SEND ) );
}
if ( time_cnt++ > EPOSMODULE_TIMEOUT_CALL_PROGRESS )
{
log_printf( &logger, " Timeoutrn" );
break;
}
}
log_printf( &logger, " Hook ONrn" );
eposmodule_hook_on ( &eposmodule );
Delay_ms ( 4000 );
#elif ( DEMO_APP == APP_ANSWERING )
uint8_t rx_data = 0;
uint8_t msg_end_buff[ 2 ] = { 0 };
log_printf( &logger, "rn Waiting for a call...rn" );
while ( !eposmodule_ring_detect ( &eposmodule ) );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
log_printf( &logger, " Hook OFFrn" );
eposmodule_hook_off ( &eposmodule );
Delay_ms ( 1000 );
log_printf( &logger, " Waiting for %u messages...rn", ( uint16_t ) NUM_MESSAGES );
eposmodule.rx_mode &= EPOSMODULE_RX_LEVEL_MASK; // No change in rx level setting
eposmodule.rx_mode |= ( EPOSMODULE_RX_MODE_V23_FSK_1200 | EPOSMODULE_RX_DATA_FORMAT_SS_NO_OVS |
EPOSMODULE_RX_DATA_PARITY_8_NO_PAR );
eposmodule_set_receive_mode ( &eposmodule, eposmodule.rx_mode );
for ( ; ; )
{
Delay_ms ( 1 );
if ( !eposmodule_get_irq_pin ( &eposmodule ) )
{
if ( EPOSMODULE_STATE_IDLE != state )
{
log_printf( &logger, "rn Disconnectedrn" );
break;
}
log_printf( &logger, " Message %u: ", ( uint16_t ) msg_cnt );
state = EPOSMODULE_STATE_IRQ_SET;
time_cnt = 0;
}
if ( ( EPOSMODULE_STATE_IRQ_SET == state ) && !( time_cnt % EPOSMODULE_TIMING_RX_READY ) )
{
if ( eposmodule_unscram_1s_det ( &eposmodule ) && eposmodule_rx_ready ( &eposmodule ) )
{
eposmodule_receive_data ( &eposmodule, &rx_data );
if ( ( ( ' ' <= rx_data ) && ( '~' >= rx_data ) ) ||
( 'r' == rx_data ) || ( 'n' == rx_data ) )
{
log_printf( &logger, "%c", ( char ) rx_data );
}
if ( 'r' == rx_data )
{
msg_end_buff[ 0 ] = rx_data;
}
else if ( 'n' == rx_data )
{
msg_end_buff[ 1 ] = rx_data;
}
else
{
msg_end_buff[ 0 ] = 0;
msg_end_buff[ 1 ] = 0;
}
}
if ( ( 'r' == msg_end_buff[ 0 ] ) && ( 'n' == msg_end_buff[ 1 ] ) )
{
msg_end_buff[ 0 ] = 0;
msg_end_buff[ 1 ] = 0;
state = EPOSMODULE_STATE_IDLE;
if ( NUM_MESSAGES == ++msg_cnt )
{
Delay_ms ( 100 );
log_printf( &logger, " Terminate callrn" );
Delay_ms ( 100 );
break;
}
}
}
if ( time_cnt++ > EPOSMODULE_TIMING_WAIT_FOR_MESSAGE )
{
log_printf( &logger, "rn Timeoutrn" );
break;
}
}
log_printf( &logger, " Hook ONrn" );
eposmodule_hook_on ( &eposmodule );
Delay_ms ( 4000 );
#endif
}
The full application code, and ready to use projects can be installed directly from NECTO Studio Package Manager (recommended), downloaded from our LibStock™ or found on MIKROE github account.
Other MIKROE Libraries used in the example:
- MikroSDK.Board
- MikroSDK.Log
- Click.EPOSModule
Additional notes and informations
Depending on the development board you are using, you may need USB UART click, USB UART 2 Click or RS232 Click to connect to your PC, for development systems with no UART to USB interface available on the board. UART terminal is available in all MIKROE compilers.
mikroSDK
This Click board™ is supported with mikroSDK – MIKROE Software Development Kit. To ensure proper operation of mikroSDK compliant Click board™ demo applications, mikroSDK should be downloaded from the LibStock and installed for the compiler you are using.
For more information about mikroSDK, visit the official page.
Resources
Downloads
| Weight | 33 g |
|---|---|
| Brand | MikroElektronika |