DIGI POT 6 Click
R310.00 ex. VAT
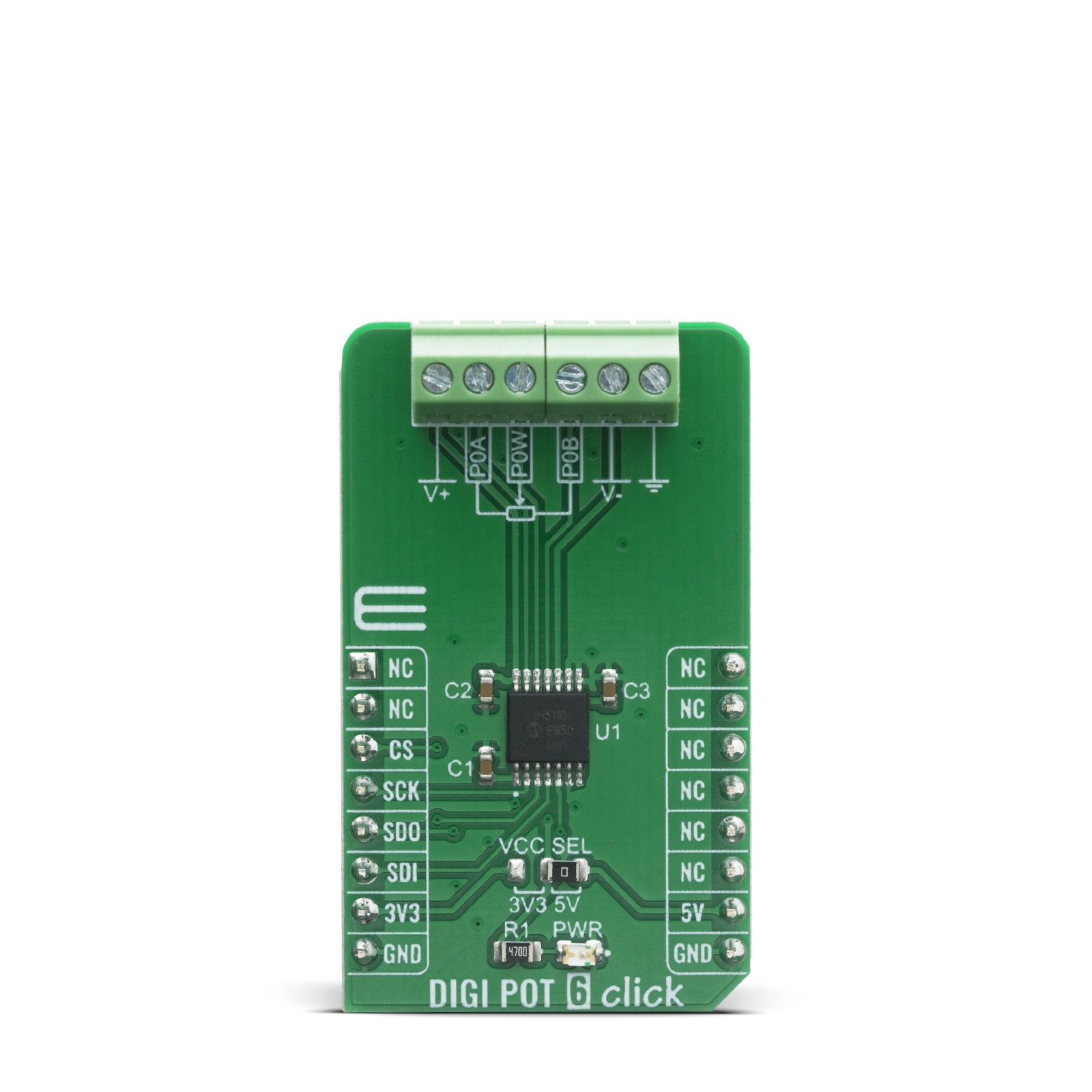
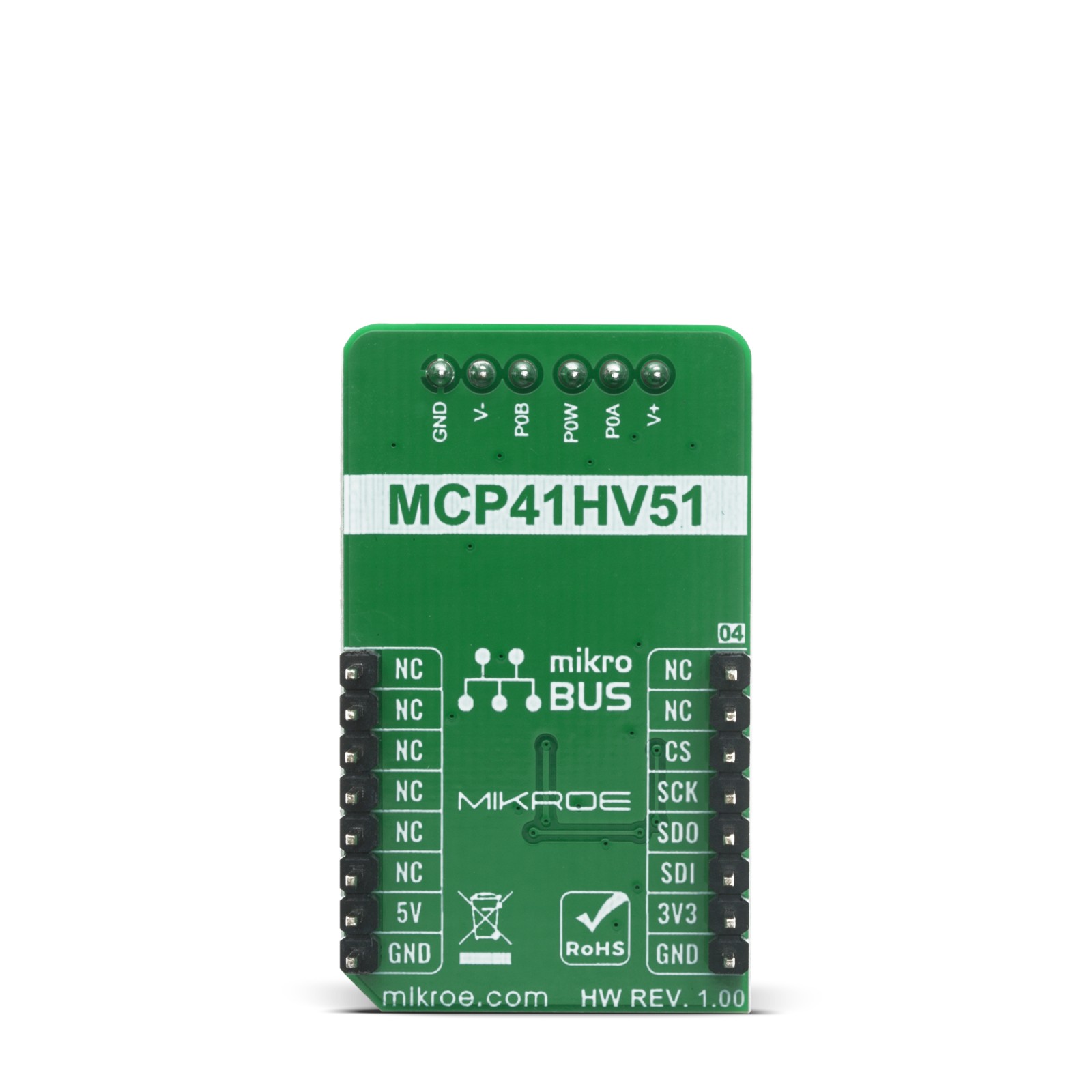
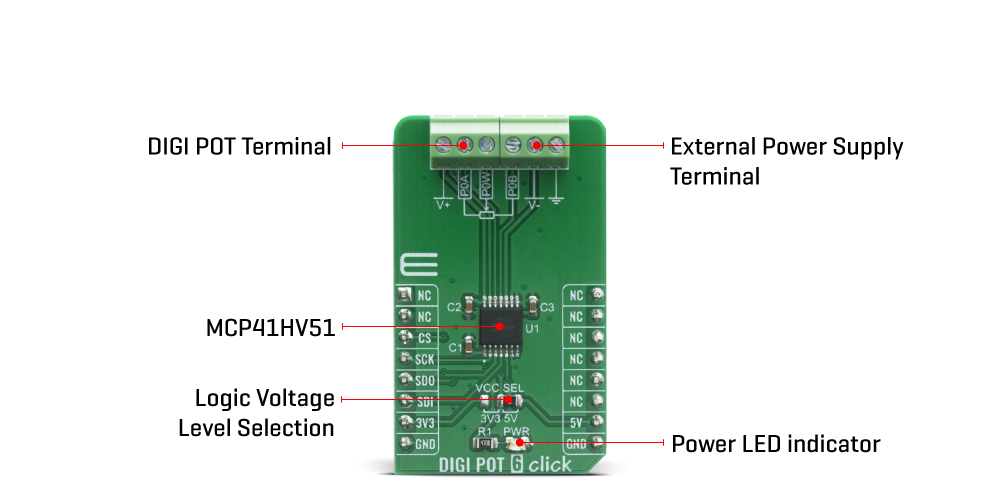
DIGI POT 6 Click is a compact add-on board used as a digitally controlled potentiometer. This board features the MCP41HV51, 8-bit dual power rails digital potentiometer with SPI serial interface and volatile memory from Microchip. The MCP41HV51 has a wide operating voltage range, analog from 10 to 36V and digital from 2.7 to 5.5V or implemented as dual-rail (±18V). Its 8-bit configuration supports 255 resistors and 256 steps and provides RAB resistance options of 100 kΩ. It also has a Write Latch function, which will inhibit the volatile wiper register from being updated with the received data. This Click board™ is suitable for precision calibration of set point thresholds, adjustable power supplies, adjustable gain amplifiers and offset trimming, and more.
DIGI POT 6 Click is supported by a mikroSDK compliant library, which includes functions that simplify software development. This Click board™ comes as a fully tested product, ready to be used on a system equipped with the mikroBUS™ socket.
Stock: Lead-time applicable.
| 5+ | R294.50 |
| 10+ | R279.00 |
| 15+ | R263.50 |
| 20+ | R253.58 |