DALI Click
R525.00 ex. VAT
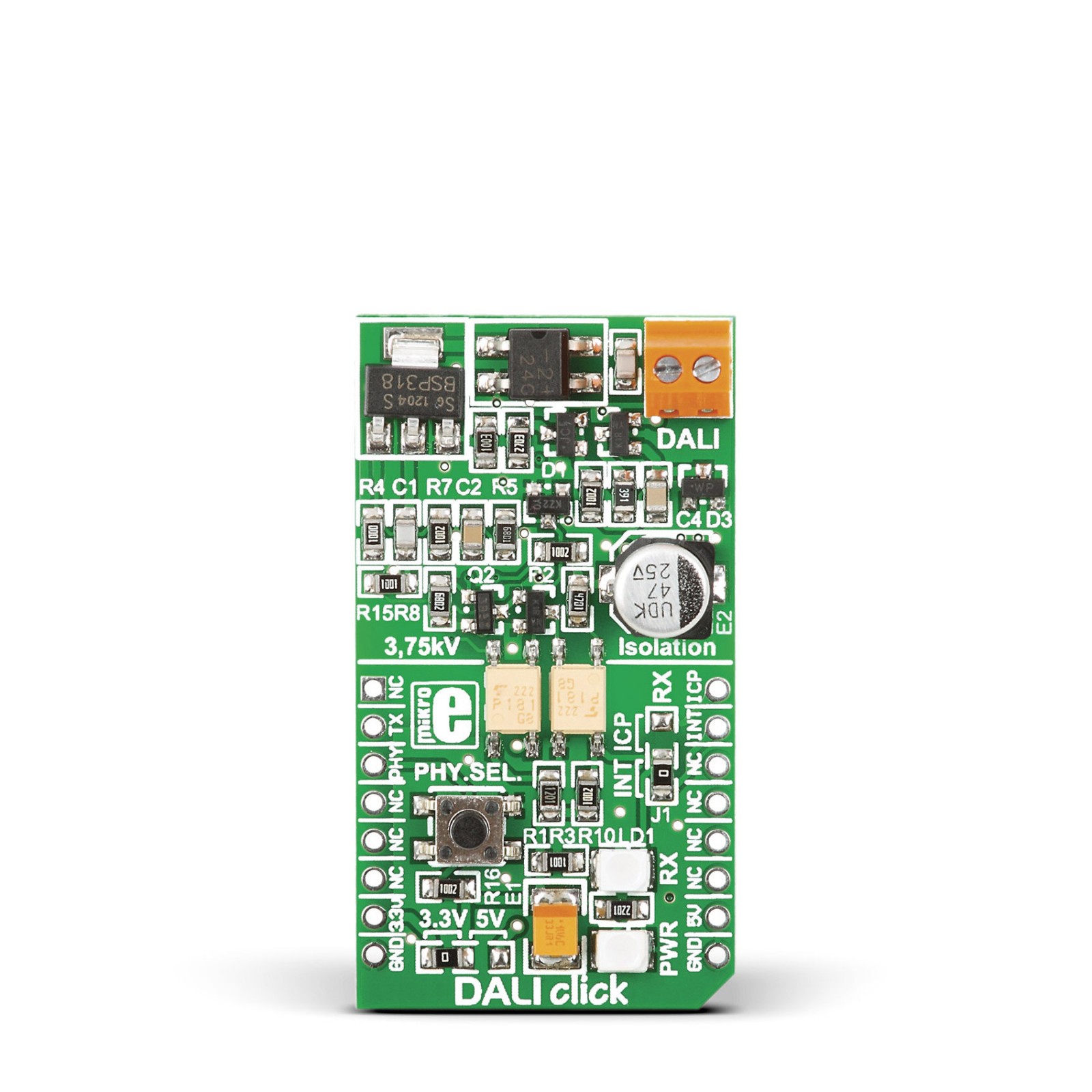
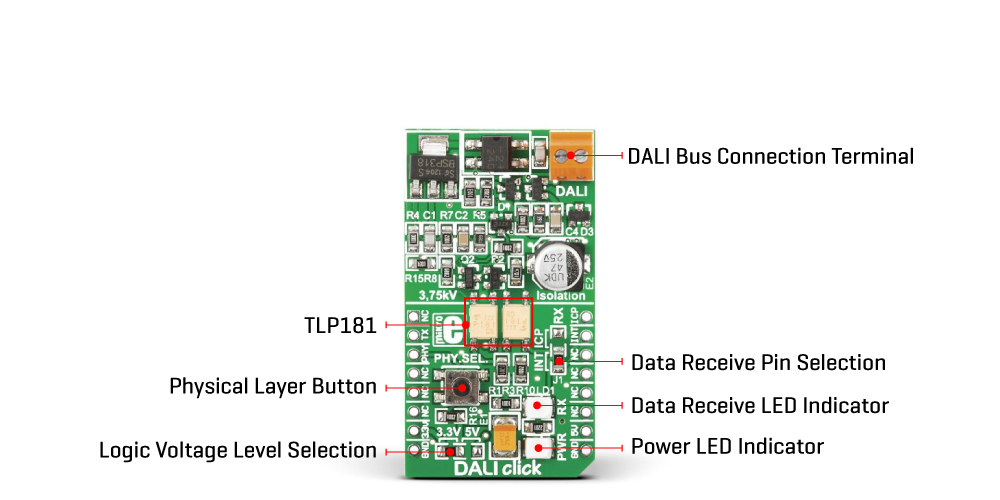
DALI Click is a compact add-on board that provides a Digital Addressable Lighting Interface (DALI) with any MCU. This board features two PS2701-1 small outline couplers capable of 3.75kV isolation from Renesas. DALI interface represents an industry-standardized protocol specified in the multi-part international standard IEC 62386. Equipped with a linear voltage regulator, a transmit/receive, and constant current circuits, this Click board™ has all the necessary parts to meet the DALI specifications. This Click board™ makes the perfect solution for intelligent digital lighting control and enables easy implementation of robust and flexible lighting networks.
DALI Click is supported by a mikroSDK compliant library, which includes functions that simplify software development. This Click board™ comes as a fully tested product, ready to be used on a system equipped with the mikroBUS™ socket.
Stock: Lead-time applicable.
| 5+ | R498.75 |
| 10+ | R472.50 |
| 15+ | R446.25 |
| 20+ | R429.45 |