Brushless 7 Click
R530.00 ex. VAT
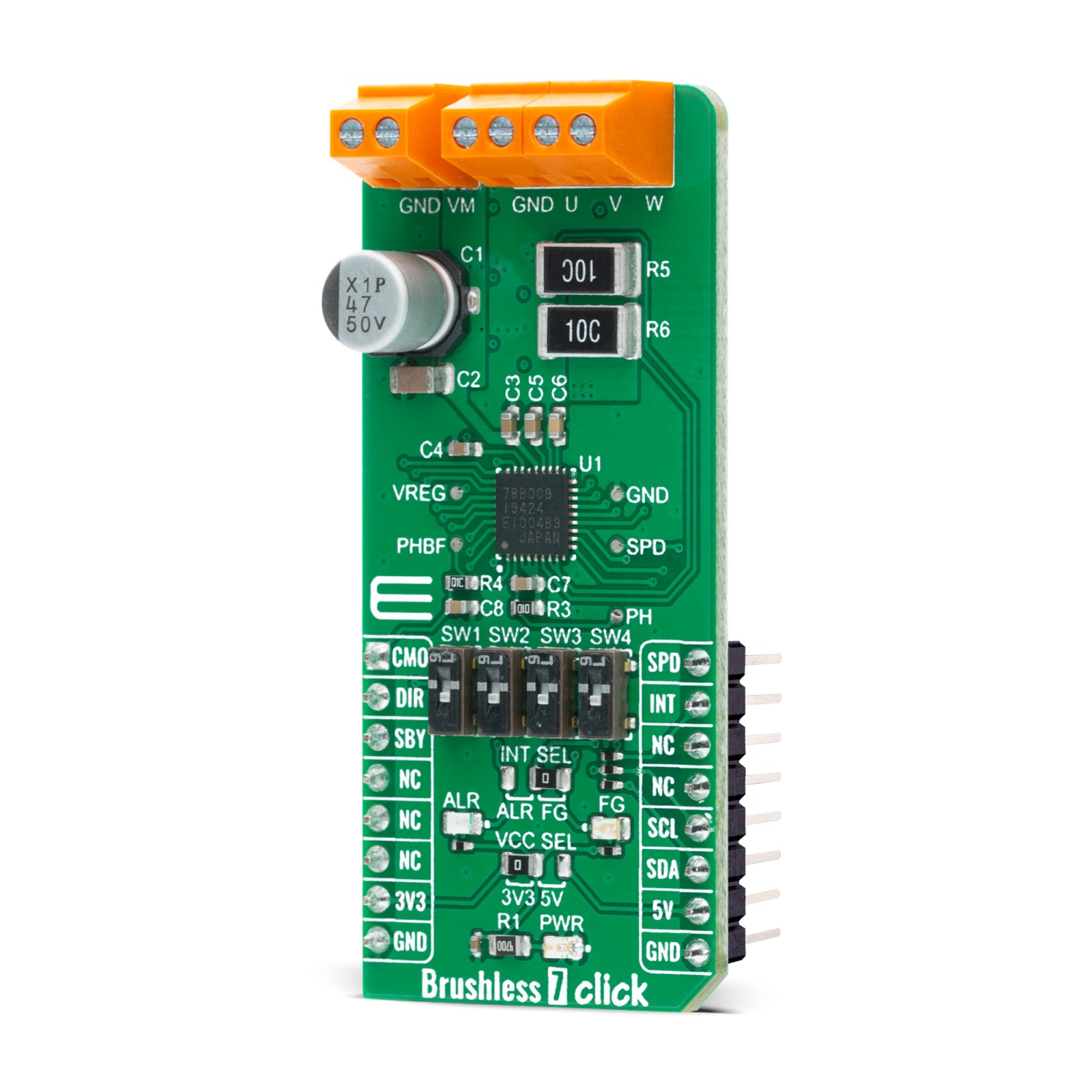
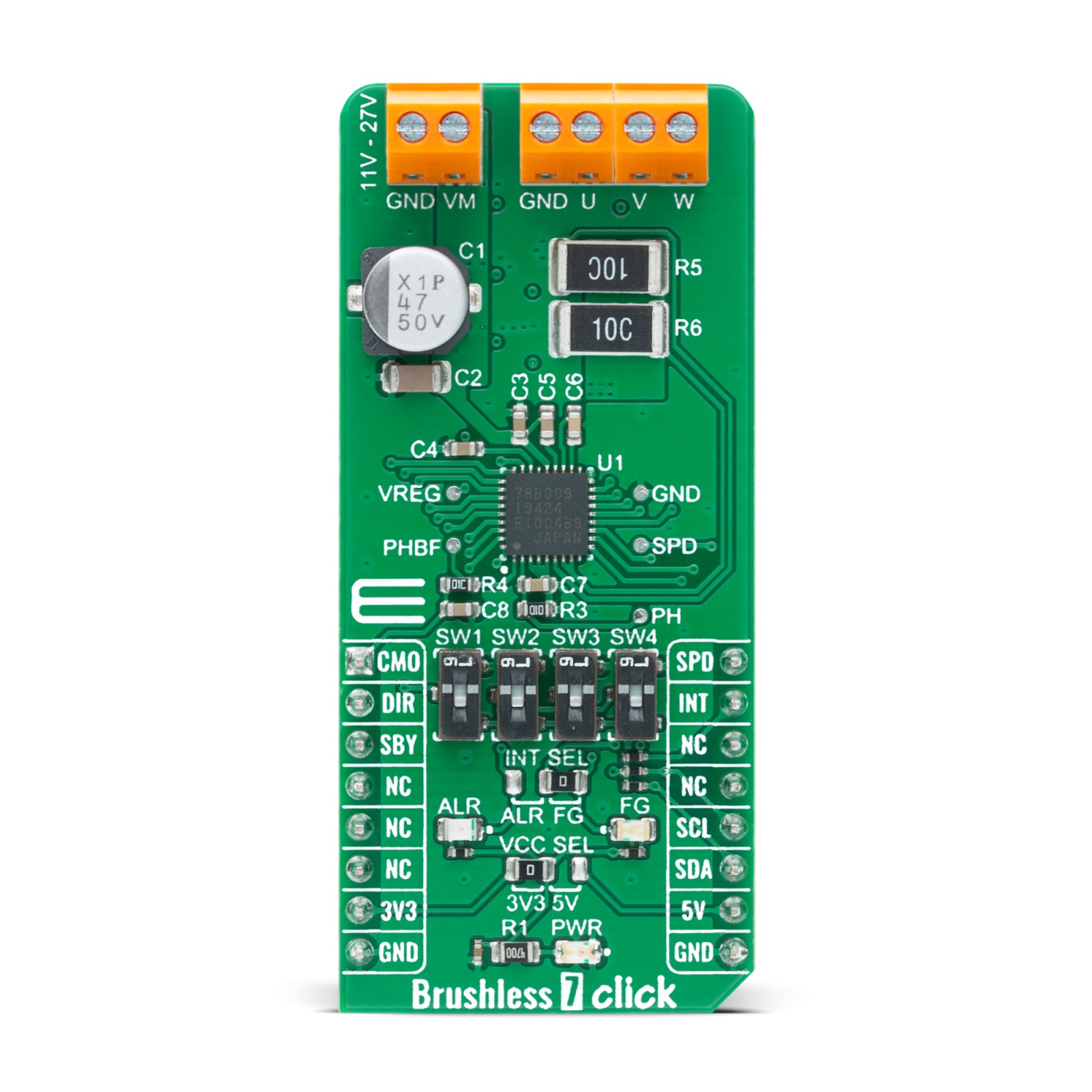
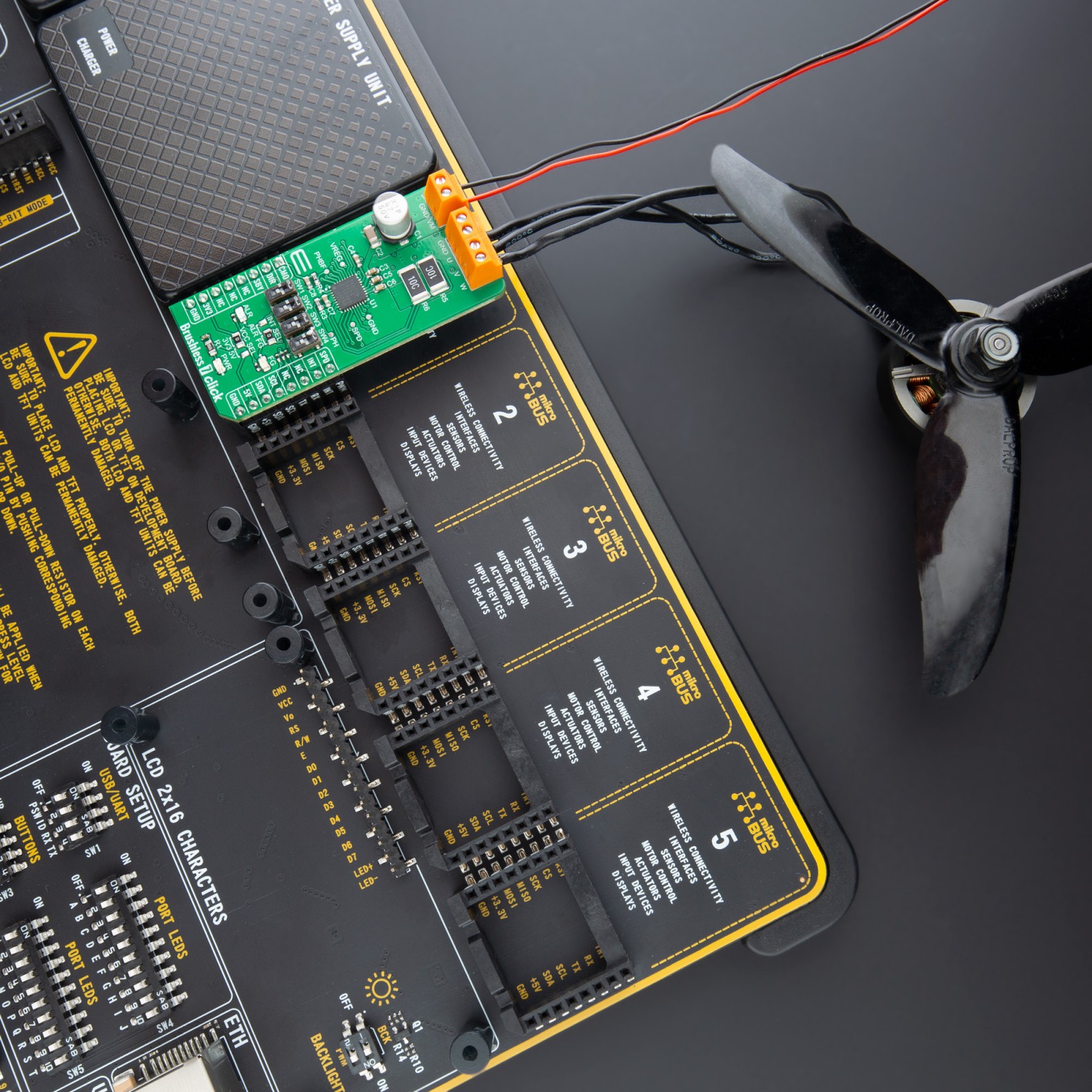
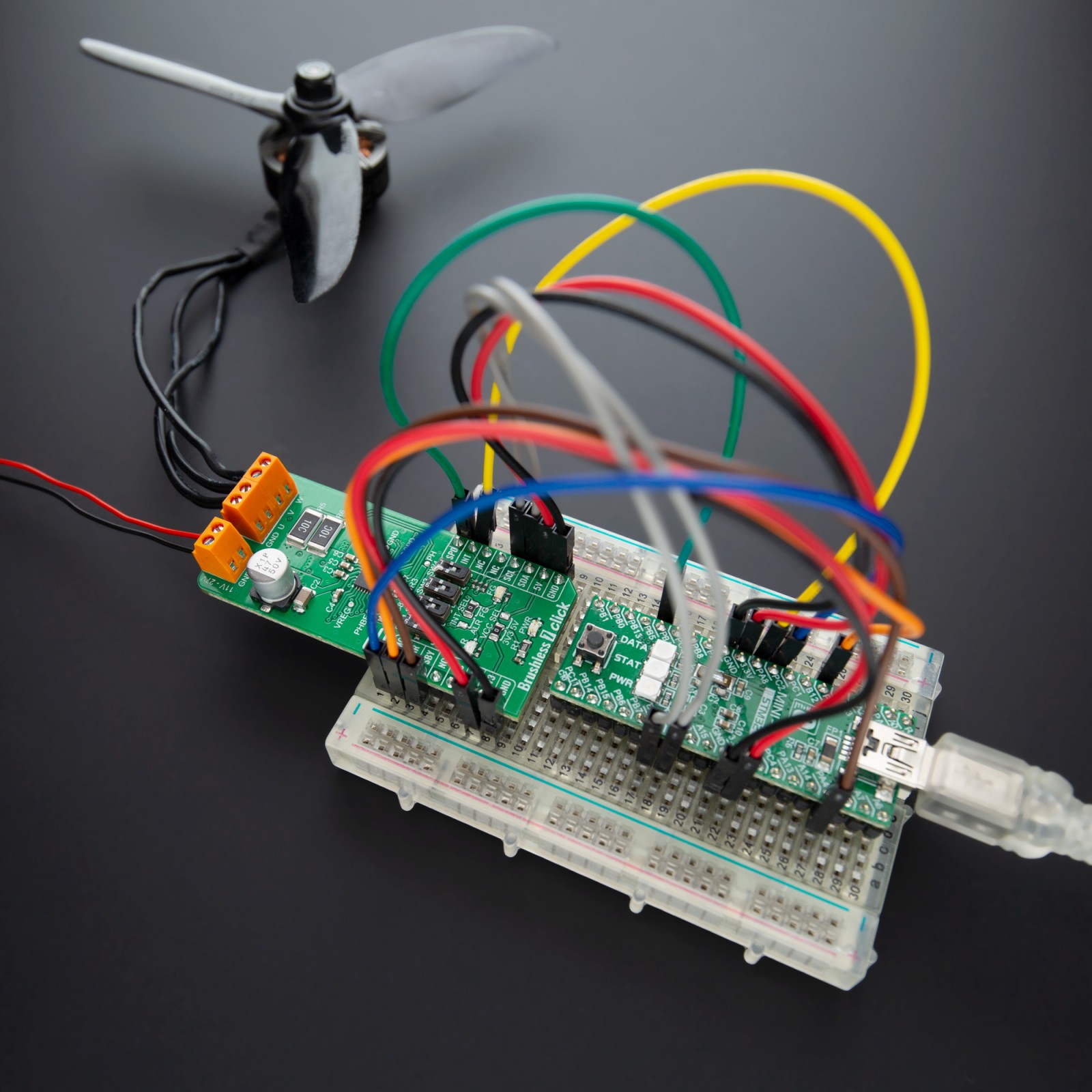
Brushless 7 Click is a compact add-on board suitable for controlling BLDC motors with any MCU. This board features the TC78B009FTG, a three-phase PWM pre-driver realized with six external MOSFETs to drive sensorless brushless motors from Toshiba Semiconductor. Some of the main features are a built-in closed-loop speed control function with internal non-volatile memory (NVM) for speed profile setting and the ability to set other features such as rotation direction selection, brake, Standby mode, and others. It also has a wide operating voltage range of 11V to 27V with an output current capacity of 5A and several built-in error detection circuits. This Click board™ provides optimum operational efficiency in applications such as high-velocity server fans, blowers, and pumps.
Brushless 7 Click is supported by a mikroSDK compliant library, which includes functions that simplify software development. This Click board™ comes as a fully tested product, ready to be used on a system equipped with the mikroBUS™ socket.
Stock: Lead-time applicable.
| 5+ | R503.50 |
| 10+ | R477.00 |
| 15+ | R450.50 |
| 20+ | R433.54 |
How does it work?
Brushless 7 Click is based on the TC78B009FTG, a three-phase sensorless PWM pre-driver capable of driving Delta or Wye configured motors from Toshiba Semiconductor. Motor rotation is controlled without Hall sensors by detecting the rotational position from the induced voltage. The TC78B009FTG has a built-in closed-loop speed control function, which regulates and maintains the motor rotational speed under dynamic power fluctuations and load variations. This function has an internal non-volatile memory (NVM) for speed profile setting. The TC78B009FTG also has protection features such as thermal shutdown, under-voltage, over-current protection, lock detection, and more.

The TC78B009FTG possesses a speed control command that can control the motor’s start, stop, and rotation count. This signal type is determined by the position of an onboard SW2 switch and register setting, allowing the selection among PWM, analog voltage signal, and standard I2C 2-Wire interface to read data and configure settings with a maximum frequency of 400kHz. The TC78B009FTG also allows choosing its I2C slave address by positioning SMD switches labeled as SW3 and SW4 to an appropriate position. In the case of PWM signal or analog voltage signal, the TC78B009FTG is controlled through the mikroBUS™ PWM signal marked as SPD.
This Click board™ has several operational modes: Standby, Idle, Brake, and Error Mode. Standby mode is available to reduce the power consumption, controlled by the SBY pin routed to the CS pin of the mikroBUS™ socket, together with register settings. After Power-on, with the SBY pin disabled, the TC78B009FTG reads parameters from NVM and stores them in the registers. After that, IC goes to Brake sequence, or controlled via SW1 switch, and then moves to Idle mode. Whit the speed control command set, the TC78B009FTG starts the motor by Start-Up sequence. When an abnormal condition is detected, IC moves to Error mode and automatically restarts after restart time. In Error mode with Stop as a speed control command, the TC78B009FTG will move to Idle mode.
Alongside I2C communication, several signals connected to the mikroBUS™ socket pins are also used to forward the information to the MCU. The DIR pin, routed on the RST pin of the mikroBUS™ socket, is used to select the direction of motor rotation (clockwise/counterclockwise), while the CMO pin, routed on the AN pin of the mikroBUS™ socket, serves as the motor’s output current monitoring. Also, the TC78B009FTG provides selectable interrupts chosen via the INT SEL jumper routed on the INT pin of the mikroBUS™ socket by positioning the SMD jumper to an appropriate position marked as ALR od FG. The default position of this jumper is the FG position which serves as a rotation speed indicator, while the ALR position represents an abnormality detection feature. Both features have visual indicators; a red LED marked as ALR, and a blue LED labeled as FG.
Brushless 7 Click is realized using six N-channel MOSFETs, the SSM6K513NU also from Toshiba Semiconductor, two for each of the three phases. Using these FETs, capable of handling 15A, allows low power dissipation when driving 5A BLDC before hitting the output current limit threshold, used to restrain the current flowing to the motor. It also supports an external power supply for the motor, which can be connected to the input terminal labeled as VM and should be within the range of 11V to 27V, while the BLDC motor coils can be connected to the terminals labeled as U, V, and W.
This Click board™ can operate with both 3.3V and 5V logic voltage levels selected via the VCC SEL jumper. This way, it is allowed for both 3.3V and 5V capable MCUs to use the communication lines properly. However, the Click board™ comes equipped with a library that contains easy-to-use functions and an example code that can be used, as a reference, for further development.
Specifications
Type
Brushless
Applications
Can be used for high-velocity server fans, blowers, and pumps
On-board modules
TC78B009FTG – three-phase PWM pre-driver for sensorless brushless motors from Toshiba Semiconductor
Key Features
Sensorless PWM drive, capable to drive Delta or Wye configured motors, low power consumption, built-in closed loop speed control with adjustable speed curve, motor speed control by analog voltage, PWM duty cycle, or I2C, integrated error detection circuits, and more
Interface
Analog,GPIO,I2C,PWM
Feature
No ClickID
Compatibility
mikroBUS™
Click board size
L (57.15 x 25.4 mm)
Input Voltage
3.3V or 5V
Pinout diagram
This table shows how the pinout on Brushless 7 Click corresponds to the pinout on the mikroBUS™ socket (the latter shown in the two middle columns).
Onboard settings and indicators
| Label | Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| LD1 | PWR | – | Power LED indicator |
| LD2 | ALR | – | Alert LED indicator |
| LD3 | FG | – | Rotation Speed LED Indicator |
| JP1 | VCC SEL | Left | Logic Level Voltage Selection 3V3/5V: Left position 3V3, Right position 5V |
| JP2 | INT SEL | Right | Interrupt Selection ALR/FG: Left position ALR, Right position FG |
| SW1 | SW1 | Upper | Brake Switch: Upper position 0, Lower position 1 |
| SW2 | SW2 | Upper | Speed Control Selection Switch: Upper position 0, Lower position 1 |
| SW3-SW4 | SW3-SW4 | Upper | I2C Address Selection Switch: Upper position 0, Lower position 1 |
| TP1 | GND | – | Ground Testpoint |
| TP2 | PHBF | – | Current Monitor Testpoint |
| TP3 | PH | – | Peak Hold Setting Testpoint |
| TP4 | SPD | – | Speed Control Command Testpoint |
| TP5 | VREG | – | Voltage Reference Testpoint |
Brushless 7 Click electrical specifications
| Description | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply Voltage VCC | 3.3 | – | 5 | V |
| External Supply Voltage VM | 11 | – | 27 | V |
| Output Current | – | – | 5 | A |
| PWM Frequency | 1 | – | 100 | kHz |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40 | +25 | +105 | °C |
Software Support
We provide a library for the Brushless 7 Click on our LibStock page, as well as a demo application (example), developed using MikroElektronika compilers. The demo can run on all the main MikroElektronika development boards.
Library Description
Library provides functions for controlling brushless motor. It has functions for communicating with device with I2C module, and controlling pins. There are function for controlling device over couple of modes.
Key functions:
void brushless7_generic_write ( uint8_t reg_adr, uint8_t tx_data )– Function for writing one byte of data to deviceuint8_t brushless7_generic_read ( uint8_t reg_adr )– Function for reading one byte of data from devicevoid brushless7_default_config ( void )– Function for setting default configuration of device
Examples description
The application is composed of three sections :
- System Initialization – Initialization of communication module
- Application Initialization – Setts default configuration and sets parameters for selected mode
- Application Task – Setts 3 different speed of motor in span of 20 seconds
void application_task ( )
{
if ( BRUSHLESS7_CTRL_TYPE_DUTY == demo_type_data )
{
mikrobus_logWrite( " ----- 20 ----- ", _LOG_LINE );
stop_start();
brushless7_change_duty( 20 );
Delay_ms( 20000 );
mikrobus_logWrite( " ----- 40 ----- ", _LOG_LINE );
stop_start();
brushless7_change_duty( 40 );
Delay_ms( 20000 );
mikrobus_logWrite( " ----- 8 ----- ", _LOG_LINE );
stop_start();
brushless7_change_duty( 8 );
Delay_ms( 20000 );
}
else if ( BRUSHLESS7_CTRL_TYPE_RPM == demo_type_data )
{
mikrobus_logWrite( " ----- 400 ----- ", _LOG_LINE );
stop_start();
brushless7_start_rpm( 400 );
Delay_ms( 20000 );
mikrobus_logWrite( " ----- 1000 ----- ", _LOG_LINE );
stop_start();
brushless7_start_rpm( 1000 );
Delay_ms( 20000 );
mikrobus_logWrite( " ----- 100 ----- ", _LOG_LINE );
stop_start();
brushless7_start_rpm( 100 );
Delay_ms( 20000 );
}
}
Additional Functions :
- void stop_start ( ) – Funcnction stops motor and then restores previous mode of working
The full application code, and ready to use projects can be found on our LibStock page.
Other mikroE Libraries used in the example:
- I2C
- UART
Additional notes and informations
Depending on the development board you are using, you may need USB UART click, USB UART 2 click or RS232 click to connect to your PC, for development systems with no UART to USB interface available on the board. The terminal available in all MikroElektronika compilers, or any other terminal application of your choice, can be used to read the message.
mikroSDK
This Click board™ is supported with mikroSDK – MikroElektronika Software Development Kit. To ensure proper operation of mikroSDK compliant Click board™ demo applications, mikroSDK should be downloaded from the LibStock and installed for the compiler you are using.
For more information about mikroSDK, visit the official page.
Resources
Downloads
| Weight | 22 g |
|---|---|
| Brand | MikroElektronika |