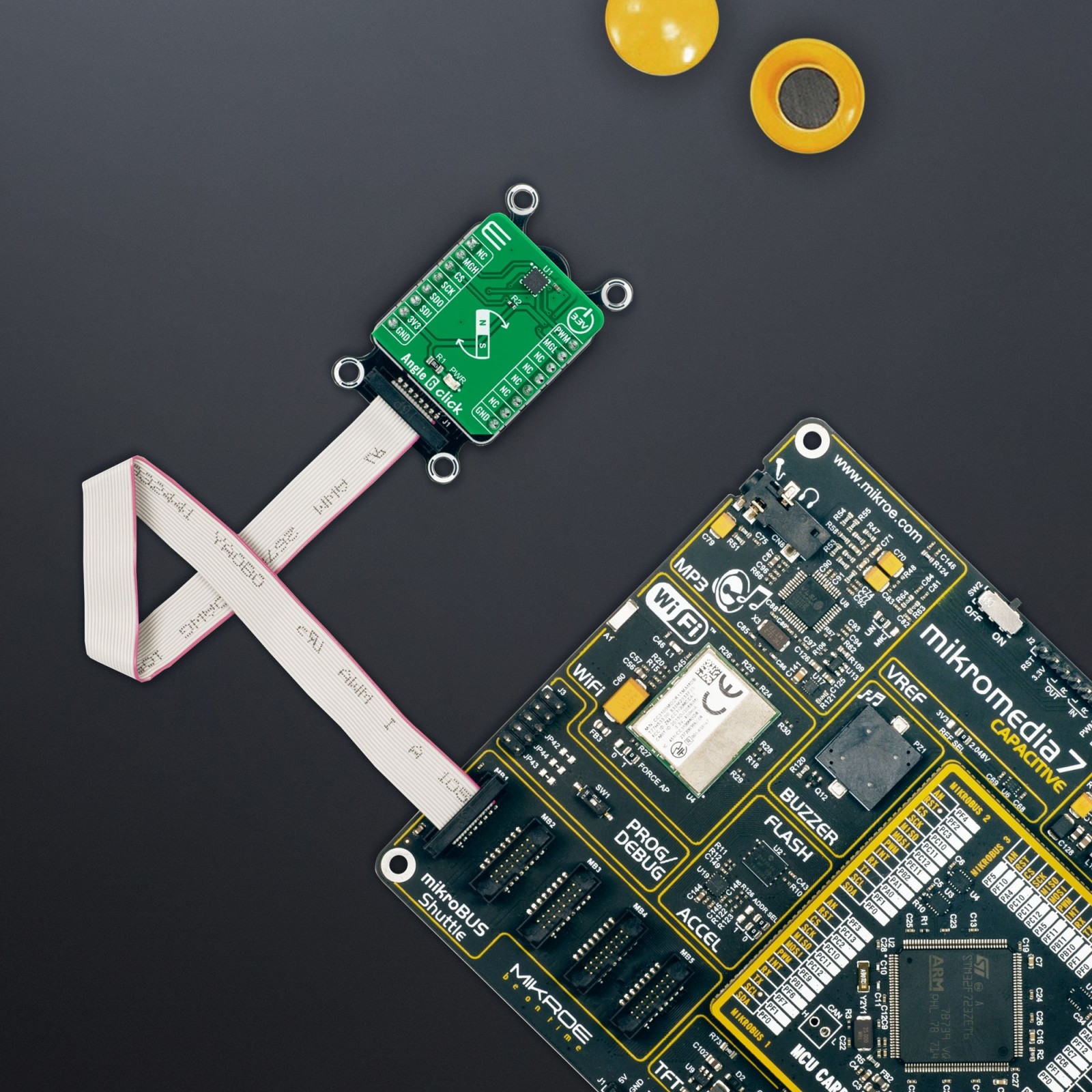
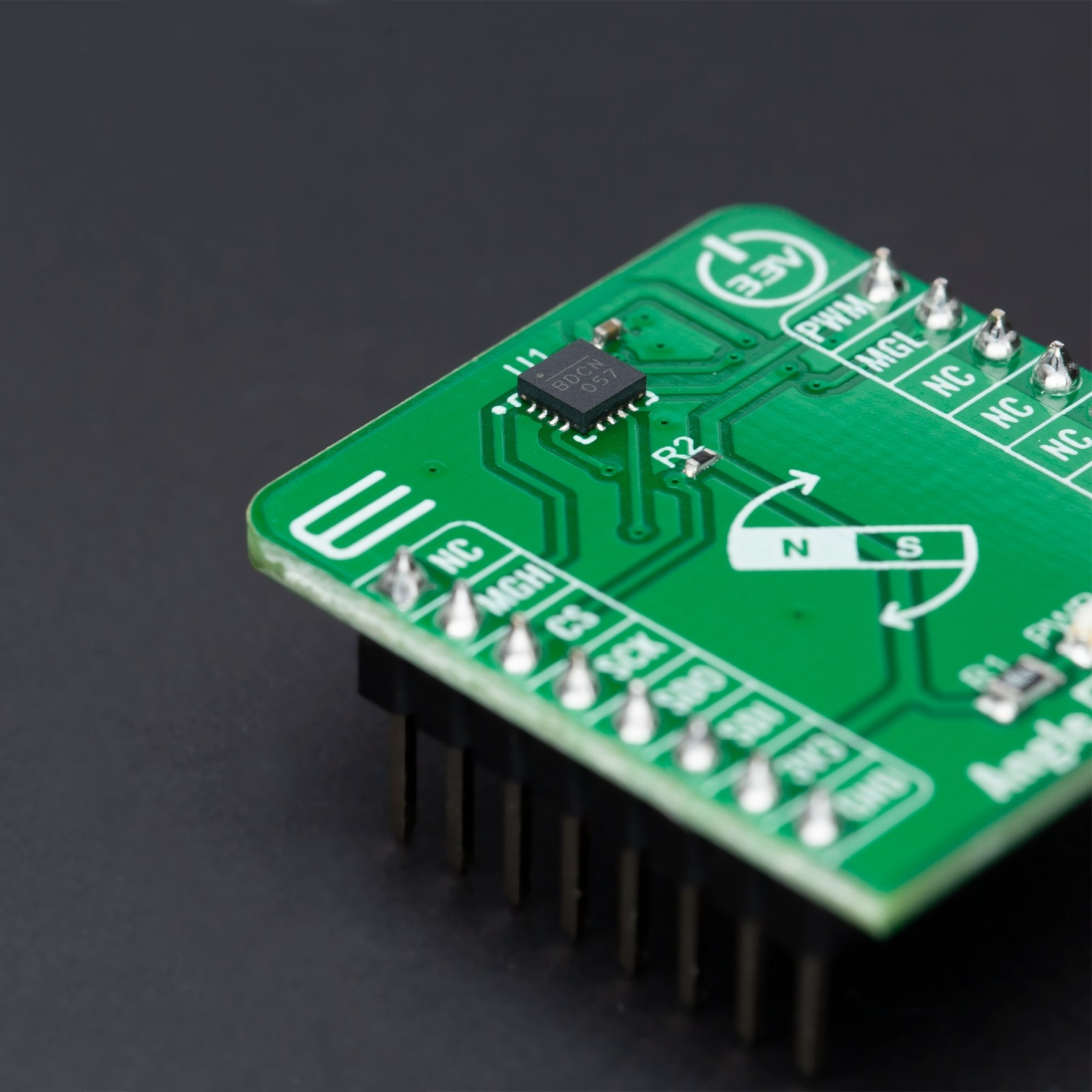
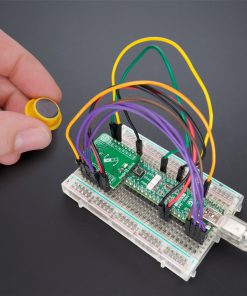
Angle 6 Click
R365.00 ex. VAT
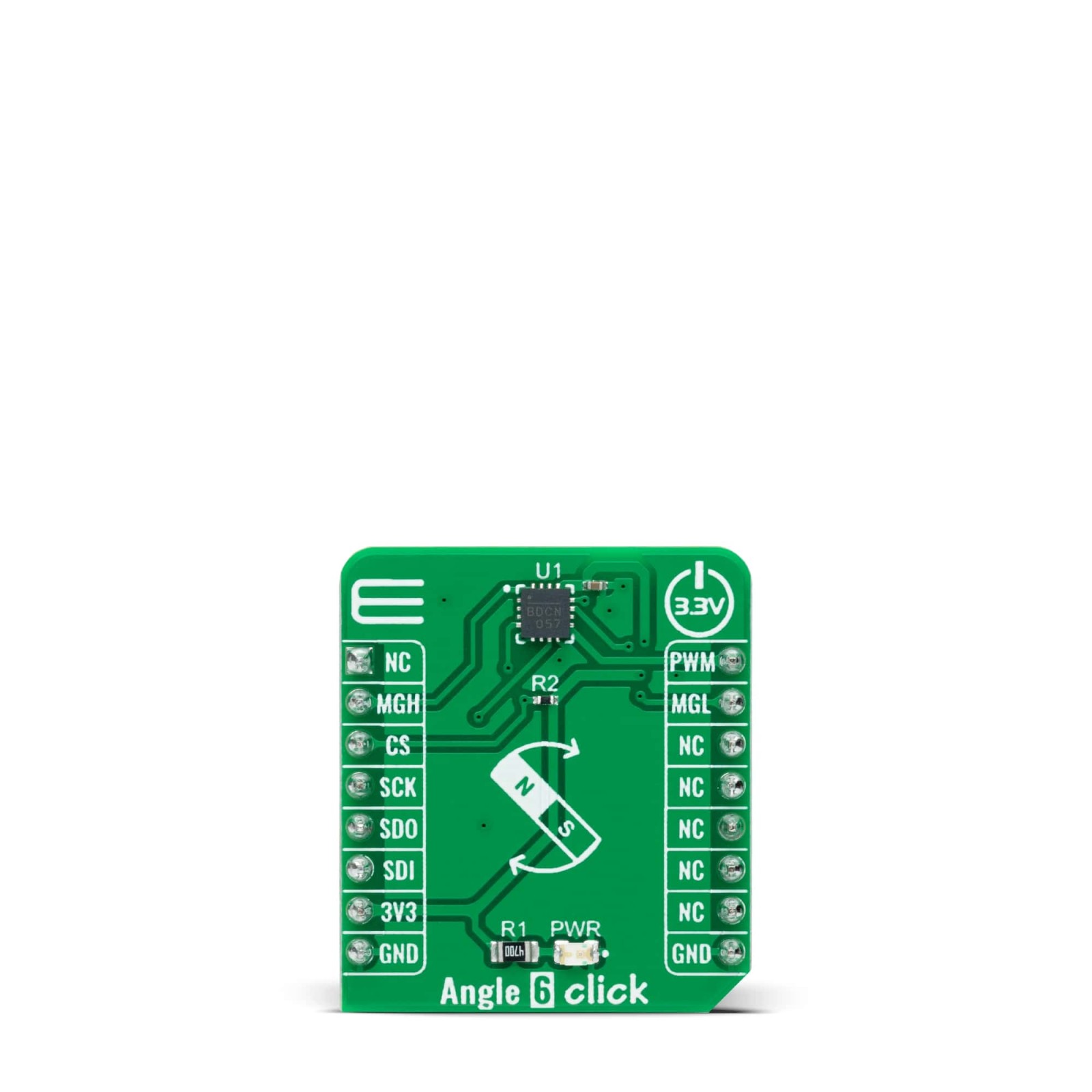
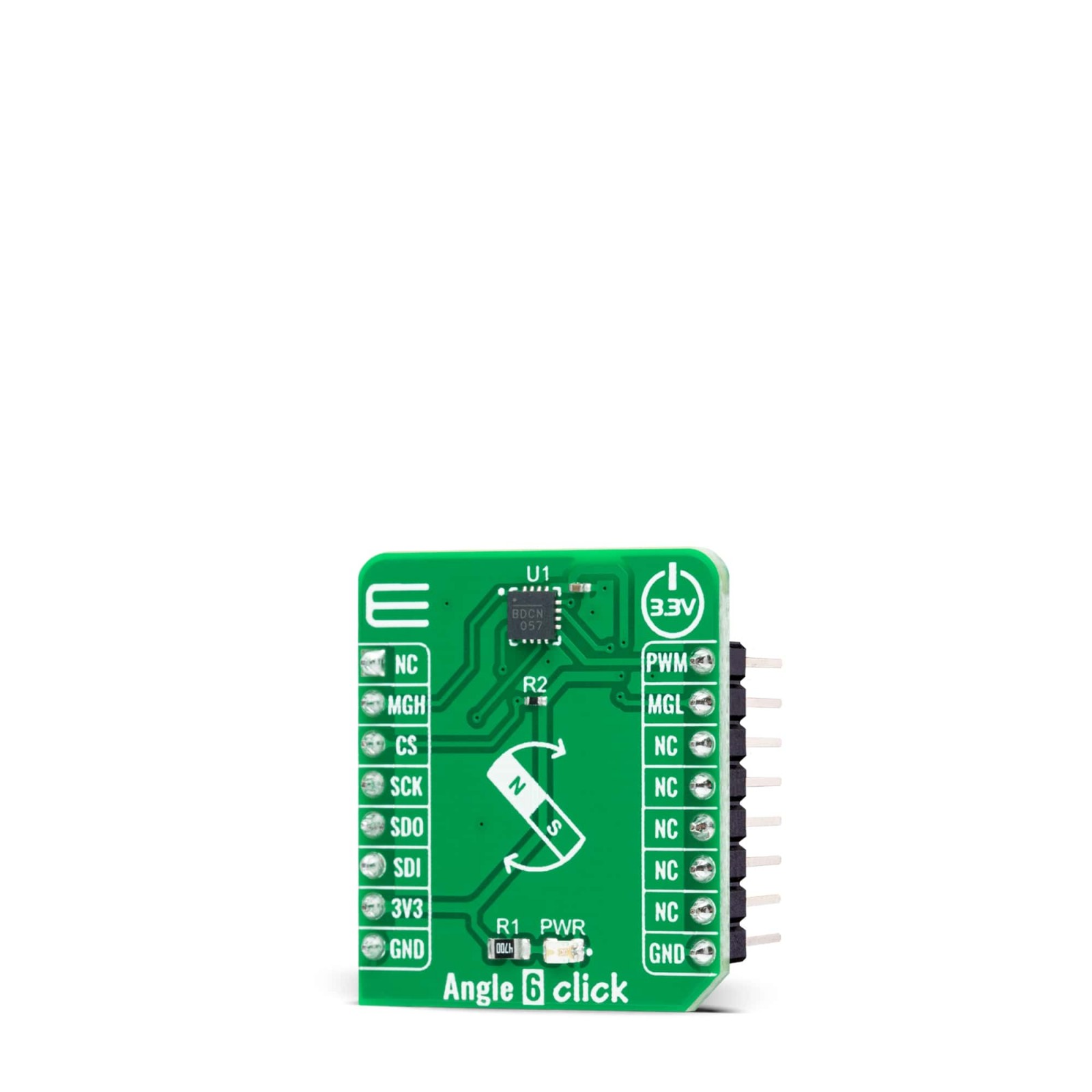
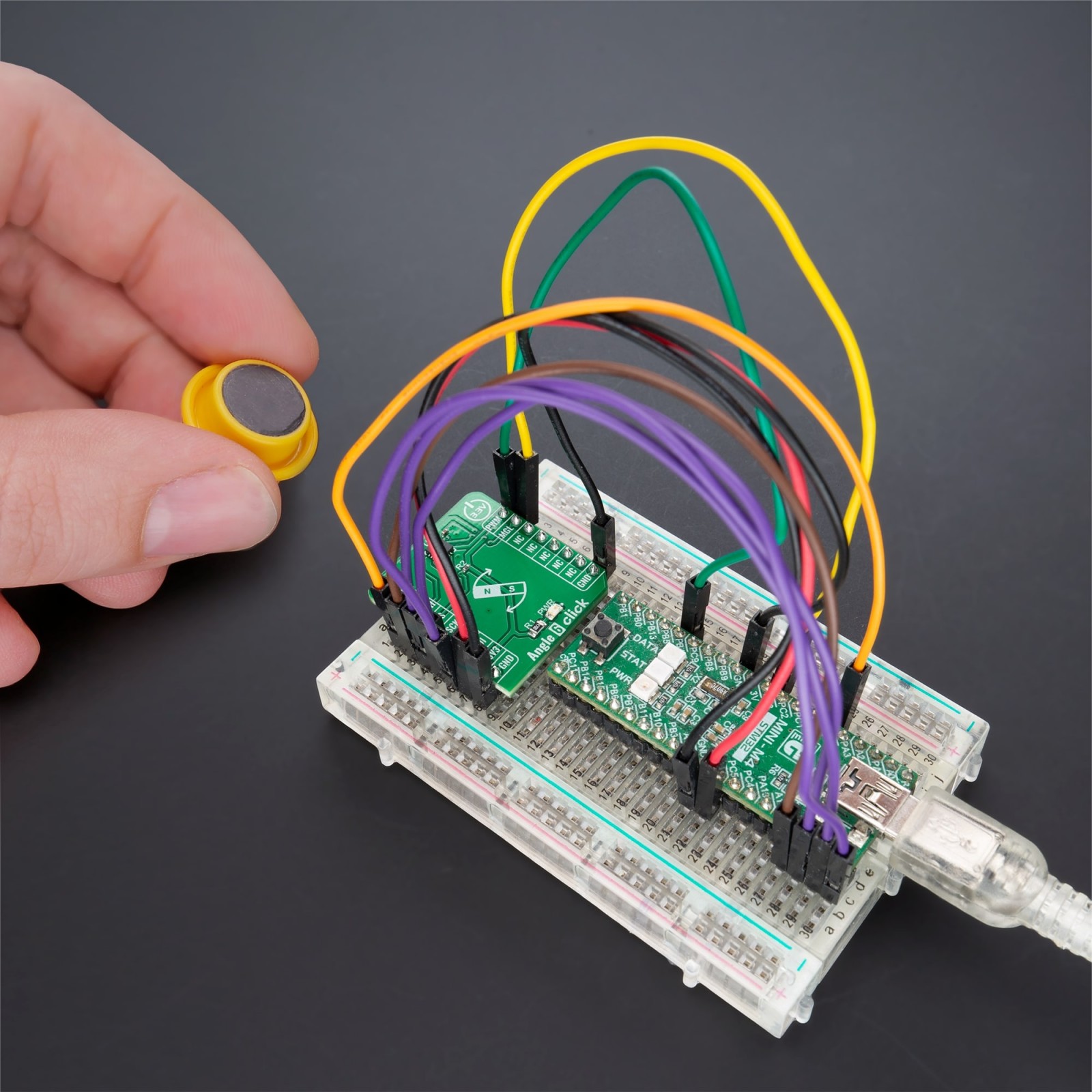
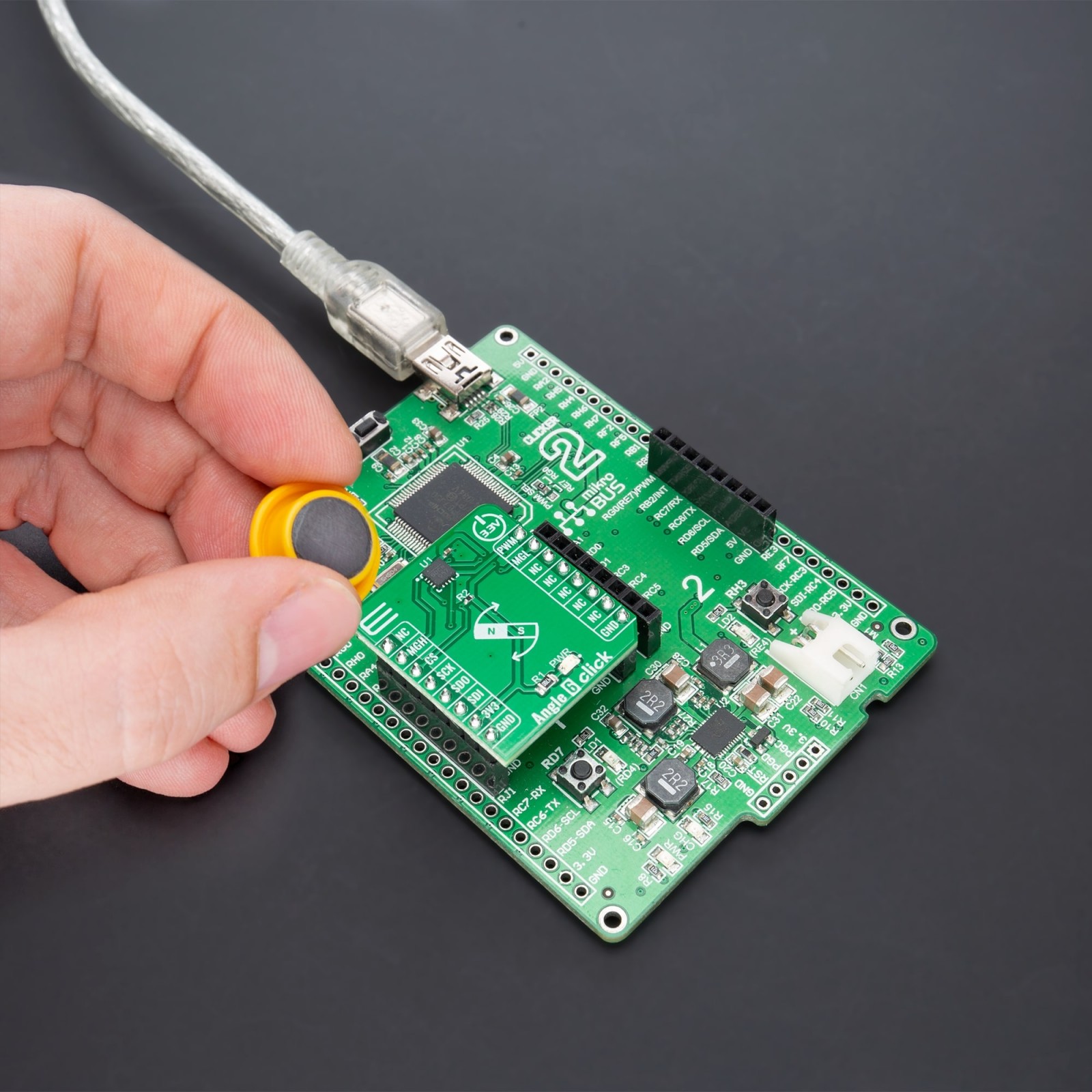
Angle 6 Click is a compact add-on board that detects the absolute angular position of a permanent magnet, typically a diametrically magnetized cylinder on a rotating shaft. This board features the MAQ470GQE, a 12-bit contactless angle sensor with PWM output from Monolithic Power Systems. It supports a wide range of magnetic field strengths and spatial configurations, with both end-of-shaft and off-axis (side-shaft mounting), supported configurations. Fast data acquisition and processing provides accurate angle measurement at speeds from 0 to 60,000 rpm, alongside magnetic field strength detection with programmable thresholds. This Click board™ offers a highly reliable and contactless method to measure various applications’ angles, position, and speed.
Angle 6 Click supports the mikroSDK compliant library, which includes functions that simplify software development. This Click board™ comes as a thoroughly tested product, ready to be used on a system equipped with the mikroBUS™ socket.
Stock: Lead-time applicable.
| 5+ | R346.75 |
| 10+ | R328.50 |
| 15+ | R310.25 |
| 20+ | R298.57 |