AMR Angle 2 Click
R585.00 ex. VAT
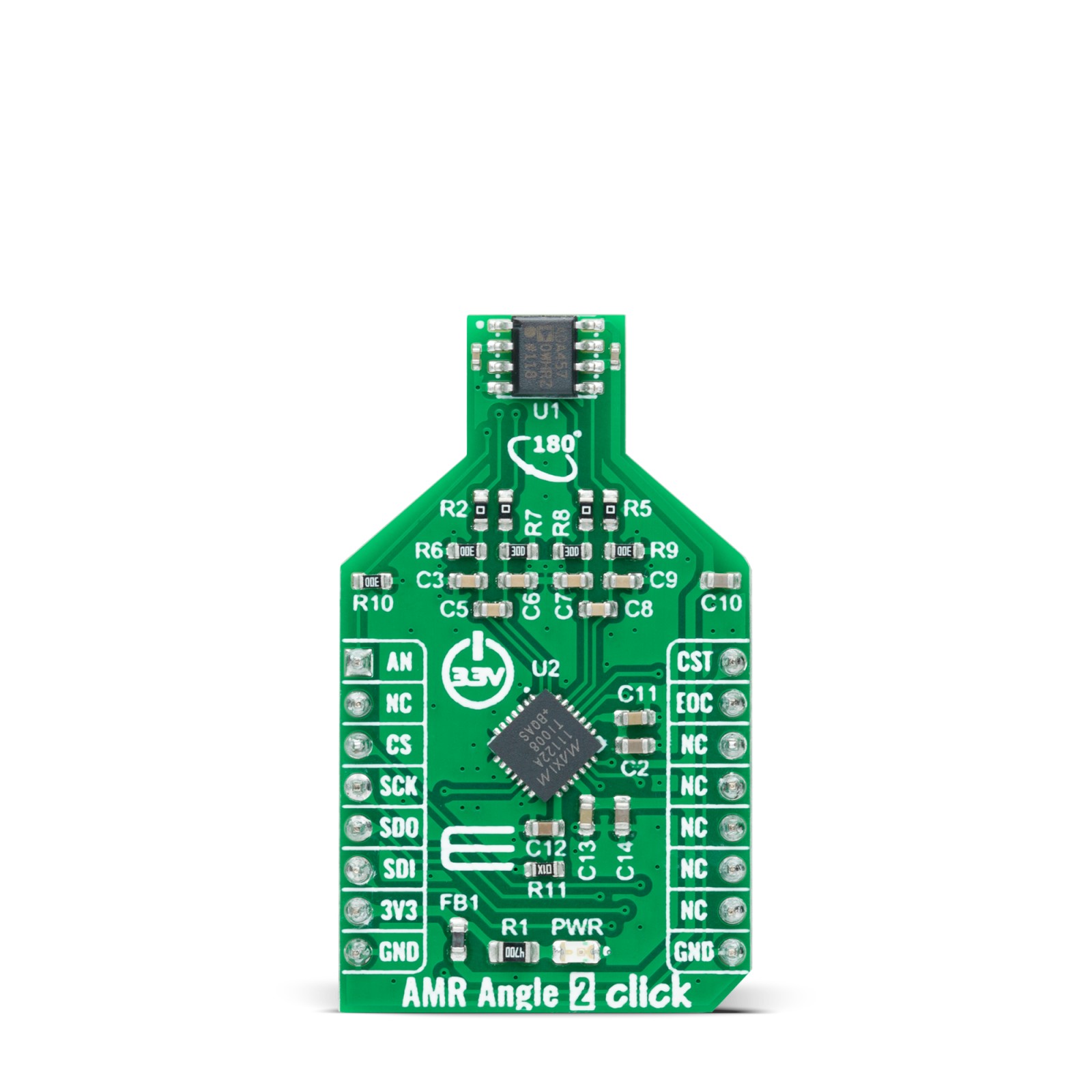
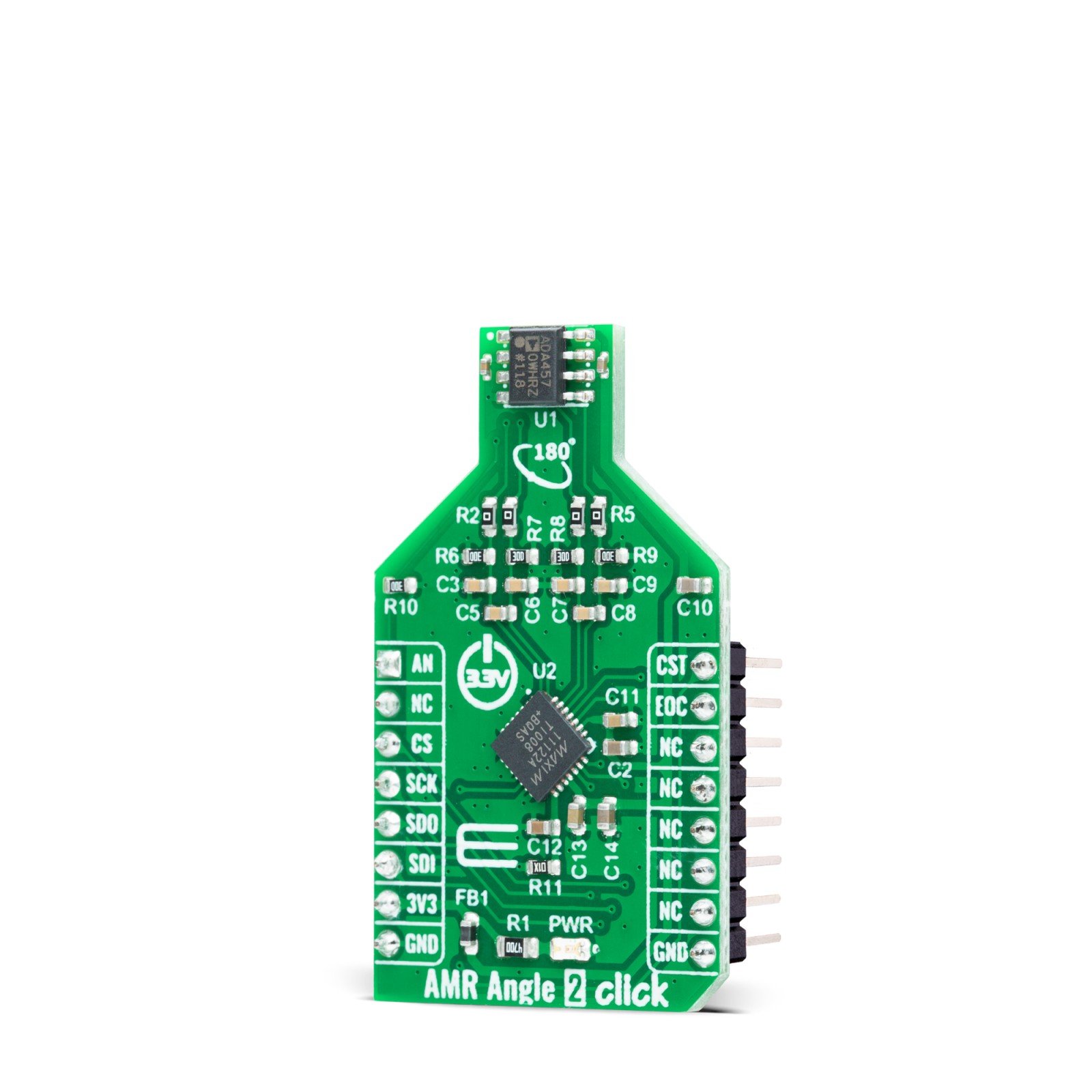
AMR Angle 2 Click is a compact add-on board containing an anisotropic magnetoresistive measurement solution ideal for either angle or linear position measurements. This board features the ADA4570, an integrated AMR angle sensor with an integrated signal conditioner and differential outputs from Analog Devices. The ADA4570 delivers amplified differential cosine and sine output signals, with respect to the angle measuring from 0° to 180° when the magnetic field is rotating in the x-axis and the y-axis (x-y) plane, processed later by MAX11122, SAR ADC, which forwards the digital angle information to MCU via SPI interface for further processing. This Click board™ is suitable for absolute position measurement (linear and angle), contactless angular measurement and detection, magnetic angular position sensing, actuator control and positioning, and more.
AMR Angle 2 Click is supported by a mikroSDK compliant library, which includes functions that simplify software development. This Click board™ comes as a fully tested product, ready to be used on a system equipped with the mikroBUS™ socket.
Stock: Lead-time applicable.
| 5+ | R555.75 |
| 10+ | R526.50 |
| 15+ | R497.25 |
| 20+ | R478.53 |