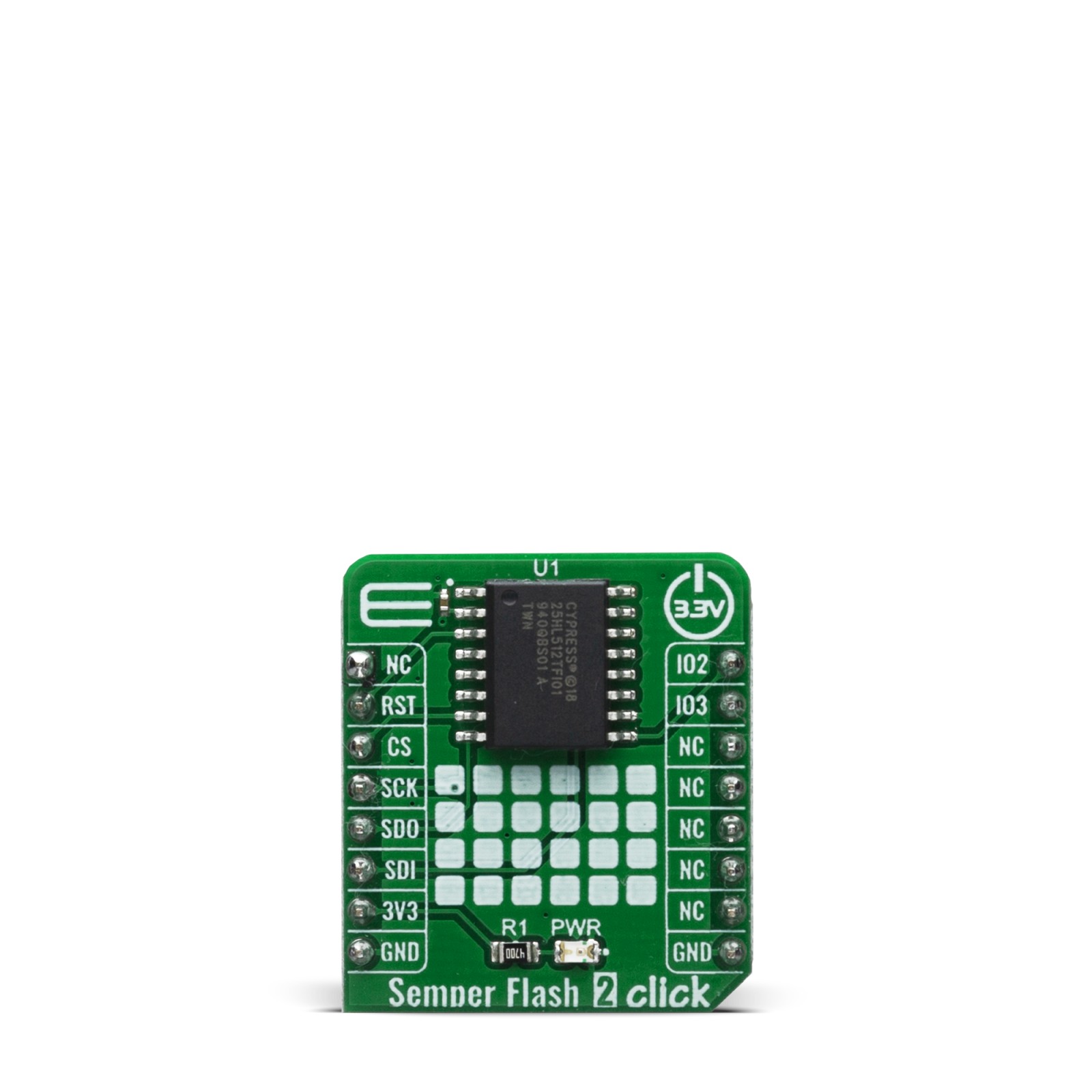
Semper Flash 2 Click
R535.00 ex. VAT
Semper Flash 2 Click is a Click board™ which features the S25HL512T from Infineon, a perfect solution for the mass storage option in various embedded applications. With fast performance being one of its key features, Semper Flash 2 click can also be used for the code shadowing, execute-in-place (XIP), and data storage. The Infineon Semper Flash with Quad SPI family of products are high-speed CMOS, MirrorBit NOR flash devices. Semper Flash is designed for Functional Safety with development according to ISO 26262 standard to achieve ASIL-B compliance and ASIL-D readiness. The 512 Mbit SPI Flash memory module is one of the fastest and most reliable Flash modules on the market module on the market with 3.0V core and I/O voltage.
The Semper Flash 2 click is supported by a mikroSDK compliant library, which includes functions that simplify software development. This Click board™ comes as a fully tested product, ready to be used on a system equipped with the mikroBUS™ socket.
Stock: Lead-time applicable.
| 5+ | R508.25 |
| 10+ | R481.50 |
| 15+ | R454.75 |
| 20+ | R437.63 |
How does it work?
Featuring both normal and double data rates over the standard, Dual/Quad SPI interface, the improved reliability of the stored information by utilizing the hardware Error Correction Code (ECC) generation, One-Time Programmable (OTP) memory block of 1024 bytes, an advanced sector protection, AutoBoot, and much more, this Click board™ is a perfect solution for the mass storage option in various embedded applications. Due to its fast performance, Semper Flash Click 2 can also be used for the code shadowing, execute-in-place (XIP), and data storage. An additional level translator IC allows Semper Flash Click 2 to be used with a wide range of MCUs.
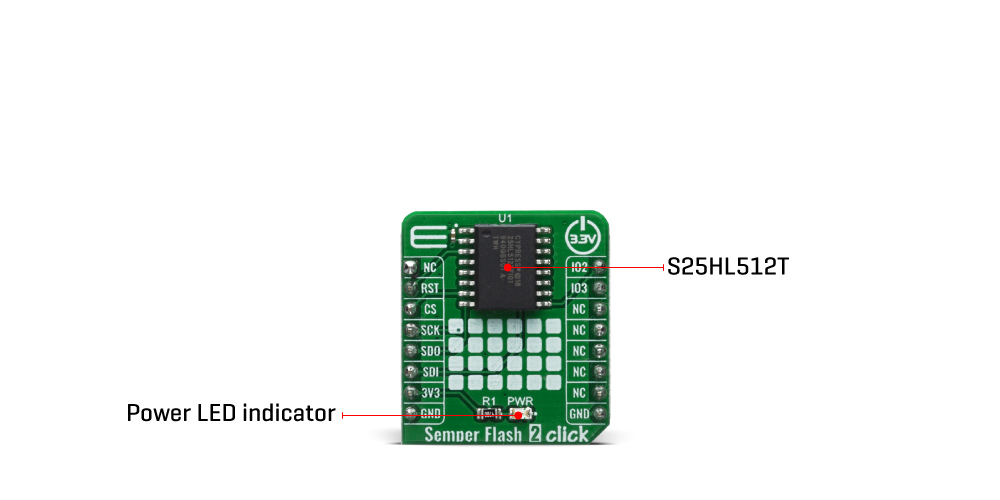
The device control logic is subdivided into two parallel operating sections: the Host Interface Controller (HIC) and the Embedded Algorithm Controller (EAC). The HIC monitors signal levels on the device inputs and drives outputs as needed to complete read, program and write data transfers with the host system. The HIC delivers data from the currently entered address map on read transfers; places write transfer address and data information into the EAC command memory, and notifies the EAC of power transition, and write transfers. The EAC interrogates the command memory, after a program or write transfer, for legal command sequences and performs the related Embedded Algorithms.
Executing code directly from Flash memory is often called Execute-In-Place (XIP). By using XIP with Semper Flash devices at the higher clock rates with Quad or DDR Quad SPI transactions, the data transfer rate can match or exceed traditional parallel or asynchronous NOR flash memories while reducing signal count dramatically.
The advanced MirrorBit® technology allows storing of two data bits in each memory array transistor (memory cell), effectively doubling the capacity of a single storage cell this way. The Eclipse™ architecture is responsible for the greatly improved erase and programming performance, compared to other Flash modules of the previous generation. Due to a higher speed, an execute-in-place (XIP), as well as the data shadowing is possible with the Semper Flash click.
One of the key features of the S25HL512T is certainly the AutoBoot feature. It allows the module to automatically initiate the memory transfer from the predefined location (memory read operation) after the reset cycle. Considering a typical communication scenario, where READ command followed by the one or more address bytes need be used, AutoBoot allows the host MCU to pull down the #CS (Chip Select) pin and start receiving a data stream over the SPI interface for as long as the #CS pin is held LOW, without any wasted cycles. As soon as the #CS pin is released, the S25HL512T returns to a normal operation.
The Advanced Sector Protection (ASP) is a powerful protection model that incorporates a set of various software and hardware methods to enable or disable programming or erase operations within a sector or an entire memory. A specialized ASP OTP register offers a password protection mode or a persistent protection mode, allowing an increased flexibility of the protection. Using the OTP memory allows the protection mode to remain in place for the whole life-cycle of the device. The Semper Flash 2 Click board is carrying S25HL memory module with 3.0V core and I/O voltage, if you are interested in 1.8V version of the same part please check our Semper Flash Click with S25HS version.
The SPI interface pins are routed to the mikroBUS™ so that the interfacing with the microcontroller unit (MCU) is easy and straightforward. Additional pins routed to the mikroBUS™ include the #WP/IO2 pin routed to the mikroBUS™ PWM pin and labeled as IO2, and #HOLD/IO3 pin routed to the mikroBUS™ INT pin and labeled as IO3. There is also the RESET pin, routed to the RST pin of the mikroBUS™, which performs a reset of the Flash module, initiating an AutoBoot sequence if enabled.
EnduraFlex Architecture provides system designers the ability to customize the NOR Flash endurance and retention for their specific application. The host defines partitions for high endurance or long retention, providing up to 1+ million cycles or 25 years of data retention.
Specifications
Type
FLASH
Applications
Mass storage option in multimedia devices, data drives, non-volatile data storage in embedded applications, secure storage, and similar applications that require reliable permanent storage of digital information.
On-board modules
S25HL512T, a 512 Mbit SPI/QSPI Flash memory module, from Cypress
Key Features
High durability of 1+ million cycles, Advanced Sector Protection (ASP), secure OTP memory block, high transfer speed, SFDP mode for easy retrieval of IC-specific information, AutoBoot function for improved startup performance
Interface
QSPI,SPI
Feature
No ClickID
Compatibility
mikroBUS™
Click board size
S (28.6 x 25.4 mm)
Input Voltage
3.3V
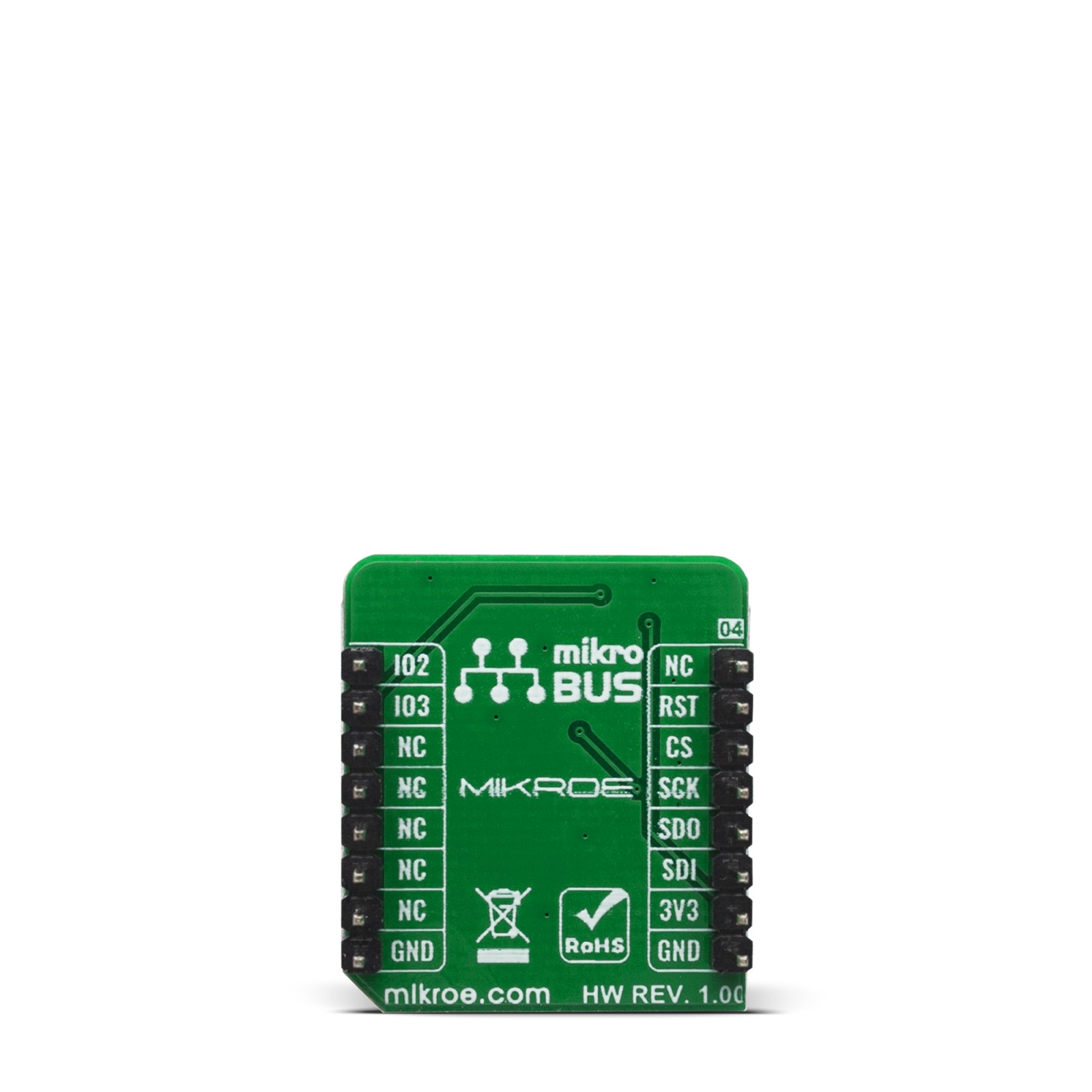
Pinout diagram
This table shows how the pinout on Semper Flash 2 click corresponds to the pinout on the mikroBUS™ socket (the latter shown in the two middle columns).
Onboard settings and indicators
| Label | Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| LD1 | PWR | – | Power LED Indicator |
Software Support
We provide a library for the Semper Flash 2 Click on our LibStock page, as well as a demo application (example), developed using MikroElektronika compilers. The demo can run on all the main MikroElektronika development boards.
Library Description
Library provides functions for using SPI module, changing pin states. Also it gives you function for controlling memory of device.
Key functions:
void semperflash2_send_cmd ( uint8_t cmd )– Function for sending one byte of datavoid semperflash2_transfer_data ( uint8_t *write_buf, uint8_t *read_buf, uint16_t buf_size )– Function for transfering data via SPI modulevoid semperflash2_write_data ( uint8_t *data_buf, uint16_t buf_size )– Function for writing data via SPI modulevoid semperflash2_write_config ( seperflash2_cfg_t *cfg_data )– Function for writing new config to deviceuint8_t semperflash2_read_memory ( uint32_t addr, uint8_t *data_buf, uint16_t buf_size )– Function for reading memory from specific addressuint8_t semperflash2_write_memory ( uint32_t addr, uint8_t *data_buf, uint16_t buf_size )– Function for writing memory to specific address
Examples description
The application is composed of three sections :
- System Initialization – Initialization of SPI module and setting pins to output
- Application Initialization – Configure device reads manufacturer id and device id and writes device id
- Application Task – Erases memory of one address and then on one cycle writes one buffer and on the other writes other one
void application_task ( )
{
memset( &read_buf_data[ 0 ], 0, 13 );
semperflash2_send_cmd( SEMPERFLASH2_WRITE_ENABLE );
semperflash2_erase_memory( ADRESS_MEMORY );
Delay_ms( 1000 );
if ( COMPANY_FLAG == txt_flag )
{
semperflash2_send_cmd( SEMPERFLASH2_WRITE_ENABLE );
status_data = semperflash2_write_memory( ADRESS_MEMORY, &write_data_com[ 0 ], 7 );
error_handler( status_data );
status_data = semperflash2_read_memory( ADRESS_MEMORY, &read_buf_data[ 0 ], 7 );
error_handler( status_data );
mikrobus_logWrite( read_buf_data, _LOG_LINE );
txt_flag = CLICK_FLAG;
}
else if ( CLICK_FLAG == txt_flag )
{
semperflash2_send_cmd( SEMPERFLASH2_WRITE_ENABLE );
status_data = semperflash2_write_memory( ADRESS_MEMORY, &write_data_clk[ 0 ], 13 );
error_handler( status_data );
status_data = semperflash2_read_memory( ADRESS_MEMORY, &read_buf_data[ 0 ], 13 );
error_handler( status_data );
mikrobus_logWrite( read_buf_data, _LOG_LINE );
txt_flag = COMPANY_FLAG;
}
mikrobus_logWrite( "....................", _LOG_LINE );
Delay_ms( 2000 );
}
Additional Functions :
- void error_handler ( uint8_t stat ) – Proceses return of the function and if it is error logs witch one it is
The full application code, and ready to use projects can be found on our LibStock page.
Other mikroE Libraries used in the example:
- SPI
- Conversions
Additional notes and informations
Depending on the development board you are using, you may need USB UART click, USB UART 2 click or RS232 click to connect to your PC, for development systems with no UART to USB interface available on the board. The terminal available in all MikroElektronika compilers, or any other terminal application of your choice, can be used to read the message.
mikroSDK
This Click board™ is supported with mikroSDK – MikroElektronika Software Development Kit. To ensure proper operation of mikroSDK compliant Click board™ demo applications, mikroSDK should be downloaded from the LibStock and installed for the compiler you are using.
For more information about mikroSDK, visit the official page.
Resources
Downloads
| Weight | 18 g |
|---|---|
| Brand | MikroElektronika |