Boost 3 Click
R445.00 ex. VAT
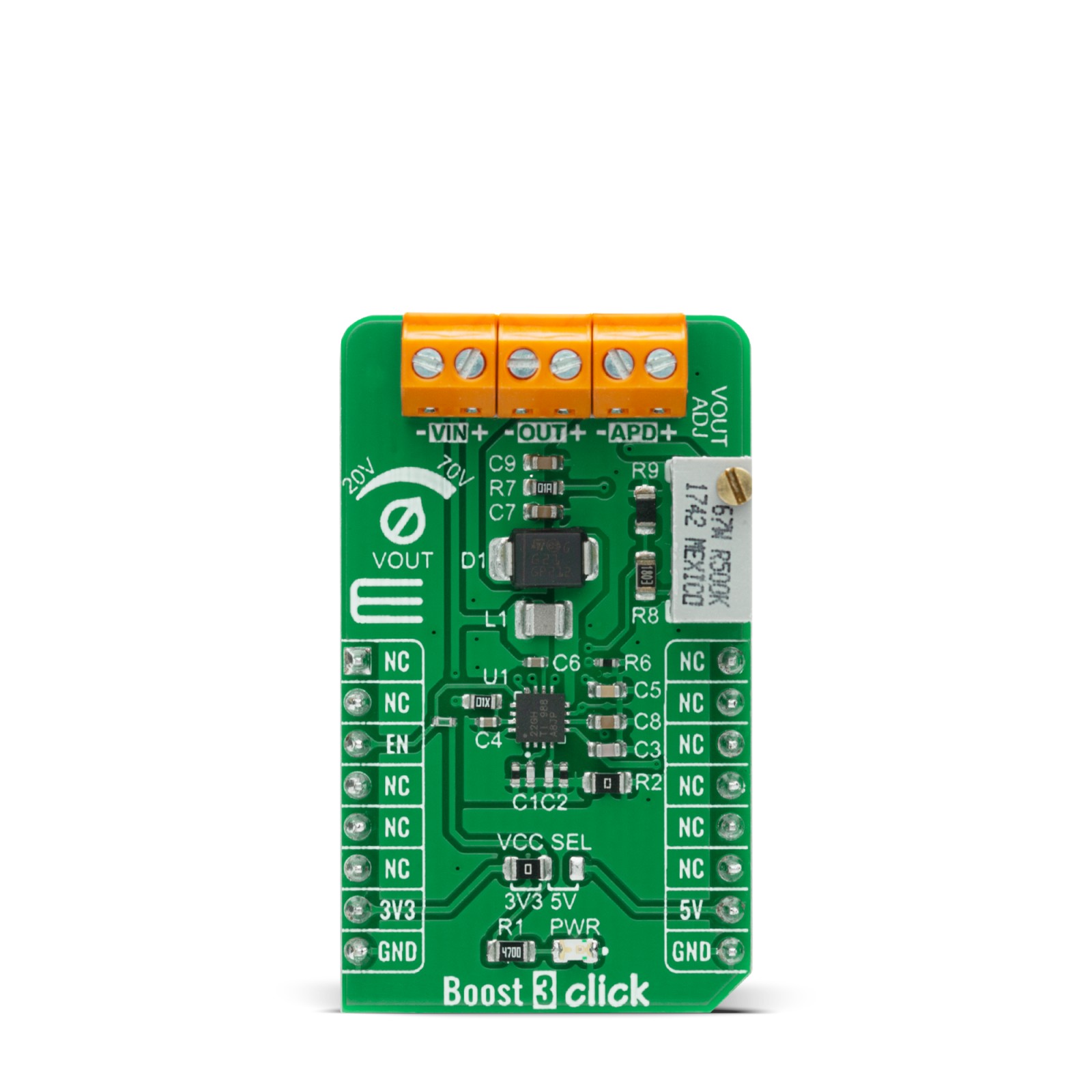
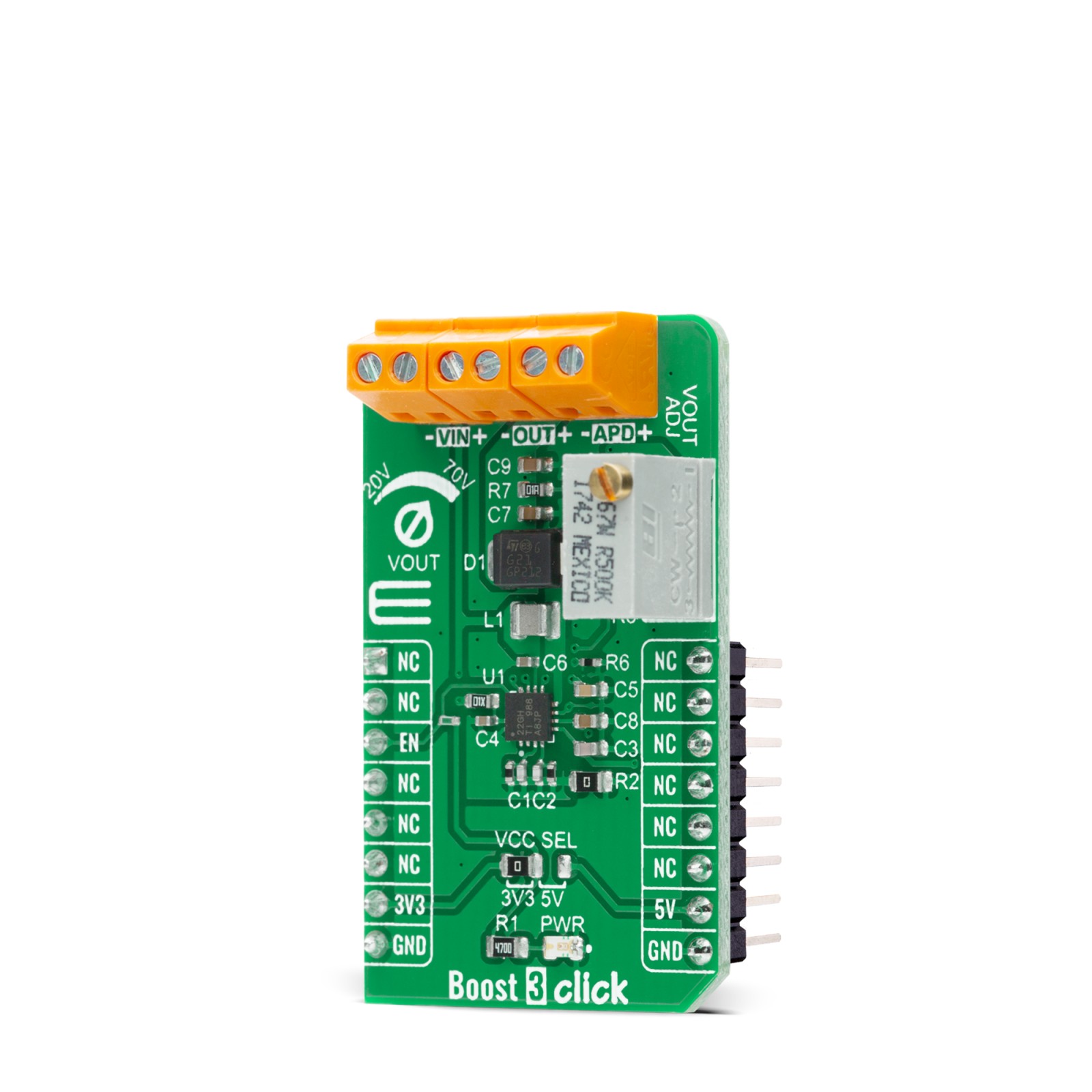
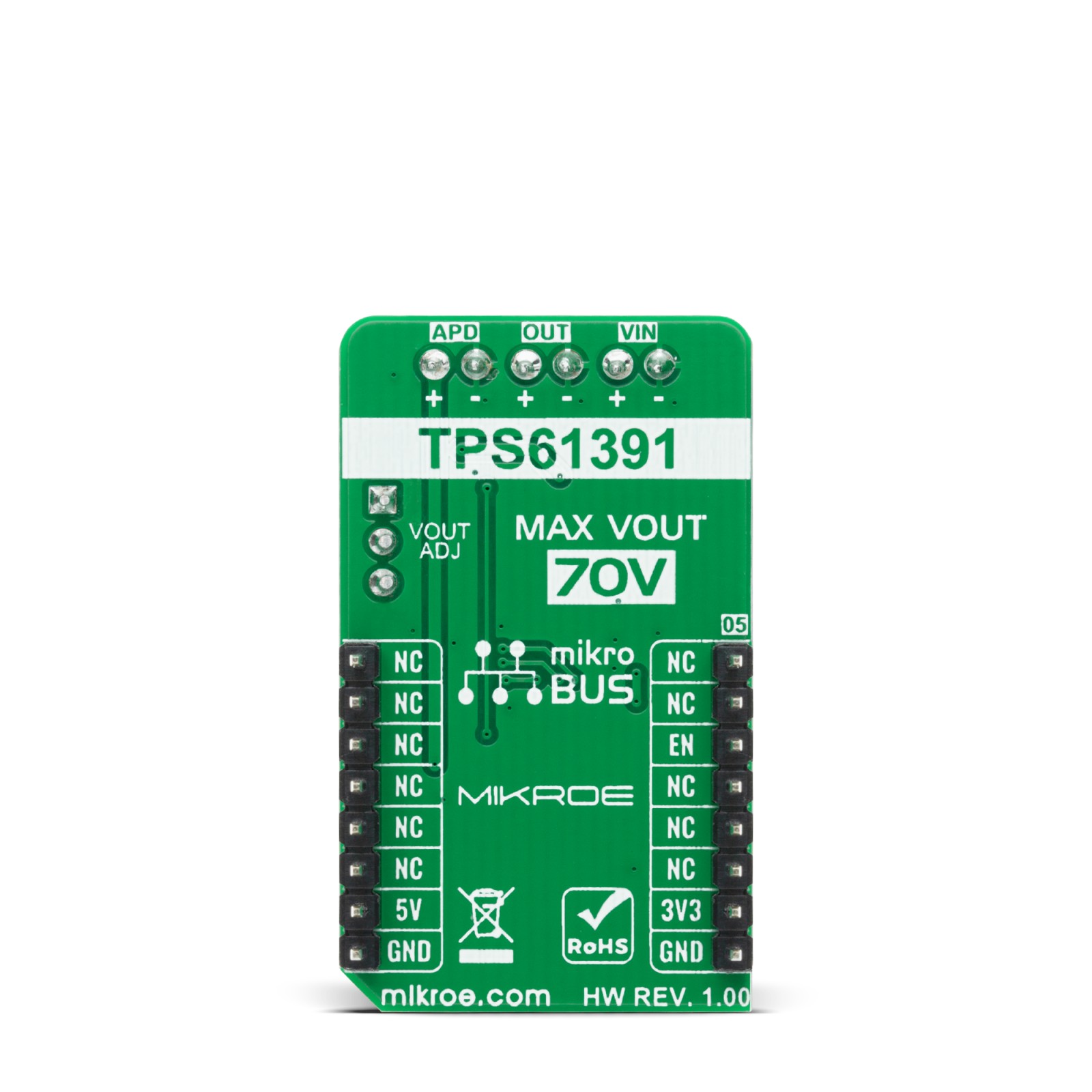
Boost 3 Click is a compact add-on board that contains a boost converter with an integrated current mirror function. This board features the TPS61391, a 700-kHz pulse-width modulating (PWM) Step-Up converter with a 70V switch FET with an input voltage up to 5.5V from Texas Instruments. The TPS61391 includes an accurate current mirror, with two selectable gain options (1:5 or 4:5), and provides high optical-power protection with an additional FET in series with the APD power path, with the typical response time of 0.5µs. This Click board™ is designed to be used for applications such as biasing and monitoring the avalanche photodiodes (APD) in the optical receivers, but it also can be used as a high voltage sensor supply or in battery-powered and automotive applications.
Boost 3 Click is supported by a mikroSDK compliant library, which includes functions that simplify software development. This Click board™ comes as a fully tested product, ready to be used on a system equipped with the mikroBUS™ socket.
Stock: Lead-time applicable.
| 5+ | R422.75 |
| 10+ | R400.50 |
| 15+ | R378.25 |
| 20+ | R364.01 |