I2C Isolator 2 click
R440.00 ex. VAT
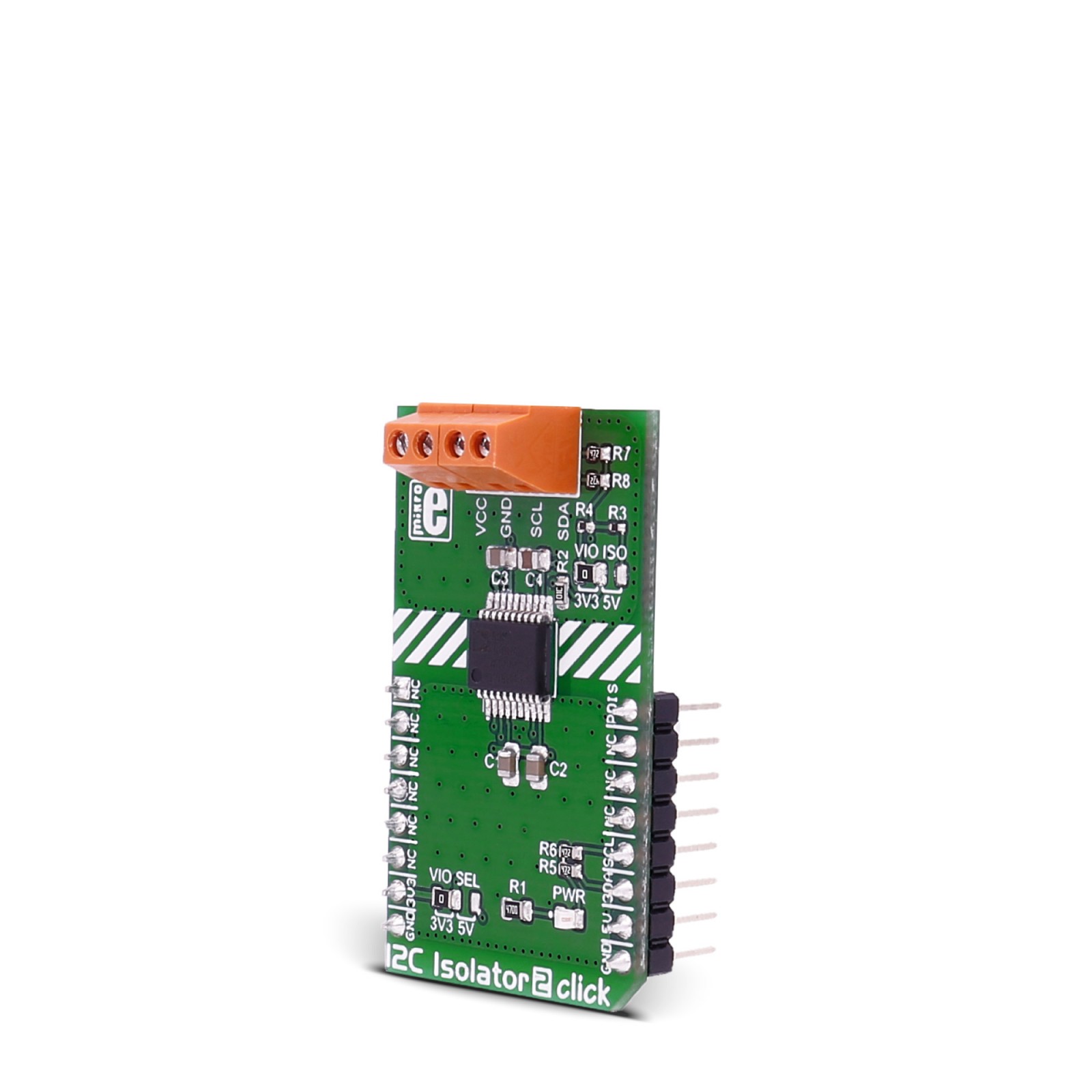
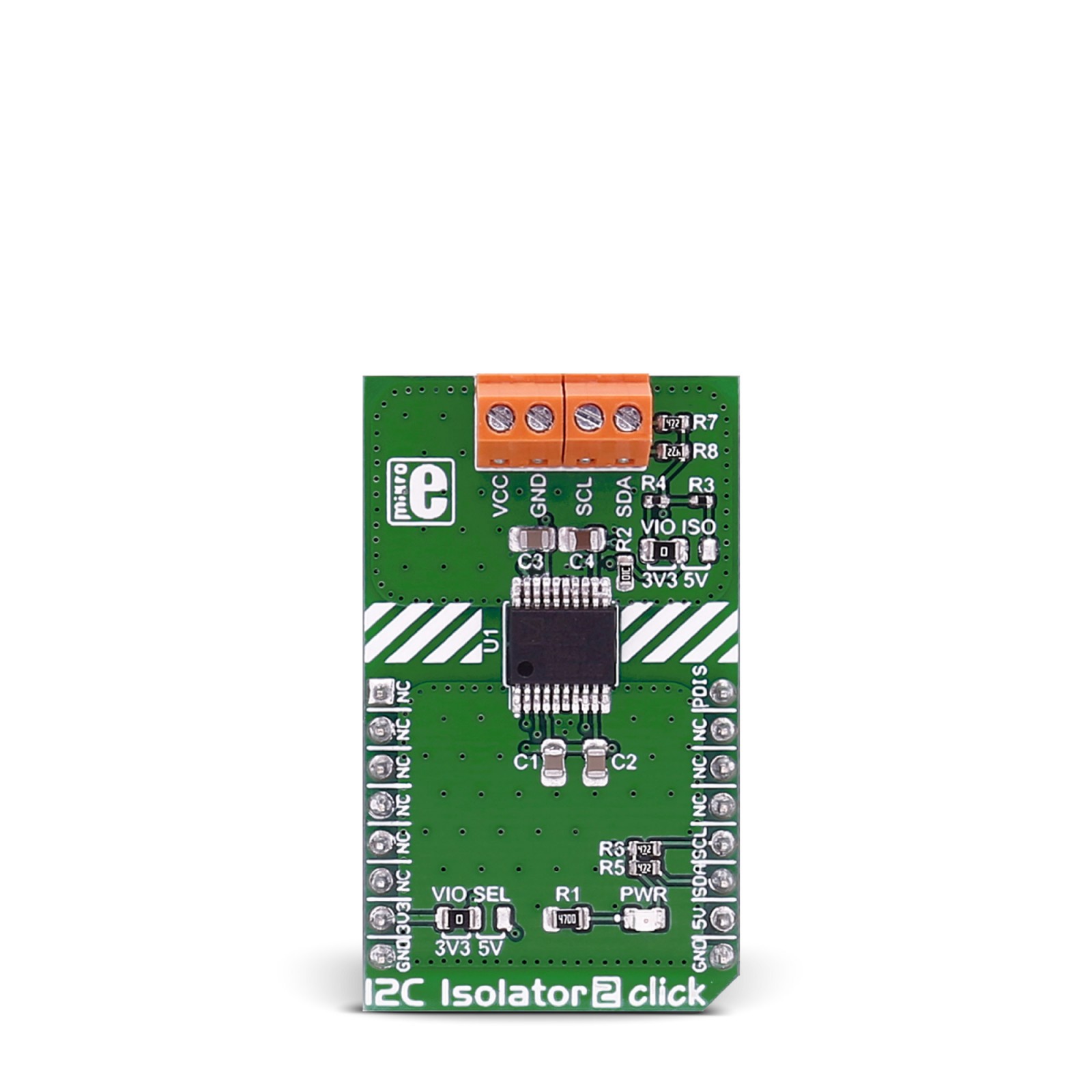
I2C Isolator 2 click provides I2C lines and power isolation for slave devices. It carries the ADM3260 dual I2C isolator with an integrated DC-to-DC converter. I2C Isolator 2 click is designed to run on either 3.3V or 5V power supply.
The click communicates with the target microcontroller over an I2C interface with additional functionality provided by the PWM pin on the mikroBUS™ line.
Stock: Lead-time applicable.
| 5+ | R418.00 |
| 10+ | R396.00 |
| 15+ | R374.00 |
| 20+ | R359.92 |