Subtotal: R1,255.00
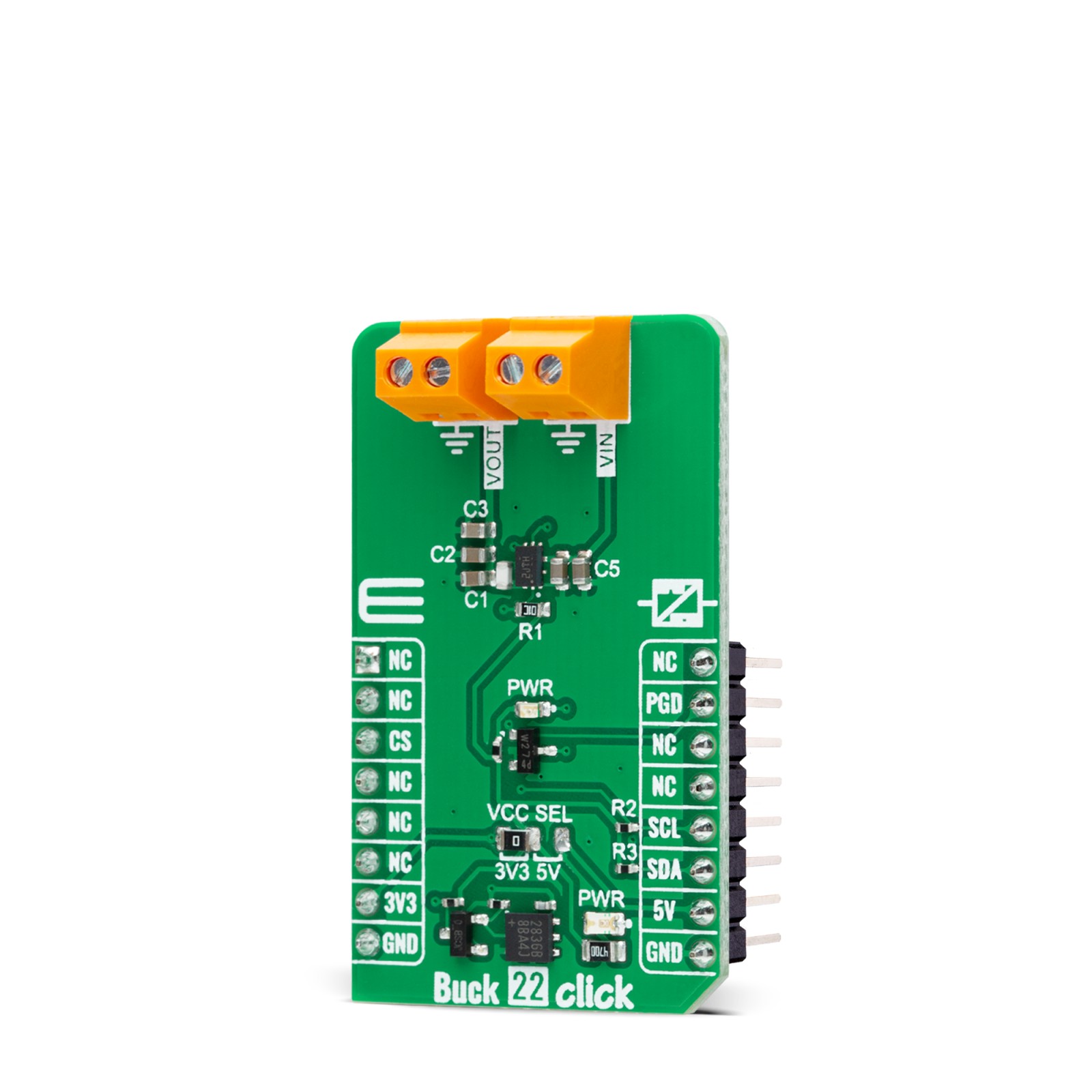
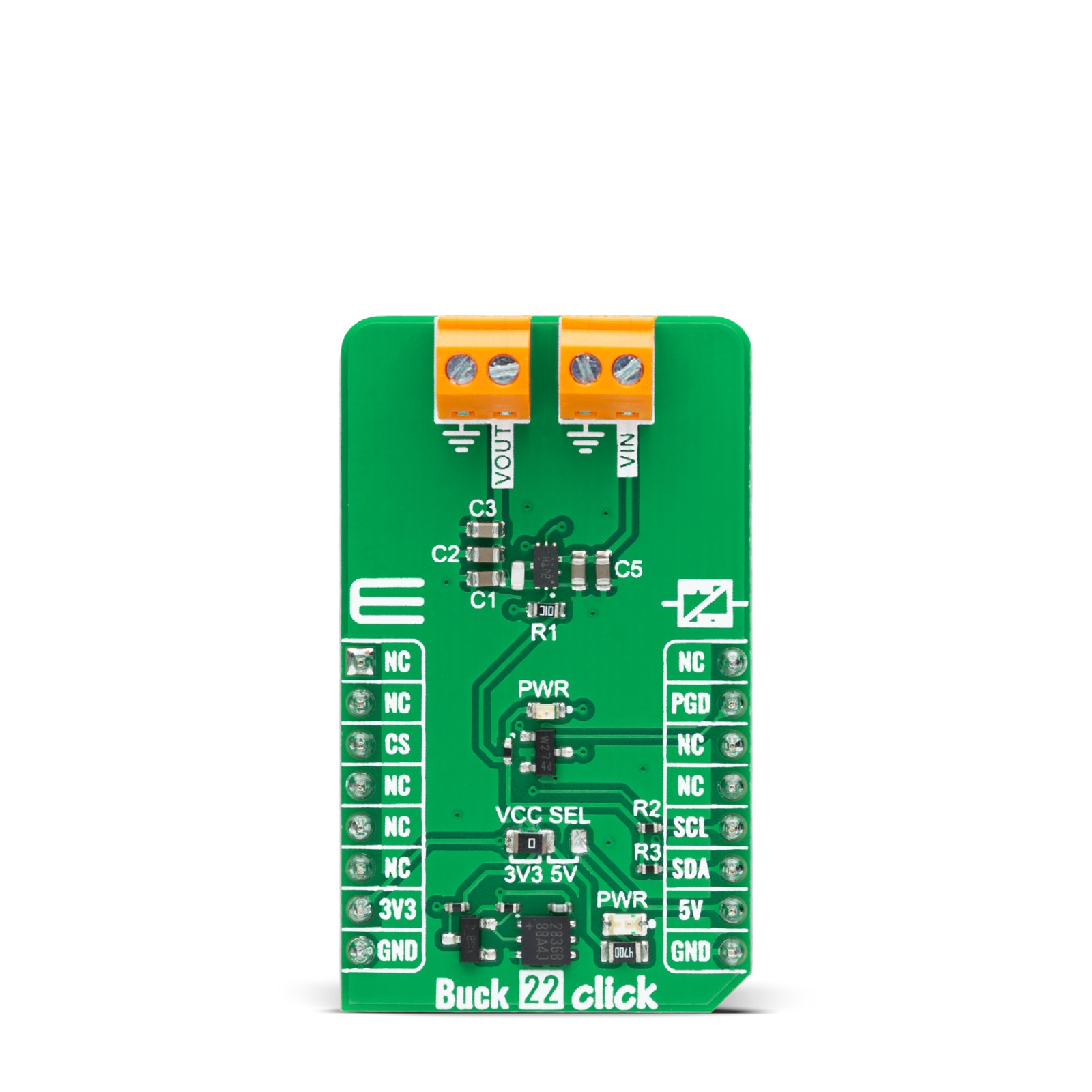
Buck 22 Click
R400.00 ex. VAT
Buck 22 Click is a compact add-on board that steps down the voltage from its input (supply) to its output (load). This board features the TPS62869, a high-frequency synchronous step-down converter with an I2C interface from Texas Instruments, providing an efficient, adaptive, and high power-density solution. The TPS62869 operates in PWM mode at medium to heavy loads (also for the slightest output voltage ripple), and it automatically enters Power-Save Mode operation at light load to maintain high efficiency over the entire output load current range. With its DCS-Control™ architecture, excellent load transient performance and tight output voltage accuracy are achieved alongside adjustable output voltage range from 0.8V to 3.35V with a 10mV step size. This Click board™ is used to derive the required lower voltage from a higher voltage source for FPGAs, ASICs, video chipsets, solid-state drives, and many more.
Buck 22 Click is fully compatible with the mikroBUS™ socket and can be used on any host system supporting the mikroBUS™ standard. It comes with the mikroSDK open-source libraries, offering unparalleled flexibility for evaluation and customization. What sets this Click board™ apart is the groundbreaking ClickID feature, enabling your host system to seamlessly and automatically detect and identify this add-on board.
Stock: Lead-time applicable.
| 5+ | R380.00 |
| 10+ | R360.00 |
| 15+ | R340.00 |
| 20+ | R327.20 |

 Alcohol Click
Alcohol Click  MP3 Click
MP3 Click  RTC 2 Click
RTC 2 Click