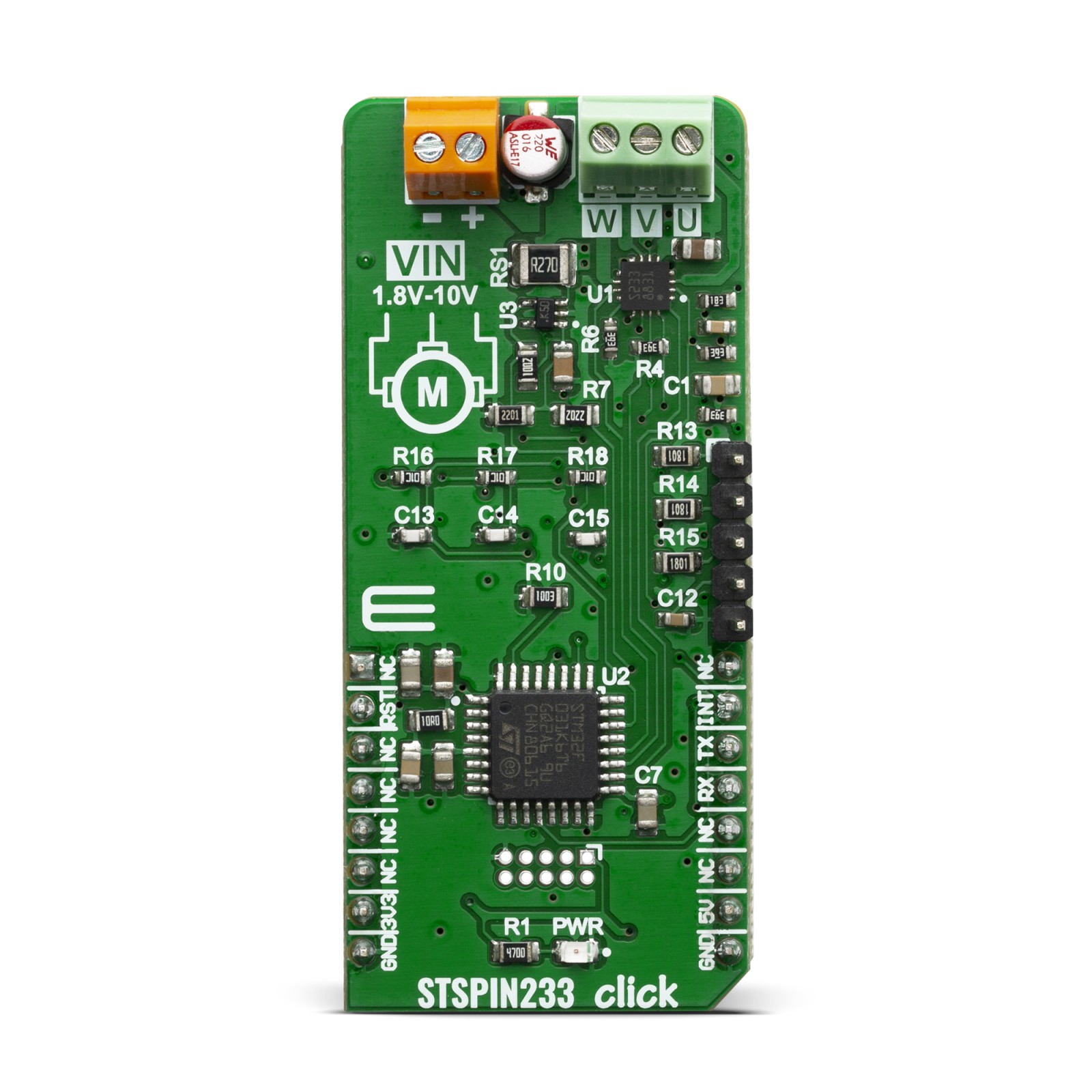
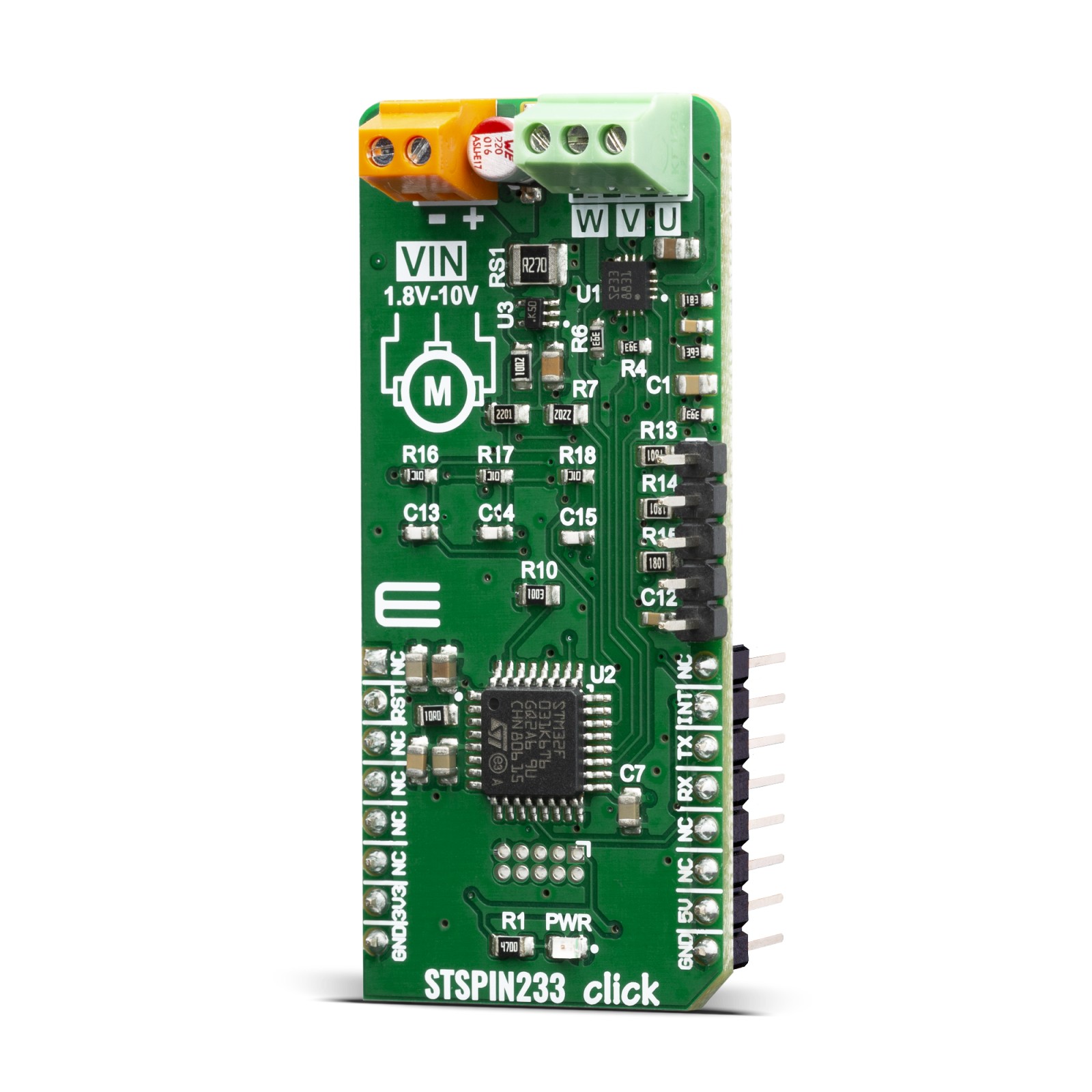
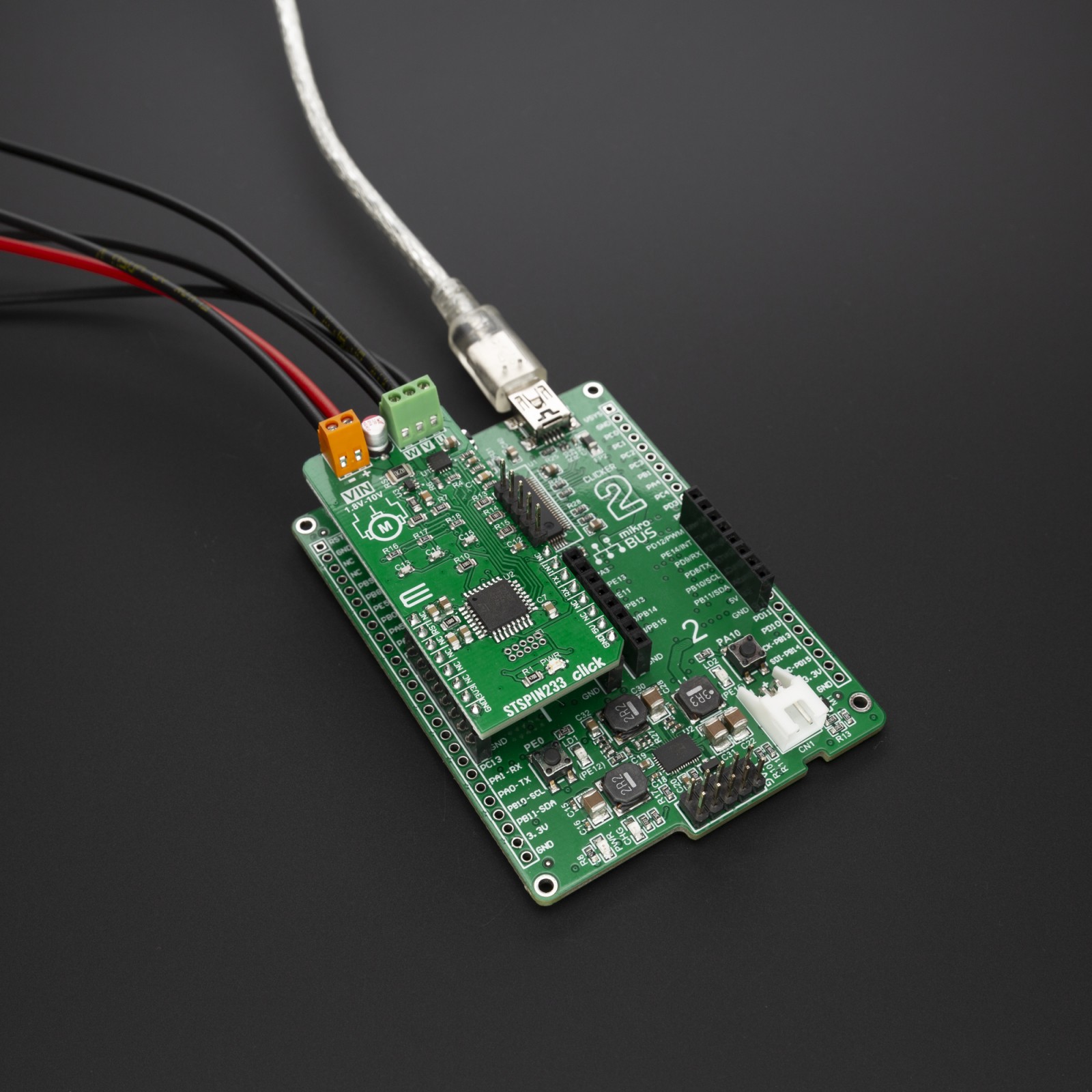
STSPIN233 Click
R355.00 ex. VAT
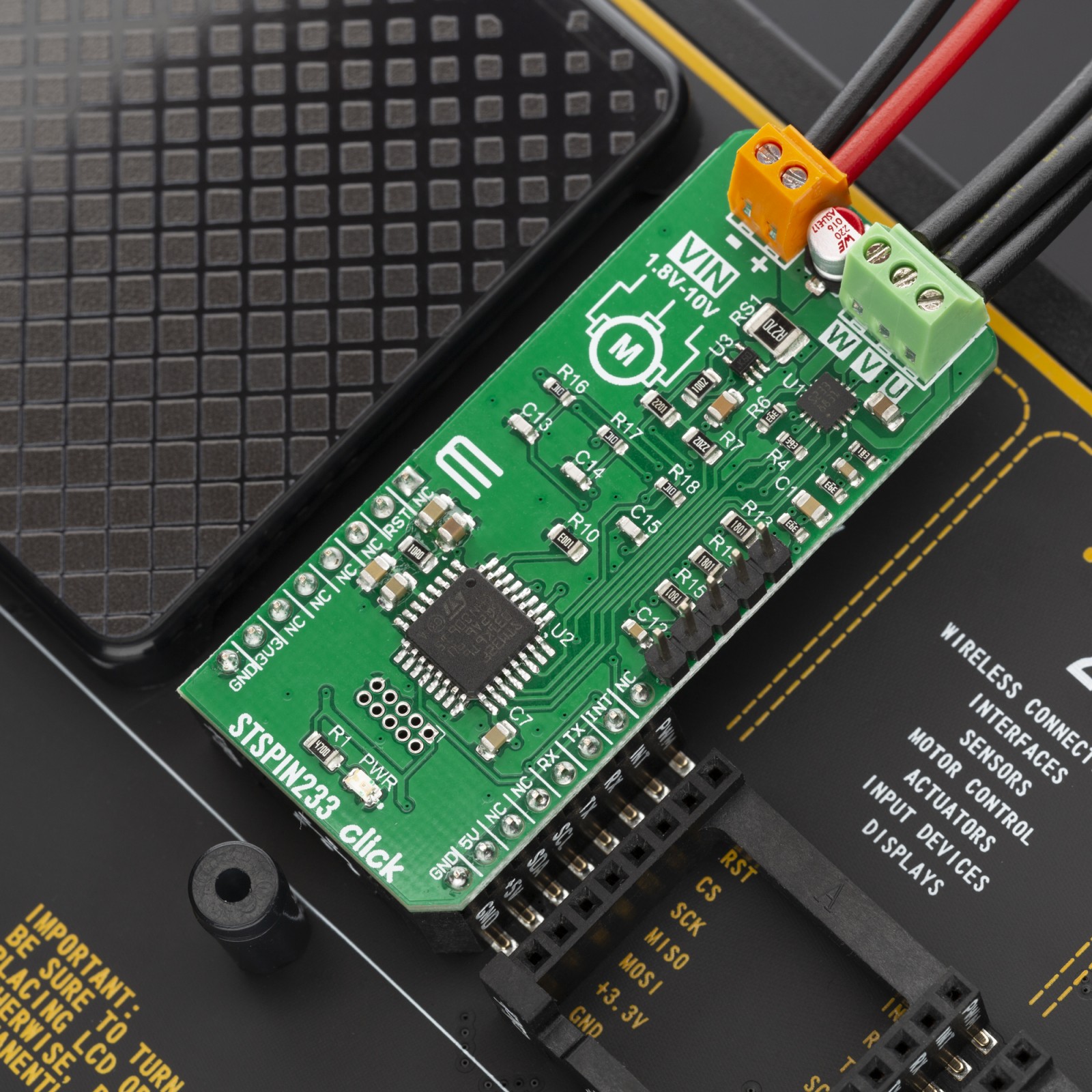
STSPIN233 click is a complete solution for a 3-phase integrated motor driver, based on the STSPIN233, Low voltage 3-phase integrated motor driver. It is optimized for battery-powered, low voltage motor driving applications, featuring the lowest standby current available on the market (max 80 nA). The STSPIN233 is a high-efficiency motor driver, featuring low ON resistance MOSFETs as the output stage, and extremely low leakage current (max 1µA). Its output stage implements the PWM current control with fixed OFF time, along with a full set of protection features. The device can be used with the step motor voltage ranging from 1.8V to 10V, and current up to 1.3A per bridge.
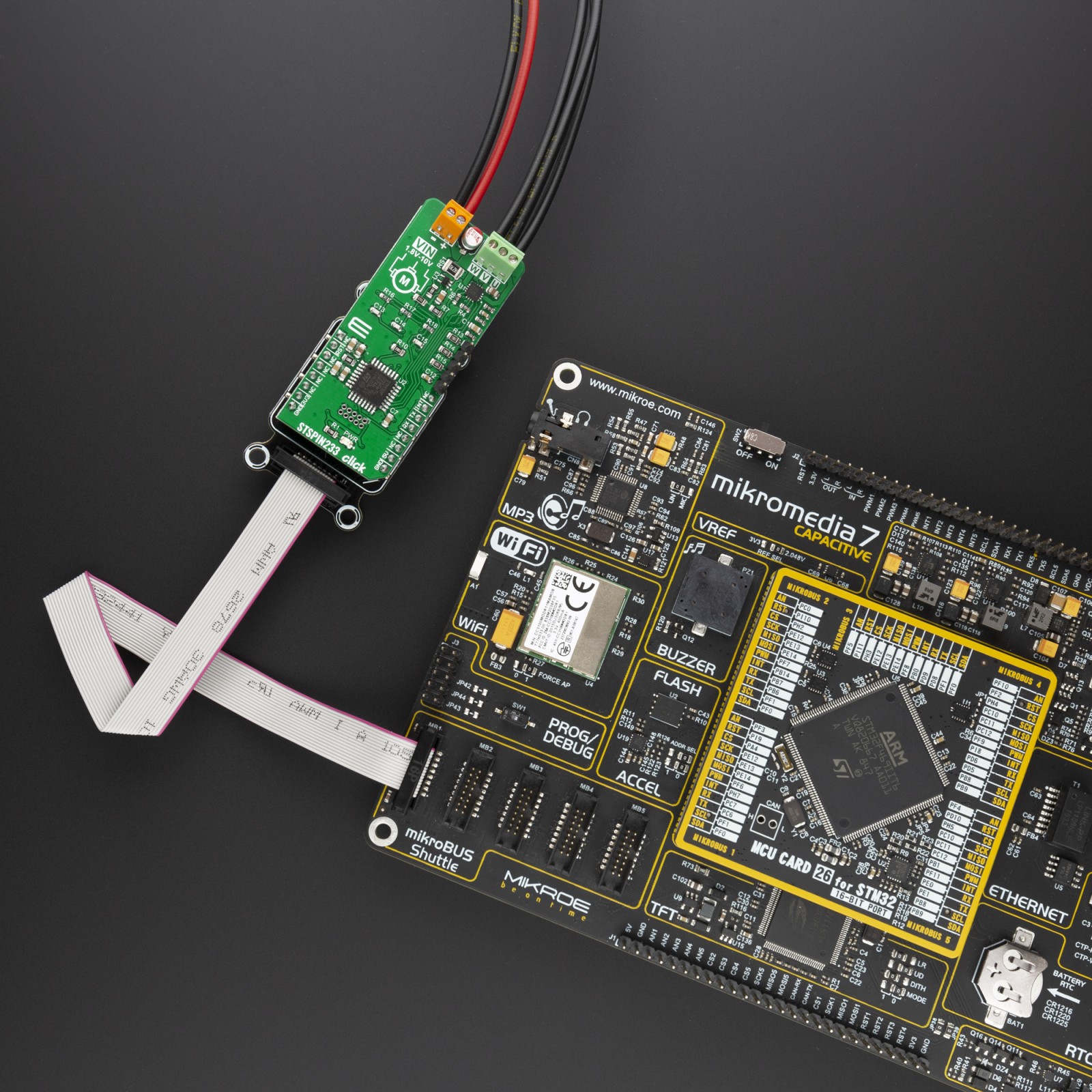
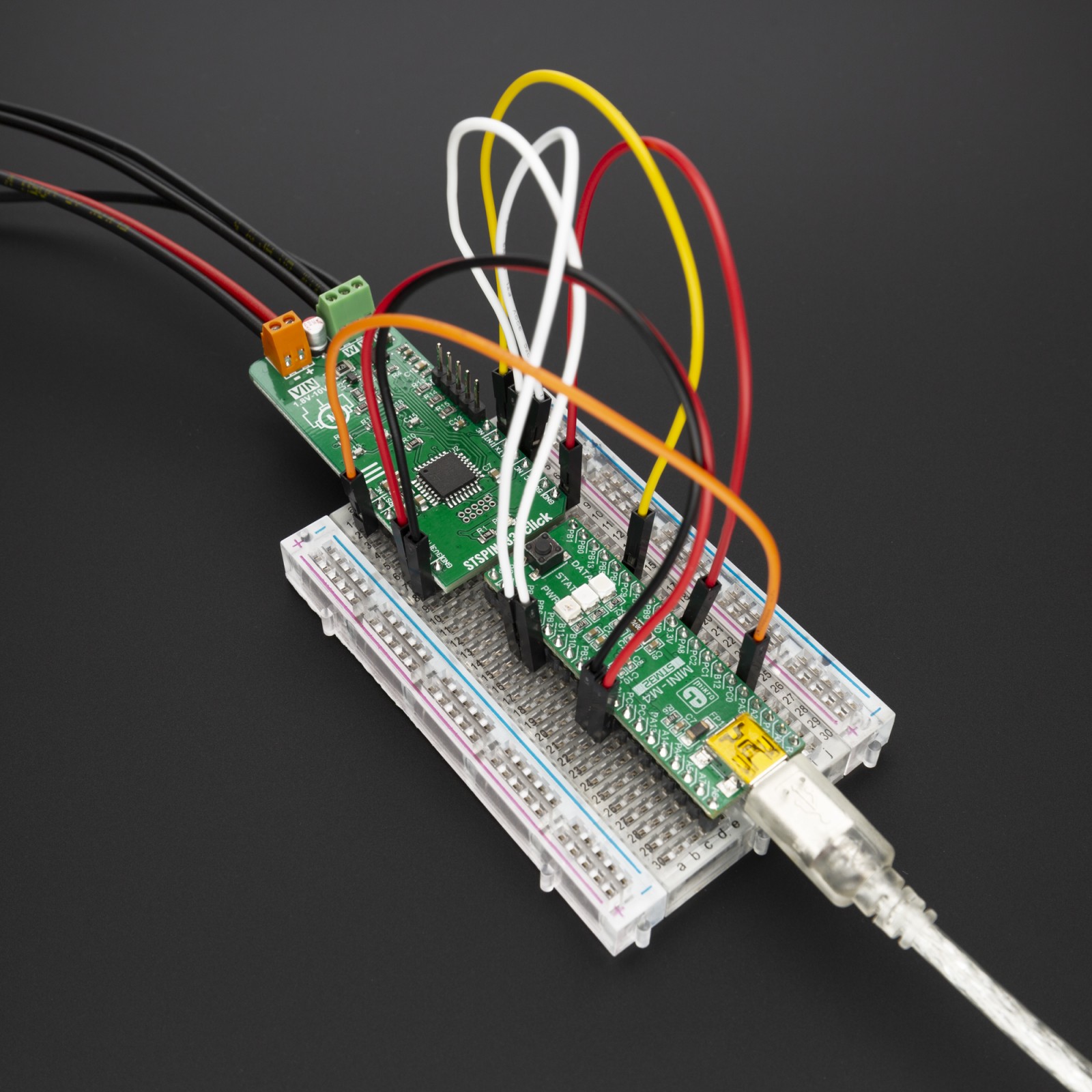
STSPIN233 click is supported by a mikroSDK compliant library, which includes functions that simplify software development. This Click board™ comes as a fully tested product, ready to be used on a system equipped with the mikroBUS™ socket.
Stock: Lead-time applicable.
| 5+ | R337.25 |
| 10+ | R319.50 |
| 15+ | R301.75 |
| 20+ | R290.39 |