Magnetic Rotary 2 Click
R1,200.00 ex. VAT
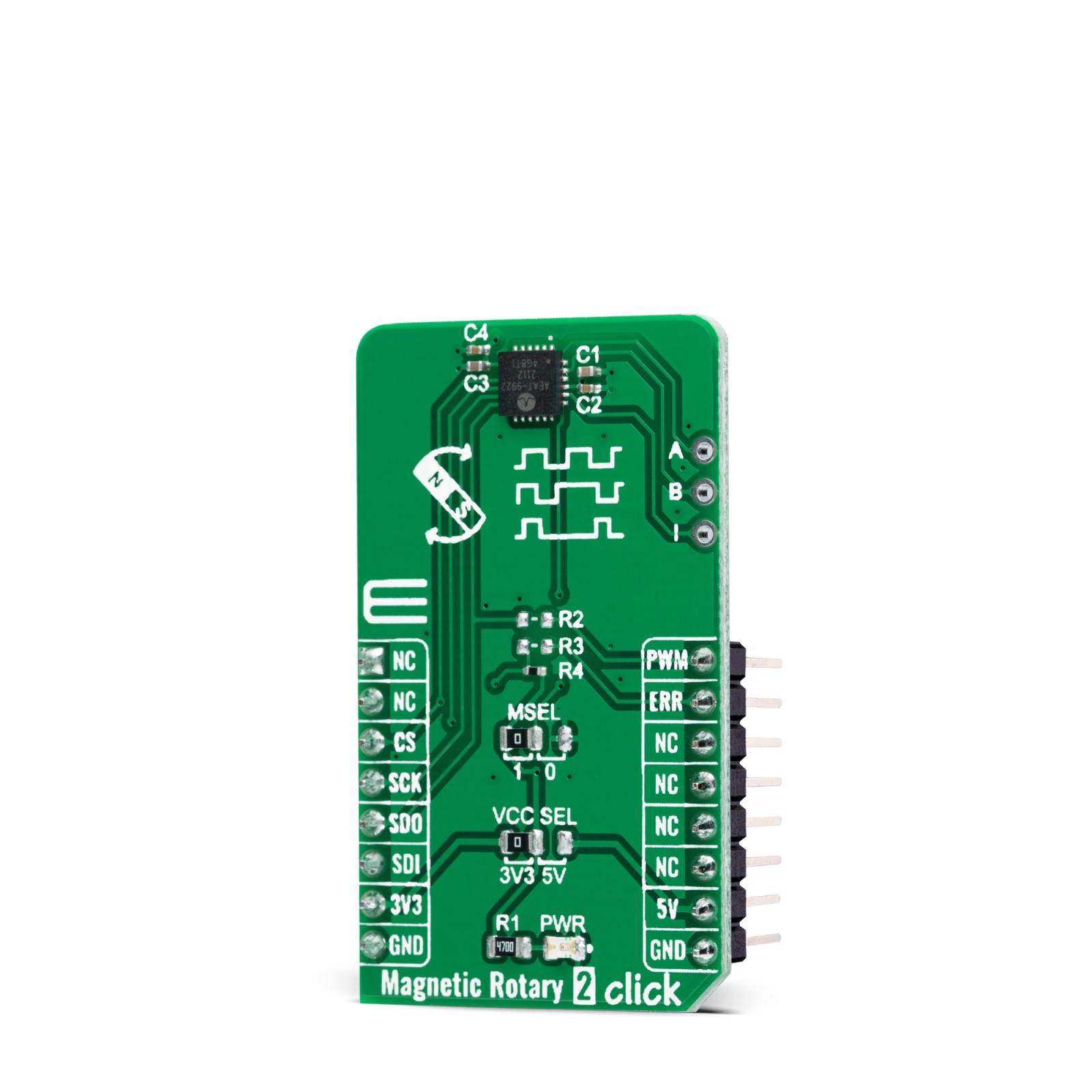
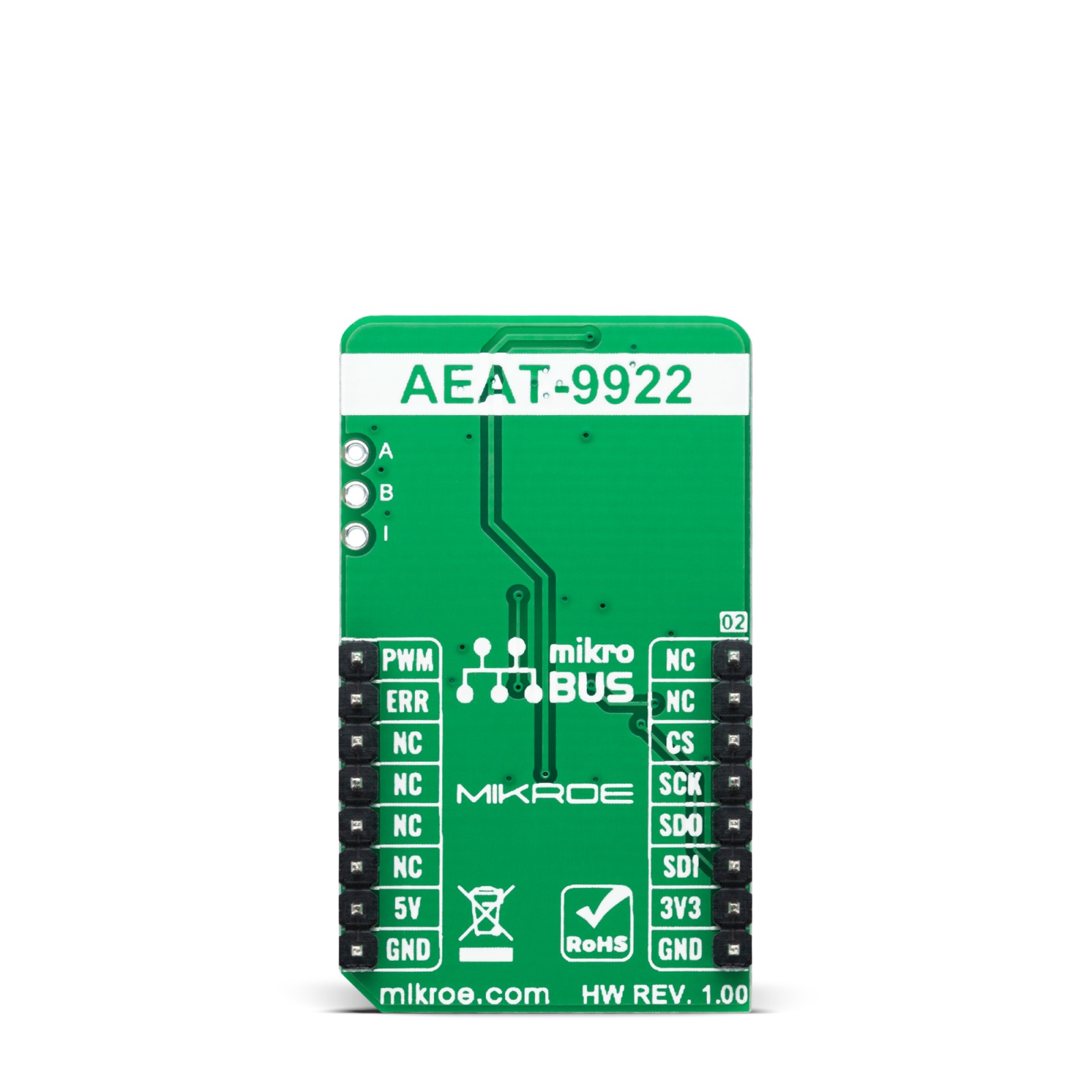
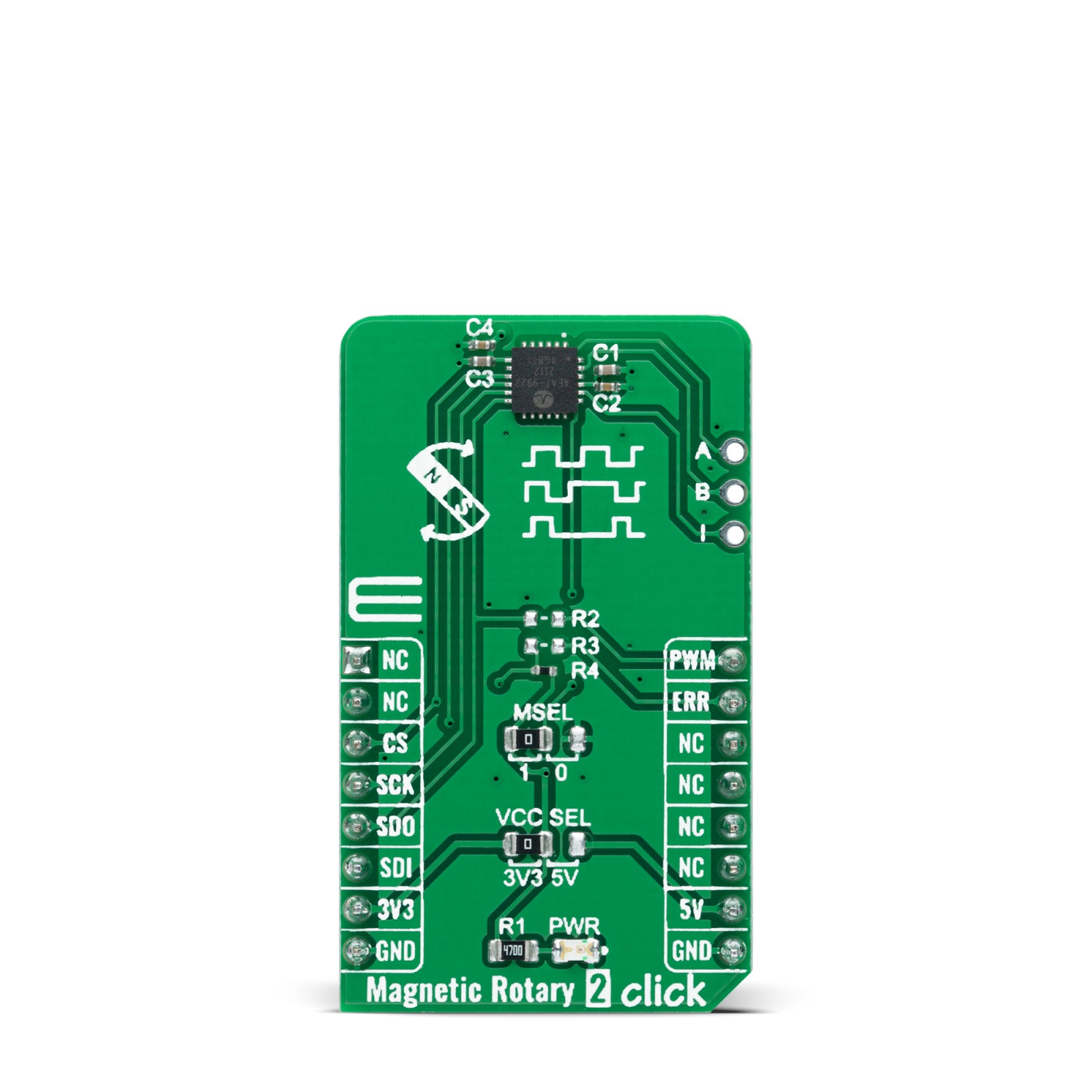
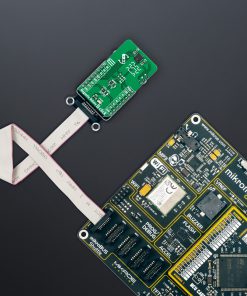
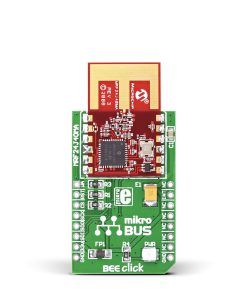
Magnetic Rotary 2 Click is a compact add-on board used for accurate magnet-position sensing. This board features the AEAT-9922, an angular magnetic rotary sensor providing accurate angular measurement over a full 360 degrees of rotation from Broadcom Limited. The AEAT-9922 uses integrated Hall sensor elements with complex analog and digital signal processing within a single device. The absolute angle measurement provides an instant indication of the magnet’s angular position with a selectable and one-time programmable resolution from 10 to 18 bits. It also comes with an onboard header reserved for incremental outputs of their respective A, B, and I pins, the same as the commutation U, V, and W signals. This Click board™ represents a versatile solution capable of supporting a broad range of applications with its robust architecture to measure and deliver absolute and incremental signals.
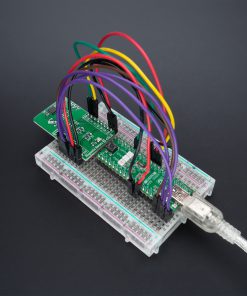
Magnetic Rotary 2 Click is supported by a mikroSDK compliant library, which includes functions that simplify software development. This Click board™ comes as a fully tested product, ready to be used on a system equipped with the mikroBUS™ socket.
Stock: Lead-time applicable.
| 5+ | R1,140.00 |
| 10+ | R1,080.00 |
| 15+ | R1,020.00 |
| 20+ | R981.60 |